
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction of dibutyl sulfide with 1 equivalent of H2O2 at 25 °C is to be predicated.
Concept introduction:
Hydrogen perioxide (H2O2) is an strong oxidizing agent. It is used in many organic synthese to produced oxidized products.
Sulfur containing organic compounds has many similar chemical properties as oxygen contain compound such as ether and aclcohol.
Answer to Problem 11.45AP
The product of the reaction of dibutyl sulfide with 1 equivalent of H2O2 at 25 °C is shown below.

Explanation of Solution
The dibutyl sulfide undergoes an oxidation reaction with hydrogen peroxide. The dibutyl sulfide reacts with 1 equivalent of H2O2 at 25 °C to form a oxidation product dibutyl sulfoxide.
The corresponding

Figure 1
The product of the reaction of dibutyl sulfide with 1 equivalent of H2O2 at 25 °C is shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction of dibutyl sulfide with 2 or more equivalents of H2O2 and heat is to be predicated.
Concept introduction:
Hydrogen perioxide (H2O2) is an strong oxidizing agent. It is used in many organic synthese to produced oxidized products.
Sulfur containing organic compounds has many similar chemical properties as oxygen contain compound such as ether and aclcohol.
Answer to Problem 11.45AP
The product of the reaction of dibutyl sulfide with 2 or more equivalents of H2O2 and heat shown below.
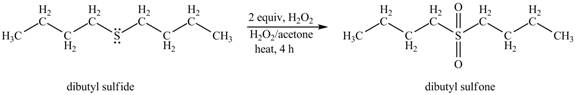
Explanation of Solution
The dibutyl sulfide undergoes an oxidation reaction with hydrogen peroxide. The dibutyl sulfide reacts with H2O2 to form a oxidation product dibutyl sulfoxide. The dibutyl sulfoxide further oxides to form dibutyl sulfone.
The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
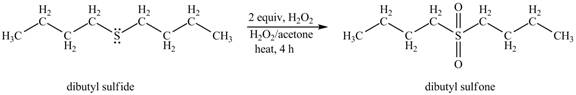
Figure 2
The product of the reaction of dibutyl sulfide with 2 or more equivalents of H2O2 and heat shown in Figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction of cis-3-hexene with magnesium monoperoxyphthalate (MMPP) is to be predicated.
Concept introduction:
The magnesium monoperoxyphthalate (MMPP) is an strong oxidizing agent. It is used in many organic synthese to produced oxidized products. It can oxides
Answer to Problem 11.45AP
The product of the reaction of cis-3-hexene with magnesium monoperoxyphthalate (MMPP) is shown below.
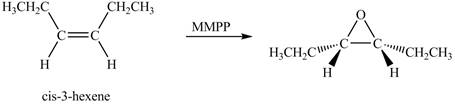
Explanation of Solution
The compound cis-3-hexene undergoes a oxidation reaction with magnesium monoperoxyphthalate (MMPP). The magnesium monoperoxyphthalate coverts the alkene into epoxide.
The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
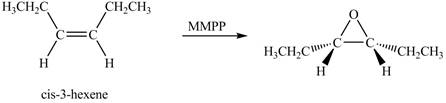
Figure 3
The product of the reaction of cis-3-hexene with magnesium monoperoxyphthalate (MMPP) is shown in Figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction of given compound with (CH3)2CuCNLi2 followed by the addition of H3O+ is to be predicated.
Concept introduction:
Epoxides undergo nucleophilic ring-opening reactions which are acid-catalyzed. If the epoxide is unsymmetrical, then the anionic nucleophile will attack the less-hindered carbon atom of the ring. If the reaction conditions are acidic, then the reaction will occur at the more substituted carbon atom.
Answer to Problem 11.45AP
The product of the reaction of given compound with (CH3)2CuCNLi2 followed by the addition of H3O+ is shown below.
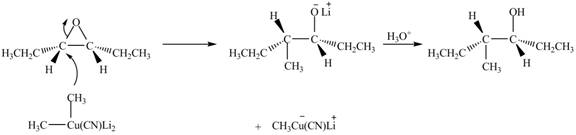
Explanation of Solution
The epoxide undergoes ring-opening reaction in the presence of acid. The dilithium dimethylcyanocuprate molecule generates a nucleophile (−CH3). This nucleophile will attack the more substituted carbon atom of the epoxide ring to from the product. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
Figure 4
The product of the reaction of given compound with (CH3)2CuCNLi2 followed by the addition of H3O+ is shown in Figure 4.
(e)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction of given compound with solvent H2O in acidic solution is to be predicated.
Concept introduction:
Epoxides undergo nucleophilic ring-opening reactions which are acid-catalyzed. If the epoxide is unsymmetrical, then the anionic nucleophile will attack the less-hindered carbon atom of the ring. If the reaction conditions are acidic, then the reaction will occur at the more substituted carbon atom.
Answer to Problem 11.45AP
The product of the reaction of given compound with solvent H2O in acidic solution is shown below.
