
Concept explainers
12-23 Draw a structural formula for each compound.
- 3-Chloropropene
- 3-Methylcyclohexene
- 1,2-Dimethylcyclohexene
- /runs-3,4-Dimethyl-3-heptene
- Cydopropene
- 3-Hexyne
(a)
Interpretation:
To draw the structural formula for the compound.
Concept Introduction:
Structural formula is the spatial arrangement of atoms of a molecule in space.
In the condensed formula is a line-angle formula, the symbol for carbon and hydrogen atoms are not shown. Only carbon-carbon bonds are shown using lines. Single bonds are shown as  double bond as
double bond as  and triple bond as
and triple bond as  . The carbon atoms are represented as vertices and end of lines.
. The carbon atoms are represented as vertices and end of lines.
Answer to Problem 12.23P
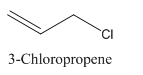
Explanation of Solution
3-Chloropropene.
Carbon atoms in the longest chain are 3.
-ene means a double bond is present at Carbon 1.
Chlorine at Carbon 3.
Structure.
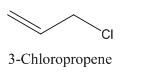
(b)
Interpretation:
To draw the structural formula for the compound.
Concept Introduction:
Structural formula is the spatial arrangement of atoms of a molecule in space. In the condensed formula is a line-angle formula, the symbol for carbon and hydrogen atoms are not shown. Only carbon-carbon bonds are shown using lines. Single bonds are shown as  double bond as
double bond as  and triple bond as
and triple bond as  . The carbon atoms are represented as vertices and end of lines.
. The carbon atoms are represented as vertices and end of lines.
Answer to Problem 12.23P
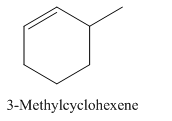
Explanation of Solution
3-Methylcyclohexene.
Carbons in longest chain=6.
Cyclo means a cyclic hydrocarbon.
-ene means a double bond is present at Carbon 1.
Methyl at Carbon 3.
Structure.
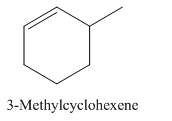
(c)
Interpretation:
To draw the structural formula for the compound.
Concept Introduction:
Structural formula is the spatial arrangement of atoms of a molecule in space. In the condensed formula is a line-angle formula, the symbol for carbon and hydrogen atoms are not shown. Only carbon-carbon bonds are shown using lines. Single bonds are shown as  double bond as
double bond as 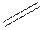 and triple bond as
and triple bond as  The carbon atoms are represented as vertices and end of lines.
The carbon atoms are represented as vertices and end of lines.
Answer to Problem 12.23P
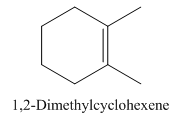
Explanation of Solution
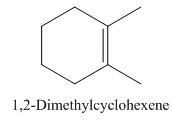
1,2-Dimethylcyclohexene.
Carbons in longest chain=6.
Cyclo means a cyclic hydrocarbon.
-ene means a double bond is present at Carbon 1.
Methyl at Carbon 1 and 2.
Structure.
(d)
Interpretation:
To draw the structural formula for the compound.
Concept Introduction:
Structural formula is the spatial arrangement of atoms of a molecule in space. In the condensed formula is a line-angle formula, the symbol for carbon and hydrogen atoms are not shown. Only carbon-carbon bonds are shown using lines. Single bonds are shown as  double bond as
double bond as 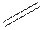 and triple bond as
and triple bond as  The carbon atoms are represented as vertices and end of lines.
The carbon atoms are represented as vertices and end of lines.
Answer to Problem 12.23P
Explanation of Solution
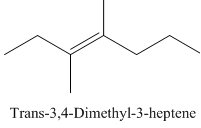
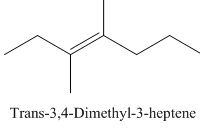
Trans-3,4-Dimethyl-3-heptene.
Carbons in longest chain=7.
-ene means a double bond is present at Carbon3.
Methyl at Carbon 3 and 4.
Trans isomer that means the two methyl are opposite in direction.
Structure.
(e)
Interpretation:
To draw the structural formula for the compound.
Concept Introduction:
Structural formula is the spatial arrangement of atoms of a molecule in space. In the condensed formula is a line-angle formula, the symbol for carbon and hydrogen atoms are not shown. Only carbon-carbon bonds are shown using lines. Single bonds are shown as  double bond as
double bond as 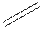 and triple bond as
and triple bond as  . The carbon atoms are represented as vertices and end of lines.
. The carbon atoms are represented as vertices and end of lines.
Answer to Problem 12.23P

Explanation of Solution
Cyclopropene.
Carbons in longest chain=3.
-ene means a double bond is present at Carbon1.
Cyclo means a cyclic hydrocarbon.
Structure.

(f)
Interpretation:
To draw the structural formula for the compound.
Concept Introduction:
Structural formula is the spatial arrangement of atoms of a molecule in space. In the condensed formula is a line-angle formula, the symbol for carbon and hydrogen atoms are not shown. Only carbon-carbon bonds are shown using lines. Single bonds are shown as  double bond as
double bond as 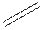 and triple bond as
and triple bond as  . The carbon atoms are represented as vertices and end of lines.
. The carbon atoms are represented as vertices and end of lines.
Answer to Problem 12.23P
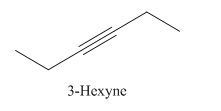
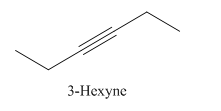
Explanation of Solution
3-Hexyne.
Carbons in longest chain=6.
-yne means a triple bond is present at Carbon3.
Structure.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 12 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
- (c) SOCI Best Lewis Structure 2 e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry:_ (d) PCls Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group geometry:_ shape/molecular geometry:_ (e) Ba(BrO2): Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- reaction scheme for C39H4202 Hydrogenation of Alkyne (Alkyne to Alkene) show reaction (drawing) pleasearrow_forwardGive detailed mechanism Solution with explanation needed. Don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forwardShow work with explanation needed....don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning



