
Concept explainers
What
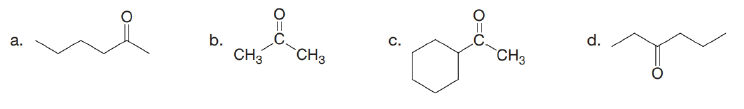
(a)
Interpretation: The alkynes that forms the given ketone as the only product after hydration with
Concept introduction: A terminal alkyne reacts with
Answer to Problem 11.40P
The alkynes that forms the given ketone as the only product after hydration with
Explanation of Solution
The alkynes that forms the given ketone as the only product after hydration with
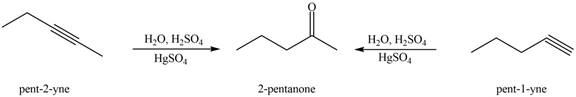
Figure 1
The terminal alkynes,
The alkynes that forms the given ketone as the only product after hydration with
(b)
Interpretation: The alkynes that forms the given ketone as the only product after hydration with
Concept introduction: A terminal alkyne reacts with
Answer to Problem 11.40P
The alkyne that forms the given ketone as the only product after hydration with
Explanation of Solution
The alkyne that forms the given ketone as the only product after hydration with
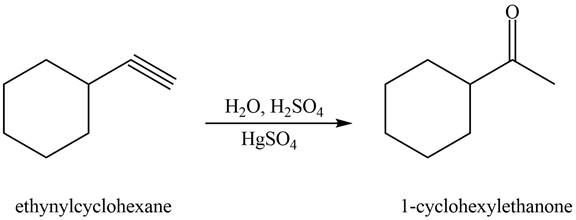
Figure 2
The terminal alkyne, ethynylcyclohexane reacts with the reagents
The alkyne that forms the given ketone as the only product after hydration with
(c)
Interpretation: The alkynes that forms the given ketone as the only product after hydration with
Concept introduction: A terminal alkyne reacts with
Answer to Problem 11.40P
The alkynes that forms the given ketone as the only product after hydration with
Explanation of Solution
The alkynes that forms the given ketone as the only product after hydration with
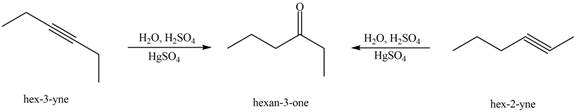
Figure 3
The terminal alkynes,
The alkynes that forms the given ketone as the only product after hydration with
(d)
Interpretation: The alkynes that forms the given ketone as the only product after hydration with
Concept introduction: A terminal alkyne reacts with
Answer to Problem 11.40P
The alkynes that forms the given ketone as the only product after hydration with
Explanation of Solution
The alkynes that forms the given ketone as the only product after hydration with
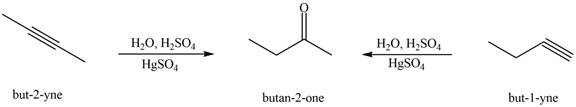
Figure 4
The terminal alkynes,
The alkynes that forms the given ketone as the only product after hydration with
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 11 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Nonearrow_forwardUnshared, or lone, electron pairs play an important role in determining the chemical and physical properties of organic compounds. Thus, it is important to know which atoms carry unshared pairs. Use the structural formulas below to determine the number of unshared pairs at each designated atom. Be sure your answers are consistent with the formal charges on the formulas. CH. H₂ fo H2 H The number of unshared pairs at atom a is The number of unshared pairs at atom b is The number of unshared pairs at atom c is HC HC HC CH The number of unshared pairs at atom a is The number of unshared pairs at atom b is The number of unshared pairs at atom c isarrow_forwardDraw curved arrows for the following reaction step. Arrow-pushing Instructions CH3 CH3 H H-O-H +/ H3C-C+ H3C-C-0: CH3 CH3 Harrow_forward
- 1:14 PM Fri 20 Dec 67% Grade 7 CBE 03/12/2024 (OOW_7D 2024-25 Ms Sunita Harikesh) Activity Hi, Nimish. When you submit this form, the owner will see your name and email address. Teams Assignments * Required Camera Calendar Files ... More Skill: Advanced or complex data representation or interpretation. Vidya lit a candle and covered it with a glass. The candle burned for some time and then went off. She wanted to check whether the length of the candle would affect the time for which it burns. She performed the experiment again after changing something. Which of these would be the correct experimental setup for her to use? * (1 Point) She wanted to check whether the length of the candle would affect the time for which it burns. She performed the experiment again after changing something. Which of these would be the correct experimental setup for her to use? A Longer candle; No glass C B Longer candle; Longer glass D D B Longer candle; Same glass Same candle; Longer glassarrow_forwardBriefly describe the compounds called carboranes.arrow_forwardPlease don't use Ai solutionarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





