
Interpretation:
Consider the hydroboration and protonation steps shown here. In each case, (a) the electrophilic atom and (b) the
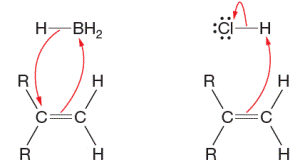
Concept introduction:
For the reaction of the
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 12 Solutions
Get Ready for Organic Chemistry
- Where do the arrows for this are suppose to go? (Intermediate) Reactant Mechanism Explorer: Sketch and Submission (Intermediate) Reactant Tip: Only add curved arrows in this sketcher Mechanism Explorer: Sketch and Submission (Intermediate) Reactant CH H H₂O Tip: Only add curved arrows in this sketcher learrow_forwardShow the three step mechanism to form the major product only for the radical bromination shown below. label the initiation, propagation, and termination steps. draw the FULL electron pushing mechanism with ALL intermediates, lone pairs, and formal charges clearly labelled. Show ALL electron pushing arrows and label the nucleophile and electrophile where appropriate for non-radical mechanisms.arrow_forwardIn the substitution reaction: The product(s) of the reaction is(are)? Select all that are correct.arrow_forward
- Follow the format of solving the problem where you should write the GIVEN, ASKED, SOLUTION, and ANSWER. Add curved arrows to the following reactions to indicate the flow of electrons for all of the bond-forming and bond-breaking steps.arrow_forwardFor the reaction given below, draw a mechanism (curved arrows) and then predict which side of the reaction is favoured under equilibrium conditions.arrow_forwardWhat is important about this slide? what is reactant and what is product?what reactant to give what?what principle is important here?what does it means that acetal can not be reduced?which one is acetal? explain the mechanism please? Lable out which is reactant and which is product please. I am totally confusedarrow_forward
- Shown here is an example of an electrophilic (i) CI aromatic substitution reaction, which we examine in Chapter 22. The mechanism consists of the four elementary steps shown. For each step (i–iv), (a) identify all electron-rich sites and all electron-poor sites, (b) draw in the appropriate curved arrows to show the bond formation and bond breaking that occur, and (c) name the elementary step. CI-CI + Fe CI (ii) CI CI (iii) CI (iv) CI CI + H,O H00arrow_forwardFor the reaction can someone please synthesize the given products from the given reactants. Multiple reactions/steps will be needed (the arrows designate the minimum number of steps). Also, for the 1st step (reaction) in each synthesis, can you please draw an energy diagram showing the correct number of hills and valleys for that step’s mechanism?arrow_forwardPart A Propose a mechanism for the free-radical chlorination of ethane. hv CH; -CH, + Cl, CH; -CH,CI + HCI Draw all missing reactants and/or products in the appropriate boxes by placing atoms on the canvas and connecting them with bonds. Add charges where needed. Electron flow arrows should start on the electron(s) of an atom or a bond and should end on an atom, bond, or location where a new bond should be created. Include all free radicals by right-clicking on an atom on the canvas and then using the Atom properties to select the monovalent radical. H CI Br Marvin JS by ChemAxon Submit Request Answer 1 0 +f .arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
