
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780133840544
Author: George F. Limbrunner, Craig D'Allaird, Leonard Spiegel
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 12, Problem 12.34SP
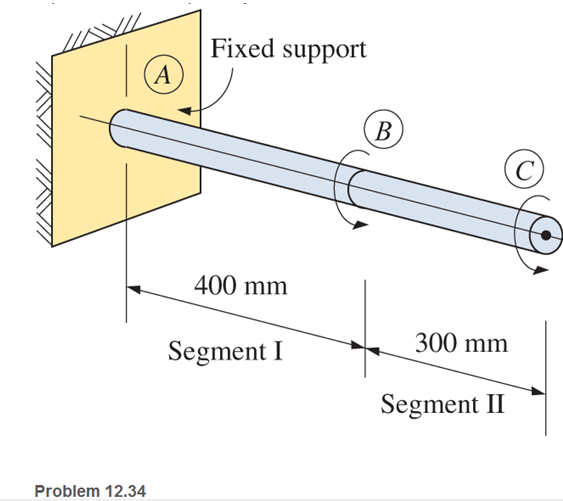
The 65-mm-diameter solid shaft shown is subjected to torques of 600 N.m and 1400 N.m at points B and C, respectively. Determine the maximum shear stress in the shaft.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The 70-mm-diameter solid shaft shown is subjected to torques of 600 N·m and 1400 N·m at points B and C, respectively, determine the maximum shear stress in the shaft. (Unit: MPa)
A solid 0.64-in.-diameter shaft is subjected to the torques shown. The bearings shown allow the shaft to turn freely. Determine the shear stress magnitude in shaft (3).
A solid 0.64-in.-diameter shaft is subjected to the torques shown. The bearings shown allow the shaft to turn freely. Determine the
shear stress magnitude in shaft (3).
...
10 lb-ft
50 lb-ft
70 lb-ft
|(1)
30 lb-ft
A
(3)
B
C
D
Chapter 12 Solutions
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
Ch. 12 - Determine the internal resisting torque in the...Ch. 12 - Determine the internal resisting torque in the...Ch. 12 - Calculate the maximum shear stress developed in a...Ch. 12 - Calculate the allowable torque for a hollow steel...Ch. 12 - Calculate the allowable torque that may be applied...Ch. 12 - A hollow circular steel shaft has a 100-mm outside...Ch. 12 - Design a solid circular steel shaft to transmit an...Ch. 12 - Calculate the shear stresses at the outer and...Ch. 12 - A hollow shaft is produced by boring a...Ch. 12 - Pulleys C and D are attached to shaft AB, as...
Ch. 12 - Calculate the angle of twist a 3-in-diameter...Ch. 12 - Calculate the angle of twist a 65-mm-diameter...Ch. 12 - Calculate the angle of twist a 4-in.-diameter...Ch. 12 - Prob. 12.14PCh. 12 - Prob. 12.15PCh. 12 - A solid steel shaft is to resist a torque of 9000...Ch. 12 - A hollow steel shaft has a 50-mm outside diameter...Ch. 12 - If the shaft of Problem 12.17 were solid, with the...Ch. 12 - An automobile engine develops 90 hp at 3500 rpm....Ch. 12 - Calculate the speed (rpm) at which a...Ch. 12 - Select the diameter of a solid circular steel...Ch. 12 - Select the diameter for a hollow steel shaft that...Ch. 12 - A 6-ft-long solid steel shaft with a diameter of 4...Ch. 12 - The outside and inside diameters of a hollow steel...Ch. 12 - Calculate the maximum shear stress developed in a...Ch. 12 - Write a program that will calculate the allowable...Ch. 12 - Write a program that will generate a table of...Ch. 12 - Rework the program of Problem 12.27 using SI...Ch. 12 - Write a program that will generate a table of...Ch. 12 - Compute the maximum shear stress in the hollow...Ch. 12 - Calculate the allowable torque that may be applied...Ch. 12 - Design a hollow steel shaft to transmit a torque...Ch. 12 - A 32-in.-long solid steel circular shaft, 3 in. in...Ch. 12 - The 65-mm-diameter solid shaft shown is subjected...Ch. 12 - Rework Problem 12.34, changing the diameter of...Ch. 12 - Compute the maximum shear stress in the circular...Ch. 12 - Determine the allowable torque a hollow steel...Ch. 12 - A 1.00-m-long steel wire, 4 mm in diameter, is...Ch. 12 - Select the outside and inside diameters for a...Ch. 12 - A solid aluminum shaft, 6 ft in length, is to...Ch. 12 - A 25-mm-diameter solid shaft with an allowable...Ch. 12 - Compute a. the maximum shear stress developed in a...Ch. 12 - What horsepower can a solid steel shaft 6 in. in...Ch. 12 - Calculate the maximum power that may be...Ch. 12 - A small ski lift has a main cable driving wheel 11...Ch. 12 - A 32-mm-diameter solid shaft transmits 100 kW of...Ch. 12 - A solid steel shaft is to transmit power of 58 kW...Ch. 12 - Select the diameter for a solid steel shaft that...Ch. 12 - A solid steel shaft is to transmit 100 hp at a...Ch. 12 - Two shafts-one a hollow steel shaft with an...Ch. 12 - A 112 -in.