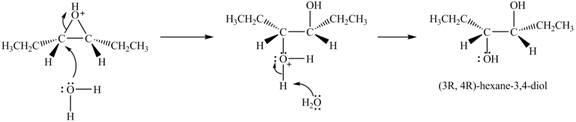
Explanation of Solution
The epoxide undergoes ring opening reaction in the presence of acid. The water molecule acts a nucleophile and attacks on the more substituted carbon atom of the epoxide ring to from

Figure 5
The product of the reaction of given compound with solvent H2O in acidic solution is shown in Figure 5.
(f)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction of given compound with periodic acid is to be predicated.
Concept introduction:
The periodic acid acts as a strong oxidizing agent. The periodic acid reacts with a vicinal diol to form two
Answer to Problem 11.45AP
The product of the reaction of given compound with periodic acid is shown below.
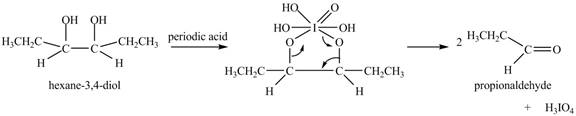
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is vicinal diol. It reacts with periodic acid to form two aldehydes. The carbon-carbon bond between the carbon atoms attached to two adjacent hydroxyl groups gets breaks. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.

Figure 6
The product of the reaction of given compound with periodic acid is shown in Figure 6.
(g)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction of given compound with NaH in THF followed by CH3I is to be predicated.
Concept introduction:
The metal hydride reagents are good reducing agents such as NaH. Sodium hydride is used in many organic syntheses as a reducing agent. Sodium hydride can also be used as a base in the organic syntheses reactions. It abstracts the acidic proton from the organic compounds.
Answer to Problem 11.45AP
The product of the reaction of given compound with NaH in THF followed by CH3I is shown below.
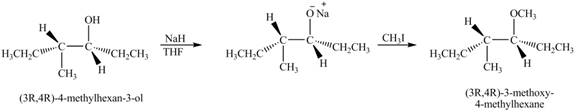
Explanation of Solution
The base NaH abstract the proton of the hydroxyl group of alcohol to form an anion. The anion acts as nucleophile and attacks on the carbon atom of CH3I. The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
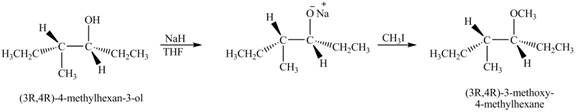
Figure 7
The product of the reaction of given compound with NaH in THF followed by CH3I is shown in Figure 7.
(h)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction of (E)-3-methyl-3-hexene with Hg(OAc)2 in ethanol solvent followed by NaBH4 is to be predicated.
Concept introduction:
Oxymercuration reaction is a type of reaction in which an alkene get converted into an alcohol. The mercuric acetate is used in the reaction as reagent. This reagent attacks the alkene to form a cyclic intermediate compound which further undergoes reduction to form alcohol.
Answer to Problem 11.45AP
The product of the reaction of (E)-3-methyl-3-hexene with Hg(OAc)2 in ethanol solvent followed by NaBH4 is shown below.
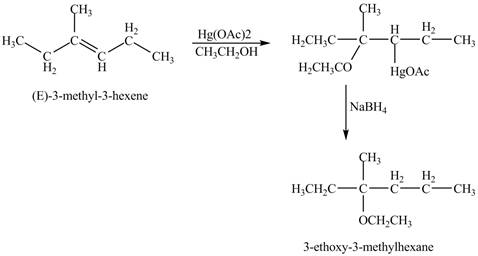
Explanation of Solution
The mercuric acetate Hg(OAc)2 in ethanol solvent reacts with (E)-3-methyl-3-hexene to from a intermediate product which is reduced by the addition of NaBH4 in the reaction mixture. The end product formed in the reaction is an ether due to the use of ethanol as solvent.
The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
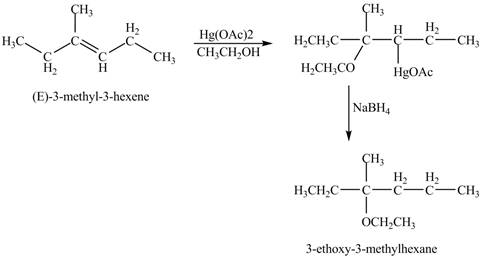
Figure 8
The product of the reaction of (E)-3-methyl-3-hexene with Hg(OAc)2 in ethanol solvent followed by NaBH4 is shown in Figure 8.
(i)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction of the given compound with acidic methanol is to be predicated.
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one
Answer to Problem 11.45AP
The product of the reaction of the given compound with acidic methanol is shown below.
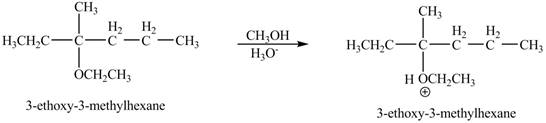
Explanation of Solution
The proton of the acid will protionate the ether. The protonated ether will increase the electrophilic characters of carbon atom attached to the oxygen atom. The methonal can acts as nuclephile, however the nucleophilic charater of methoxy-group and ethoxy group is similar. Therefore, no further reaction will take place.
