
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780134683416
Author: Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 11.2, Problem 7E
Performing a Wilcoxon Test In Exercises 3–8,
- (a) identify the claim and state H0 and Ha.
- (b) decide whether to use a Wilcoxon signed-rank test or a Wilcoxon rank sum test.
- (c) find the critical value(s).
- (d) find the test statistic.
- (e) decide whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis.
- (f) interpret the decision in the context of the original claim.
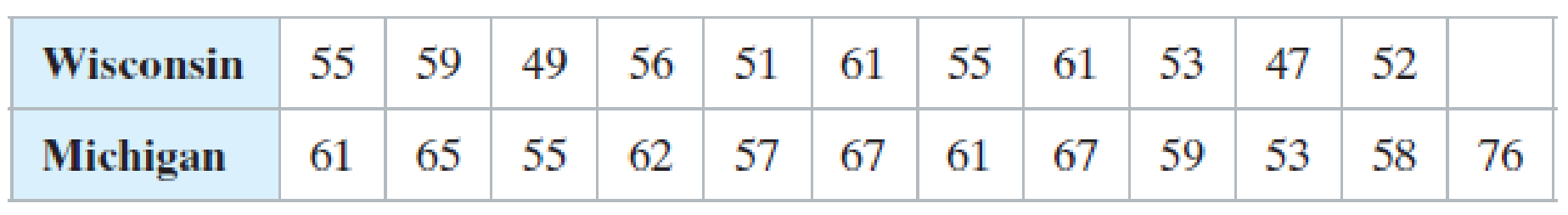
7. Teacher Salaries A teacher’s union representative claims that there is a difference in the salaries earned by teachers in Wisconsin and Michigan. The table shows the salaries (in thousands of dollars) of a random sample of 11 teachers from Wisconsin and 12 teachers from Michigan. At a = 0.05, is there enough evidence to support the representative’s claim? (Adapted from National Education Association)
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Type I and Type I l Errors. In Exercises 29–32, provide statements that identify the type I error and the type II error that correspond to the given claim. (Although conclusions are usually expressed in verbal form, the answers here can be expressed with statements that include symbolic expressions such as p = 0.1.)
The proportion of people with blue eyes is equal to 0.35.
Type I and Type I l Errors. In Exercises 29–32, provide statements that identify the type I error and the type II error that correspond to the given claim. (Although conclusions are usually expressed in verbal form, the answers here can be expressed with statements that include symbolic expressions such as p = 0.1.
The proportion of people who require no vision correction is less than 0.25.
Hypothesis Testing
Chapter 11 Solutions
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Ch. 11.1 - A real estate agency claims that the median number...Ch. 11.1 - An organization claims that the median age of...Ch. 11.1 - A medical researcher claims that a new vaccine...Ch. 11.1 - Prob. 1ECh. 11.1 - When the sign test is used, what population...Ch. 11.1 - Describe the test statistic for the sign test when...Ch. 11.1 - In your own words, explain why the hypothesis test...Ch. 11.1 - Explain how to use the sign test to test a...Ch. 11.1 - List the two conditions that must be met in order...Ch. 11.1 - Performing a Sign Test In Exercises 722, (a)...
Ch. 11.1 - Temperature A meteorologist claims that the median...Ch. 11.1 - Prob. 9ECh. 11.1 - Temperature During a weather report, a...Ch. 11.1 - Credit Card Debt A financial services institution...Ch. 11.1 - Financial Debt A financial services accountant...Ch. 11.1 - Prob. 13ECh. 11.1 - Social Networking A research group claims that the...Ch. 11.1 - Unit Size A renters organization claims that the...Ch. 11.1 - Prob. 16ECh. 11.1 - Hourly Wages A labor organization claims that the...Ch. 11.1 - Prob. 18ECh. 11.1 - Prob. 19ECh. 11.1 - Prob. 20ECh. 11.1 - Prob. 21ECh. 11.1 - Prob. 22ECh. 11.1 - Prob. 23ECh. 11.1 - Contacting Parents A research organization...Ch. 11.1 - In Exercises 2528, use a right-tailed test and (a)...Ch. 11.1 - Prob. 26ECh. 11.1 - Prob. 27ECh. 11.1 - Ages of Grooms A marriage counselor claims that...Ch. 11.2 - A quality control inspector wants to test the...Ch. 11.2 - Prob. 2TYCh. 11.2 - Prob. 1ECh. 11.2 - Prob. 2ECh. 11.2 - Prob. 3ECh. 11.2 - Prob. 4ECh. 11.2 - Prob. 5ECh. 11.2 - Prob. 6ECh. 11.2 - Performing a Wilcoxon Test In Exercises 38, (a)...Ch. 11.2 - Performing a Wilcoxon Test In Exercises 38, (a)...Ch. 11.2 - Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test for n 30 When you are...Ch. 11.2 - Prob. 10ECh. 11.2 - Construct a side-by-side box-and-whisker plot for...Ch. 11.2 - Prob. 2CSCh. 11.2 - In Exercises 25, use the sign test to test the...Ch. 11.2 - In Exercises 25, use the sign test to test the...Ch. 11.2 - In Exercises 25, use the sign test to test the...Ch. 11.2 - In Exercises 6 and 7, use the Wilcoxon rank sum...Ch. 11.2 - In Exercises 6 and 7, use the Wilcoxon rank sum...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 1TYCh. 11.3 - Prob. 1ECh. 11.3 - Explain why the Kruskal-Wallis test is always a...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 3ECh. 11.3 - Performing a Kruskal-Wallis Test In Exercises 36,...Ch. 11.3 - Prob. 5ECh. 11.3 - Prob. 6ECh. 11.3 - Comparing Two Tests In Exercises 7 and 8, (a)...Ch. 11.3 - Comparing Two Tests In Exercises 7 and 8, (a)...Ch. 11.4 - Prob. 1TYCh. 11.4 - Prob. 1ECh. 11.4 - Prob. 2ECh. 11.4 - Prob. 3ECh. 11.4 - Prob. 4ECh. 11.4 - Prob. 5ECh. 11.4 - Prob. 6ECh. 11.4 - Prob. 7ECh. 11.4 - Prob. 8ECh. 11.4 - Prob. 9ECh. 11.4 - Prob. 10ECh. 11.4 - Prob. 11ECh. 11.4 - Prob. 12ECh. 11.4 - Prob. 13ECh. 11.4 - Prob. 14ECh. 11.5 - A machine produces engine parts. An inspector...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 2TYCh. 11.5 - Prob. 3TYCh. 11.5 - In your own words, explain why the hypothesis test...Ch. 11.5 - Describe the test statistic for the runs test when...Ch. 11.5 - Finding the Number of Runs In Exercises 36,...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 4ECh. 11.5 - Finding the Number of Runs In Exercises 36,...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 6ECh. 11.5 - Prob. 7ECh. 11.5 - Prob. 8ECh. 11.5 - Prob. 9ECh. 11.5 - Prob. 10ECh. 11.5 - Finding Critical Values In Exercises 1114, use the...Ch. 11.5 - Prob. 12ECh. 11.5 - Prob. 13ECh. 11.5 - Prob. 14ECh. 11.5 - Prob. 15ECh. 11.5 - Prob. 16ECh. 11.5 - Prob. 17ECh. 11.5 - Prob. 18ECh. 11.5 - Prob. 19ECh. 11.5 - Prob. 20ECh. 11.5 - Prob. 21ECh. 11.5 - Prob. 22ECh. 11.5 - Runs Test with Quantitative Data In Exercises...Ch. 11 - Using an Inappropriate Test Discuss the...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.1.1RECh. 11 - Prob. 11.1.2RECh. 11 - Prob. 11.1.3RECh. 11 - Prob. 11.1.4RECh. 11 - Prob. 11.1.5RECh. 11 - Prob. 11.1.6RECh. 11 - In Exercises 7 and 8, use a Wilcoxon test to test...Ch. 11 - In Exercises 7 and 8, use a Wilcoxon test to test...Ch. 11 - Prob. 11.3.9RECh. 11 - Prob. 11.3.10RECh. 11 - Prob. 11.4.11RECh. 11 - Prob. 11.4.12RECh. 11 - Prob. 11.5.13RECh. 11 - Prob. 11.5.14RECh. 11 - Prob. 1CQCh. 11 - Prob. 2CQCh. 11 - Prob. 3CQCh. 11 - Prob. 4CQCh. 11 - Prob. 5CQCh. 11 - Prob. 1CTCh. 11 - Prob. 2CTCh. 11 - Prob. 3CTCh. 11 - An employment agency claims that there is a...Ch. 11 - Prob. 5CTCh. 11 - How Would You Do It? (a) What sampling technique...Ch. 11 - In a recent year, according to the Bureau of Labor...Ch. 11 - Prob. 3RSRDCh. 11 - Construct a box-and-whisker plot for each region....Ch. 11 - In Exercises 15, refer to the annual incomes of...Ch. 11 - Use technology to perform a Wilcoxon rank sum test...Ch. 11 - Prob. 4TCh. 11 - Prob. 5TCh. 11 - Prob. 6T