-diameter solid steel shaft is 40 ft in...Ch. 12 - A solid steel shaft is to transmit 120 hp. The...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The torque of 250 kN.m produces a maximum shear stress of 48 MPa in the 8 m-long hollow steel shaft. The inne diameter of the shaft is two-thirds of its outer diameter D. (a) Determine the outer diameter D (b) Find the angle of twist of the shaft. Use G = 80 GPa.arrow_forwardA circular solid shaft has a diameter of 60 mm and is subjected to a torque load of 8.7 kN•m. Determine the resulting torque maximum and minimum shear stress.arrow_forwardA solid shaft 50 mm in diameter is subject to the torques applied in thegears. Determine the maximum shear stress on the shaft.arrow_forward
- ..arrow_forwardThe motor on the left provides a torque of 5500 N•m to the gear shaft shown. The motor runs machines connected to gears B, C and D requiring torques of 3000 N•m, 1500 N•m and 1000 N•m respectively. A, B, C and D are spaced 2000 mm apart and the diameter of the shaft is 75 mm. The shear modulus of the shaft material is 80x109 N/m2. Determine: Minimum diameter required (in millimeters) if the shearing stress in the shaft is limited to 100x106 N/m2 Rotation of D with respect to A Note: Draw the Free Body Diagram, Compute for all of the necessary elements, Include the units/dimensions, use the proper formula and round-off all the answers and final answers to 3 decimal places.arrow_forwardA compound shaft consists of brass segment (1) and aluminum segment (2). Segment (1) is a solid brass shaft with an outside diameter of 0.51 in. and an allowable shear stress of 4500 psi. Segment (2) is a solid aluminum shaft with an outside diameter of 0.41 in. and an allowable shear stress of 6000 psi. Determine the magnitude of the largest torque TC that may be applied at C. Express your answer in lb-in rounded to the nearest tenths.arrow_forward
- (1) The shaft has an outer diameter of 1.5 in. and an inner diameter of 0.8 in. If it is subjected to the applied torques as shown, determine the shear stress distribution on the cross-section within region EA. The smooth bearings at A and B do not resist torquearrow_forwardFor the steel shaft shown in Fig. Determine the maximum torque transmitted by any transverse cross section of the shaft. 30 kN-m 15 kN-m 5 kN-m B 10 kN-m 40 kN-marrow_forwardCompound shaft ACB is fixed at A and consisting of two solid circular sections AC & CB, as shown, and is subjected to the given distributed torque. The diameter of part AC is D1, and the diameter of part CB is D2. The material of the shaft having a shear modulus of 69 GPa. Determine (a) the maximum shear stress (KPa) developed in shaft AB, (b) the angle of twist of point B. The values of L1, L2, D1, and D2 are given in table below for each student. D1 D2 50 Nm/m A B 0.2 m L1 L2 =l13 mm 1.3 L2=0,7 mm 80mm 60mm D, =arrow_forward
- 1. The 40-mm-diameter steel shaft is subjected to the torques shown. Determine the angle of twist of end B with respect to A. Use the sign convention for internal torques and take G= 75GPa. FBDs of cut sections OR an internal torque diagram is required for full credit. 80 N-m 20 N-m 30 N-m 600 mm 800 mm 200 mmarrow_forward5. Determine the torsional shear stress in a solid circular shaft having a diameter of 1.25in. that is transmitting 110 hp at a speed of 560 rpmarrow_forwardA solid 0.64-in.-diameter shaft is subjected to the torques shown. The bearings shown allow the shaft to turn freely. Determine the shear stress magnitude in shaft (1). 10 lb-ft 50 lb-ft 70 Ib-ft | (1) 30 lb-ft A (3) B D 3150 psi O 2524 psi 1876 psi O 2331 psi O 2932 psiarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Understanding Torsion; Author: The Efficient Engineer;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1YTKedLQOa0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY