
University Physics Volume 2
18th Edition
ISBN: 9781938168161
Author: OpenStax
Publisher: OpenStax
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 11, Problem 47P
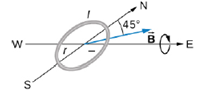
Repeat the previous problem, but with the loop lying flat on the ground with its current circulating counterclockwise (when viewed from above) in a location where Earth’s field is north, but at an angle 45.0° below the horizontal and with a strength of
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Please solve
A piece of silicon semiconductor has length L=0.01cm and cross-section in a square shape with an area of A=5×10−4cm2 . The semiconductor is doped with 1012cm−3 Phosphorus atoms and 1017cm−3 Boron atoms. An external electric field E=1.5×104N/C is applied to the silicon piece along the length direction, through the cross section. What is the total current in the silicon at T=300K? Assume the mobility of silicon is 1400cm2V−1s−1 for electrons and 450cm2V−1s−1 for holes, respectively. Assume the intrinsic carrier concentration in silicon is 1010cm−3 . Give your answer in mA, rounded to 3 significant figures. Just enter the number, nothing else.
An impurity with a charge of 2e is placed in a three-dimensional metal. Assume that the Friedel sum rule holds for this system, and only the scattering phase shifts from the electrons contribute to this sum (we don't need to consider ion phase shifts). This metal has a spherical Fermi surface with Fermi wave vector kF . The only degeneracy for the electrons at the Fermi surface is spin (two-fold) and angular momentum ( 2l+1 for each angular momentum l ). Ignore scattering for l>2 and assume that the scattering doesn't depend on the spin degree of freedom. Denote the scattering phase shift at the Fermi wave vector in the l -th angular momentum channel as δl(kF) . If δ0(kF)=11π31 , and δ1(kF)=π29 , what is δ2(kF)? Round your answer to three significant figures. Just enter the number, nothing else.
Chapter 11 Solutions
University Physics Volume 2
Ch. 11 - Check Your Understanding Repeat the previous...Ch. 11 - Check Your Understanding A uniform magnetic field...Ch. 11 - Check Your Understanding A straight, flexible...Ch. 11 - Check Your Understanding In what orientation would...Ch. 11 - Check Your Understanding A Hall people consists of...Ch. 11 - Check Your Understanding A cyclotron is to be...Ch. 11 - Discuss the similarities and differences between...Ch. 11 - (a) Is it possible for the magnetic force on a...Ch. 11 - At a given instant, an electron and a proton are...Ch. 11 - Does increasing the magnitude of a uniform...
Ch. 11 - An electron passes through a magnetic field...Ch. 11 - If a charged particle moves in a straight line,...Ch. 11 - How could you determine which pole of an...Ch. 11 - Describe the error that results from accidently...Ch. 11 - Considering the magnetic force law, are the...Ch. 11 - Why can a nearby magnet distort a cathode ray tube...Ch. 11 - A magnetic field exerts a force on the moving...Ch. 11 - There are regions where the magnetic field of...Ch. 11 - Hall potentials are much larger for poor...Ch. 11 - Describe the primary function of the electric...Ch. 11 - What is the direction of the magnetic force on a...Ch. 11 - Repeat previous exercise for a negative charge.Ch. 11 - What is the direction of the velocity of a...Ch. 11 - Repeat previous exercise for a positive charge.Ch. 11 - What is the direction of the magnetic field that...Ch. 11 - Repeat previous exercise for a negative charge.Ch. 11 - (a) Aircraft sometimes acquire small static...Ch. 11 - (a) A cosmic ray proton moving toward Earth at...Ch. 11 - An electron moving at 4.00103 m/s in a 1.25-T...Ch. 11 - (a) A physicist performing a sensitive measurement...Ch. 11 - A cosmic-ray electron moves at 7.5 × 106 m/sinches...Ch. 11 - (a) Viewers of Star Trek have heard of an...Ch. 11 - (a) An oxygen-16 ion with a mass of 2.661026 kg...Ch. 11 - An electron in a TV CRT moves with a