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Overtime Rule in Football The accompanying table lists results of overtime football games before and after the overtime rule was changed in the National Football League in 2011. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim of independence between winning an overtime game and whether playing under the old rule or the new rule. What do the results suggest about the effectiveness of the rule change?arrow_forwardTo test whether the mean time needed to mix a batch of material is the same for machines produced by three manufacturers, a chemical company obtained the following data on the time (in minutes) needed to mix the material. Manufacturer 1 2 3 21 29 21 26 25 18 25 32 22 20 26 23 (a) Use these data to test whether the population mean times for mixing a batch of material differ for the three manufacturers. Use a = 0.05. State the null and alternative hypotheses. O Ho: H1 # H2 # Hz Hai H1 = H2 = H3 O H,: Not all the population means are equal. Ha: H1 = H2 = Mz O H,: At least two of the population means are equal. H: At least two of the population means are different. O Ho: H1 = H2 = H3 O Ho: H1 = H2 = Mz H: Not all the population means are equal. Find the value of the test statistic. (Round your answer to two decimal places.) Find the p-value. (Round your answer to three decimal places.) p-value = State your conclusion. O Do not reject H.. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the…arrow_forwardHelp!arrow_forward
- Where did the 1.463 and +- 1.960 came from ?arrow_forwardData set presents a sample of the number of defective flash drives produced by a small manufacturing company over the last 30 weeks. The company's operations manager believes that the number of defects produced by the process is less than seven defective flash drives per week. Construct a hypothesis test to verify the operations manager's claim. Hypothesis test should include a t test statistic value, a p value, a decision, and a conclusion. This is the null hypotheses (see attachment): Data: Mean 7.0300 SD 1.3700 SEM 0.2501 N 30arrow_forwardHypothesis testing will consist of four hypothesis tests which you need to complete. While you will not need to show your work or upload any files, each test will require the following: Type of Test: Null Hypothesis: Alternate Hypothesis: SE: Test Statistic: P-value: Decision: Sentence:arrow_forward
- Which of these 3 statements is not true?arrow_forwardA statistician wishing to test a hypothesis that students score at least 75% on the final exam in an introductory statistics course decides to randomly select 20 students in the class and have them take the exam early. The average score of the students on the exam is 78%. The hypothesis the statistician wants to test is: a. H0: = 75 vs. Ha: > 78. b. H0: = 75 vs. Ha: > 75. c. H0: = 75 vs. Ha: = 78. d. H0: = 75 vs. Ha: < 75arrow_forwardWhat are the hypotheses for the test? A. H0: β1≠0 and Ha: β1=0 B. H0: β1=0 and Ha: β1<0 C. H0: β1=0 and Ha: β1>0 Your answer is not correct. D. H0: β1=0 and Ha: β1≠0 This is the correct answer. What is the test statistic? t= (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Find the P-value. P-value= (Round to three decimal places as needed.) Part 4 Which of the following is the correct conclusion for the hypothesis test? A. Do not reject H0; the data provide sufficient evidence to conclude that x is useful for predicting y. B. Reject H0; the data do not provide sufficient evidence to conclude that x is useful for predicting y. C. Do not reject H0; the data do not provide sufficient evidence to conclude that x is useful for predicting y. Your answer is correct. D. Reject H0; the data provide sufficient evidence to conclude that x is useful for predicting y. Part 5 b. Find a 95%…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Cengage
Hypothesis Testing using Confidence Interval Approach; Author: BUM2413 Applied Statistics UMP;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Hq1l3e9pLyY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Hypothesis Testing - Difference of Two Means - Student's -Distribution & Normal Distribution; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UcZwyzwWU7o;License: Standard Youtube License