The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
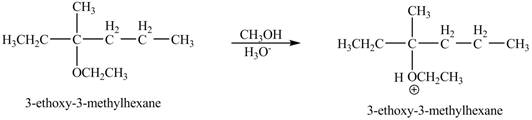
Figure 9
The product of the reaction of the given compound with acidic methanol is shown in Figure 9.
(j)
Interpretation:
The product of the reaction of (R)-3-Methyl-1-bromopentane with Mg in ether followed by addition of ethylene oxide, then with CH3I is to be predicated.
Concept introduction:
Grignard reagents are
Answer to Problem 11.45AP
The product of the reaction of (R)-3-Methyl-1-bromopentane with Mg in ether followed by addition of ethylene oxide, then with CH3I is shown below.
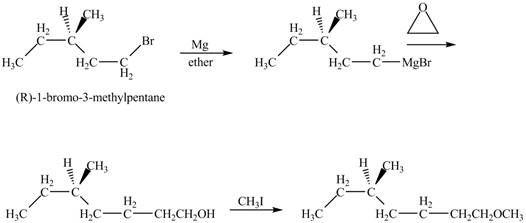
Explanation of Solution
The alkyl halide will react with magnisum metal to from gridnard reagent. These Grignard reagent reacts with epoixde to form alcohol. The alcohol reacts with CH3I to form ether.
The corresponding chemical reaction is shown below.
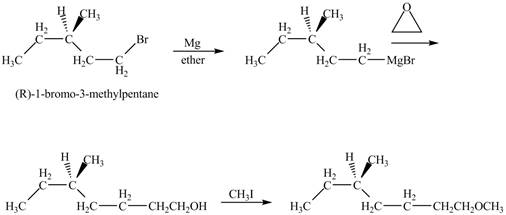
Figure 10
The product of the reaction of (R)-3-Methyl-1-bromopentane with Mg in ether followed by addition of ethylene oxide, then with CH3I is shown in Figure 10.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- If a high molecular weight linear polyethylene is chlorinated by inducing the substitution of chlorine atoms by hydrogen, if 5% of all hydrogen atoms are replaced, what approximate percentage of chlorine by weight would the product have?arrow_forwardO Macmillan Learning Chemistry: Fundamentals and Principles Davidson presented by Macmillan Learning Poly(ethylene terephthalate), known as PET or industrially as Dacron, is a polyester synthesized through a condensation reaction between two bifunctional monomers. The monomers, ethylene glycol and terepthalic acid, are given. Add bonds and remove atoms as necessary to show the structure of a two repeat unit portion of a longer polymer chain of PET. You may need to zoom out to see the complete structure of all four monomer units. Select Draw / || | C H 0 3 © Templates More ° ° ° || C CC - OH HO OH HOC - C Erase CC OH HO C C 〃 C H₂ Q2Qarrow_forwardc) + H₂Oarrow_forward
- 으 b) + BF. 3 H2Oarrow_forwardQ4: Draw the product of each Lewis acid-bas reaction. Label the electrophile and nucleophile. b) S + AICI 3 + BF 3arrow_forwardQ1 - What type(s) of bonding would be expected for each of the following materials: solid xenon, calcium fluoride (CaF2), bronze, cadmium telluride (CdTe), rubber, and tungsten? Material solid xenon CaF2 bronze CdTe rubber tungsten Type(s) of bonding Q2- If the atomic radius of lead is 0.175 nm, calculate the volume of its unit cell in cubic meters.arrow_forward
- Determine the atomic packing factor of quartz, knowing that the number of Si atoms per cm3 is 2.66·1022 and that the atomic radii of silicon and oxygen are 0.038 and 0.117 nm.arrow_forwardUse the following data for an unknown gas at 300 K to determine the molecular mass of the gas.arrow_forward2. Provide a complete retrosynthetic analysis and a complete forward synthetic scheme to make the following target molecule from the given starting material. You may use any other reagents necessary. Brarrow_forward
- 146. Use the following data for NH3(g) at 273 K to determine B2p (T) at 273 K. P (bar) 0.10 0.20 0.30 0.40 0.50 0.60 (Z -1)/10-4 1.519 3.038 4.557 6.071 7.583 9.002 0.70 10.551arrow_forward110. Compare the pressures given by (a) the ideal gas law, (b) the van der Waals equation, and (c) the Redlic-Kwong equation for propane at 400 K and p = 10.62 mol dm³. The van der Waals parameters for propane are a = 9.3919 dm6 bar mol-2 and b = 0.090494 dm³ mol−1. The Redlich-Kwong parameters are A = 183.02 dm bar mol-2 and B = 0.062723 dm³ mol-1. The experimental value is 400 bar.arrow_forwardResearch in surface science is carried out using stainless steel ultra-high vacuum chambers with pressures as low as 10-12 torr. How many molecules are there in a 1.00 cm3 volume at this pressure and at a temperature of 300 K? For comparison, calculate the number of molecules in a 1.00 cm3 volume at atmospheric pressure and room temperature. In outer space the pressure is approximately 1.3 x 10-11 Pa and the temperature is approximately 2.7 K (determined using the blackbody radiation of the universe). How many molecules would you expect find in 1.00 cm3 of outer space?arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