speed of...Ch. 11 - (a) At what speed will a proton move in a circular...Ch. 11 - (a) What voltage will accelerate electrons to a...Ch. 11 - An alpha-particle ( m=6.641027kg , q=3.21019C )...Ch. 11 - A particle of charge q and mass m is accelerated...Ch. 11 - What is the direction of the magnetic force on the...Ch. 11 - What is the direction of a current that...Ch. 11 - What is the direction of the magnetic field that...Ch. 11 - (a) What is the force per meter on a lightning...Ch. 11 - (a) A dc power line for a light-rail system caries...Ch. 11 - A wire carrying a 30.0-A current passes between...Ch. 11 - (a) By how many percent is the torque of a motor...Ch. 11 - (a) What is the maximum torque on a 150-tum square...Ch. 11 - Find the current through a loop needed to create a...Ch. 11 - Calculate the magnetic field strength needed on a...Ch. 11 - Since the equation for torque on a...Ch. 11 - , (a) At what angle 0 is tlie torque on a current...Ch. 11 - A proton has a magnetic field due to its spin. The...Ch. 11 - (a) A 200-turn circular loop of radius SO.0 cm is...Ch. 11 - Repeat the previous problem, but with the loop...Ch. 11 - A strip of copper is placed in a uniform magnetic...Ch. 11 - The cross-sectional dimensions of the copper strip...Ch. 11 - The magnitudes of the electric and magnetic fields...Ch. 11 - A charged particle moves through a velocity...Ch. 11 - A Hall probe gives a reading of 1.5V for a current...Ch. 11 - A physicist is designing a cyclotron to accelerate...Ch. 11 - The strengths of the fields in the velocity...Ch. 11 - The magnetic field in a cyclotron is 1.25 T, and...Ch. 11 - A mass spectrometer is being used to separate...Ch. 11 - (a) Triply charged uranium-235 and uranium-238...Ch. 11 - Calculate the magnetic force on a hypothetical...Ch. 11 - Repeat the previous problem with a new magnetic...Ch. 11 - An electron is projected into a uniform magnetic...Ch. 11 - The mass and chaise of a water droplet are 1.0104g...Ch. 11 - Four different proton velocities are given. For...Ch. 11 - An electron of kinetic energy 2000 eV passes...Ch. 11 - An alpha-particle (m=6.641027kg,q=3.21019C) moving...Ch. 11 - An electron moving with a velocity...Ch. 11 - At a particular instant an electron is traveling...Ch. 11 - Repeat the calculations of the previous problem...Ch. 11 - What magnetic field is required in order to...Ch. 11 - An electron and a proton move with the same speed...Ch. 11 - A proton and an alpha-particle have the same...Ch. 11 - A singly charged ion takes 2.0 × 10-3 s to...Ch. 11 - A particle moving downward at a speed of 6.0106...Ch. 11 - , A proton, deuteron, and an alpha-particle ae all...Ch. 11 - A singly charged ion is moving in a uniform...Ch. 11 - Two particles have the same linear momentum, but...Ch. 11 - A uniform magnetic field of magnitude is directed...Ch. 11 - An electron moving along the +x -axis at 5.0106m/s...Ch. 11 - (a) A 0.750-m-long section of cable carrying...Ch. 11 - (a)What is the angle between a wire carrying an...Ch. 11 - A 1.0-rn-long segment of wire lies along the...Ch. 11 - A 5.0-m section of a long, straight wire carries a...Ch. 11 - An electromagnet produces a magnetic field of...Ch. 11 - The current loop shown in the accompanying figure...Ch. 11 - A circular coil of radius 5.0 cm is wound with...Ch. 11 - Acircularcoiofwireofradius5.Ocmhas2Otums and...Ch. 11 - A current-carrying coil in a magnetic field...Ch. 11 - A 40-cm by 6.0-cm rectangular current loop carries...Ch. 11 - A circular coil with 200 turns Las a radius of 2.0...Ch. 11 - The current through a circular wire loop of radius...Ch. 11 - A wire of length 1.0 m is wound into a single-turn...Ch. 11 - Consider an electron rotating in a circular orbit...Ch. 11 - The Hall effect is to be used to find the sign of...Ch. 11 - The density of charge carriers far copper is...Ch. 11 - The Hall effect is to be used to find the density...Ch. 11 - Show tliat the Hall voltage across wires made of...Ch. 11 - A velocity