
Interpretation:
The resonance structure of the radical should be identified for the given molecule.
Concept introduction:
Radical or free radical: unpaired valence electron of an atom, molecule, or ion is called as radical
Answer to Problem 22PP
Answer
An unpaired electron occupies the allylic position and in is involving in resonance. The arrow pattern of radical resonance is given below (a).

An unpaired electron occupies the allylic position and in is involving in resonance. The arrow pattern of radical resonance is given below (b).
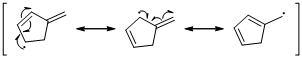
An unpaired electron occupies the allylic position and in is involving in resonance. The arrow pattern of radical resonance is given below (c).
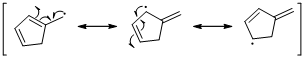
Unpaired electrons resonance with allylic double bonds. The arrow pattern of radical resonance is given below (d).
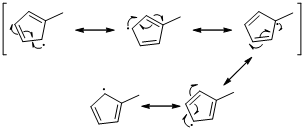
Unpaired electrons resonance with allylic double bonds. The arrow pattern of radical resonance is given below (f)
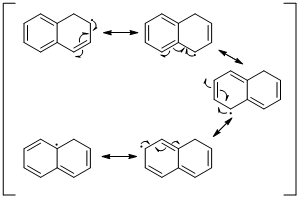
Explanation of Solution
The radical resonance structure of the given molecule
The radical resonance structure of the molecule is given below.

An unpaired electron occupies the allylic position and in is involving in resonance. Here three fishhook arrows were used to show the resonance.
The radical resonance structure of the molecule is given below.

An unpaired electron occupies the allylic position and in is involving in resonance. Here three fishhook arrows were used to show the resonance. The resulting resonance structure exhibits an unpaired electrons, the unpaired electrons allylic to another π bond that also involving resonance. Again three fishhook arrows were used for the resonance.
The radical resonance structure of the molecule is given below.
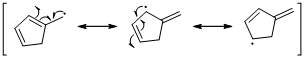
An unpaired electron occupies the allylic position and in is involving in resonance. Here three fishhook arrows were used to show the resonance. The resulting resonance structure exhibits an unpaired electrons, the unpaired electrons allylic to another π bond that also involving resonance. Again three fishhook arrows were used for the resonance.
The radical resonance structure of the molecule is given below.
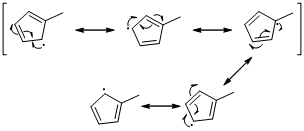
An unpaired electron occupies the allylic position and in is involving in resonance. Here three fishhook arrows were used to show the resonance. The resulting resonance structure exhibits an unpaired electrons, the unpaired electrons allylic to another π bond that also involving resonance. Again three fishhook arrows were used for the resonance. Similarly the five resonances structure is exist in same manner as shown above structure.
The radical resonance structure of the molecule is given below.
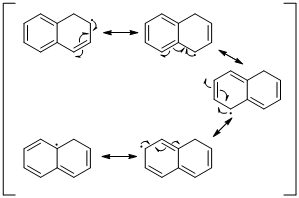
An unpaired electron occupies the allylic position and in is involving in resonance. Here three fishhook arrows were used to show the resonance. The resulting resonance structure exhibits an unpaired electrons, the unpaired electrons allylic to another π bond that also involving resonance. Again three fishhook arrows were used for the resonance. Similarly the five resonances structure is exist in same manner as shown above structure.
Conclusion
The resonance structure of the radical for the given molecule is found.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