selector in a mass spectrometer uses a...Ch. 11 - Find the radius of curvature of the path of a...Ch. 11 - Unreasonable results To construct a non-mechanical...Ch. 11 - Unreasonable results A charged particle having...Ch. 11 - Unreasonable results An inventor wants to generate...Ch. 11 - Unreasonable results Frustrated by the small Hall...Ch. 11 - A particle of charge +q and mass m moves with...Ch. 11 - A proton of speed v=6105m/s enters a region of...Ch. 11 - A particle’s path is bent when it passes through a...Ch. 11 - In a region a non-uniform magnetic field exists...Ch. 11 - A copper rod of mass in and length L is hung from...Ch. 11 - The accompanied figure shows an arrangement for...Ch. 11 - A wire ismade into a circular shape of radius R...Ch. 11 - A long-rigid wire lies along the x-axis and cairns...Ch. 11 - A circular loop of wire of area 10 cm2 carries a...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
2. List the subdivisions of the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities.
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
a. Draw the mechanism for the following reaction if it a involves specific-base catalysis. b. Draw the mechanis...
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
MAKE CONNECTIONS The gene that causes sickle-cell disease is present in a higher percentage of residents of su...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
1. Compare and contrast the following terms:
a. dominant and recessive
b. genotype and phenotype
c. homozyg...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
60. How does the kinetic energy of the particle in Figure P24.59 change as it traverses the velocity .selector?...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Which one of the following is not a fuel produced by microorganisms? a. algal oil b. ethanol c. hydrogen d. met...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A pilot with a mass of 75 kg is flying an airplane at a true airspeed of 55m/s in air that is still relative to the ground. The pilot enters a coordinated turn of constant bank angle and constant altitude, and the pilot experiences an effective weight of 1471.5N normal to the wings of the plane. What is the rate of turn (in degrees per second) for the aircraft? Round your answer to three significant figures. Just enter the number, nothing else.arrow_forwardImagine you are out for a stroll on a sunny day when you encounter a lake. Unpolarized light from the sun is reflected off the lake into your eyes. However, you notice when you put on your vertically polarized sunglasses, the light reflected off the lake no longer reaches your eyes. What is the angle between the unpolarized light and the surface of the water, in degrees, measured from the horizontal? You may assume the index of refraction of air is nair=1 and the index of refraction of water is nwater=1.33 . Round your answer to three significant figures. Just enter the number, nothing else.arrow_forwardRed, yellow, green, and blue light with wavelengths of λred=700 nm , λyellow=580 nm , λgreen=520 nm , and λblue=475 nm are directed at a slit that is 20 μm wide at normal incidence. The light hits a screen 1 m behind the slit. Which color of light will have an interference minimum closest to a point 10 cm away from its central maxima? You may assume the small angle approximation sinθ≈tanθ≈θ for angles smaller than 10∘ . Just enter the wavelength of that color in nm, nothing else.arrow_forward
- In the circuit shown, the switch is initially open and the capacitor isuncharged. What will be the current through R1 the instant after the switch isclosed? Take V=10 V, R1 = 20 W, R2 = 20 W, R3 = 10 W and C = 2 mF.arrow_forwardIn the circuit shown take: V1 = 20V, V2 = 40V, R1 = 5W, R2 = 2W and R3 =10W. If i1 = 2A, what is i3 if the assumed direction of the current is as shown.arrow_forwardConsider the circuit shown in the figure below. (Let R = 12.0 (2.) 25.0 V 10.0 www 10.0 Ω b www 5.00 Ω w R 5.00 Ω i (a) Find the current in the 12.0-0 resistor. 1.95 × This is the total current through the battery. Does all of this go through R? A (b) Find the potential difference between points a and b. 1.72 × How does the potential difference between points a and b relate to the current through resistor R? Varrow_forward
- 3.90 ... CP A rocket designed to place small payloads into orbit is carried to an altitude of 12.0 km above sea level by a converted airliner. When the airliner is flying in a straight line at a constant speed of 850 km/h, the rocket is dropped. After the drop, the air- liner maintains the same altitude and speed and continues to fly in a straight line. The rocket falls for a brief time, after which its rocket motor turns on. Once its rocket motor is on, the combined effects of thrust and gravity give the rocket a constant acceleration of magnitude 3.00g directed at an angle of 30.0° above the hori- zontal. For reasons of safety, the rocket should be at least 1.00 km in front of the airliner when it climbs through the airliner's alti- tude. Your job is to determine the minimum time that the rocket must fall before its engine starts. You can ignore air resistance. Your answer should include (i) a diagram showing the flight paths of both the rocket and the airliner, labeled at several…arrow_forward1. In an industrial fabrication process, a fluid, with density p = 800 kg/m and specific heat capacity c = 5000 J/kg-C°, emerges from a tank at a temperature, T, = 400 °C. The fluid then enters a metal pipe with inner radius a = 2.0 cm and outer radius b = 3.0 cm and thermal conductivity k = 180 W/m•C°. Outside the pipe the temperature is fixed at Tout = 15 °C. If the fluid flows at speed v = 8.0 m/s and the length of the pipe is L = 25 m, what is the temperature of the fluid at the end of the pipe? (Answer: 83 °C) please I need to show All work problems step by steparrow_forwardIn an isothermal process, you are told that heat is being added to the system. Which of the following is not true? (a) The pressure of the gas is decreasing. (b) Work is being done on the system. (c) The average kinetic energy of the particles is remaining constant. (d) The volume of the gas is increasing. (e) Work is being done by the system.arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward8.114 CALC A Variable-Mass Raindrop. In a rocket-propul- sion problem the mass is variable. Another such problem is a rain- drop falling through a cloud of small water droplets. Some of these small droplets adhere to the raindrop, thereby increasing its mass as it falls. The force on the raindrop is dp dv dm Fext = + dt dt dt = Suppose the mass of the raindrop depends on the distance x that it has fallen. Then m kx, where k is a constant, and dm/dt = kv. This gives, since Fext = mg, dv mg = m + v(kv) dt Or, dividing by k, dv xgx + v² dt This is a differential equation that has a solution of the form v = at, where a is the acceleration and is constant. Take the initial velocity of the raindrop to be zero. (a) Using the proposed solution for v, find the acceleration a. (b) Find the distance the raindrop has fallen in t = 3.00 s. (c) Given that k = 2.00 g/m, find the mass of the raindrop at t = 3.00 s. (For many more intriguing aspects of this problem, see K. S. Krane, American Journal of…arrow_forward8.13 A 2.00-kg stone is sliding Figure E8.13 F (kN) to the right on a frictionless hori- zontal surface at 5.00 m/s when it is suddenly struck by an object that exerts a large horizontal force on it for a short period of 2.50 time. The graph in Fig. E8.13 shows the magnitude of this force as a function of time. (a) What impulse does this force exert on t (ms) 15.0 16.0 the stone? (b) Just after the force stops acting, find the magnitude and direction of the stone's velocity if the force acts (i) to the right or (ii) to the left.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning


Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning