
Concept explainers
A strain gauge is mounted on a steel cantilever beam of rectangular cross section. The gauge is connected in a Wheatstone bridge; initially /?gauge = /?2 = ^3 = ^4 = 120Q. A gauge resistance change of 0.1 Q is measured for the loading condition and gauge orientation shown in Figure 11.24. If the gauge factor is 2.05 ± 1% (95%) estimate the strain. Suppose the uncertainty in each resistor value is 1% (95%). Estimate an uncertainty in the measured strain due to the uncertainties in the bridge resistances and gauge factor. Assume that the bridge operates in a null mode, which is detected by a galvanometer. Also assume reasonable values for other necessary uncertainties and parameters, such as input voltage or galvanometer sensitivity.
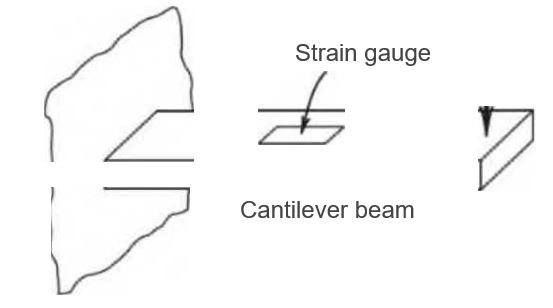
Figure 11.24 Loading for Problem 11.20.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 11 Solutions
Theory and Design for Mechanical Measurements
- 650 600 550 500 450 400 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0.002 0.004 0.006 0.008 0.01 0.012 0.014 0.016 0.018 0.02 Strain mm/mm The graph above shows the stress-strain relationship of a steel bar under tension test. The steel bar diameter = 8 mm and the bar gauge length = 100 mm. Determine the following: If the specimen is loaded to 550 MPa and then unloaded. What would be the modulus of resilience of the sample after reloading? Stress (MPa)arrow_forwardi. If you know that any strain gauge has a sensitivity towards temperature.In other words, any change in the temperature could also affect theresistance value. How can we get a correct reading from strain gaugesand get rid of the temperature effect?ii. In an AC LVDT system, measuring the output voltage alone gives anindication of the displacement from the center, but not the direction ofdisplacement. Explain why, and also explain a method for solving thisproblem.iii. In a vortex flow meter, there are many methods that could be used tomeasure the effect of vortices and measure the flow rate. Explain howvortices could occur in this flow meter, and explain three methods thatcould be used for measuring the effects of vortices in a vortex flowmeter.iv. Explain in details how can we use a capacitor to indicate the lever ofwater in a tank (use drawings and electrical diagram to elaborate on yourexplanation).Page 5 of 63v. Bimetallic strip could be used as a temperature detector. Explain…arrow_forwardA metallic strain gauge produces an electrical resistance change when subjected to mechanical strain. However, engineers don't measure this voltage drop directly using a voltmeter. Why don't we directly measure the voltage drop across the strain gauge, and instead, use a Wheatstone Bridge? Damgraph >arrow_forward
- Four strain gauges are formed into bridge with only one active gauge. The nominal resistance of all of them is 120 W. The gauge factor is 2.1 and the supply voltage is 10 V. Calculate the strain when the output from the bridge is 20 mV.arrow_forward1) A compressive force is applied to a structural member. Two separate strain gauges are attached to the structural member; one is a nickel wire strain gauge having a gauge factor of -12.1 and the other is nichrome wire strain gauge having a gauge factor of 2. Calculate the value of resistance of the two gauges after they are strained, if the resistance of strain gauges before being strained is 120 2, and the compressive strain is 5 micro-strain. Assume positive value for tensile strain and negative for compressive strain. (Answer: For Nickel, R = 120.00726 Q. For Nichrome, R = 119.9988 Q)arrow_forwardC27 Which of the following is not a base SI unit? С. cd В. Hz A. kg D. mol C28 What is the percentage change in resistance of a semiconductor strain gauge with a temperature coefficient of 2e-5 °C-1, gauge factor of 2.1, under a strain of 1 µ at 100 °C. A. 0.15% B. 0.25% C. 0.2% D. 0.1% 15 C29 Consider a hydraulic press that lifts a weight of 128 kg by applying a 4 kg force. What is the ratio of area of the 'load' piston to the area of the force' piston? С. 16 А. 32 В. 4/2 D. 64arrow_forward
- A strain gauge is used to measure the tension force in a 2-cm diameter bar of steel with Young modulus of 2.07 x 107 N/cm2 (30 x 106 lb./in.2). The strain gauge has a nominal resistance of 160 Ω and a GF of 5. The gauge is connected to a bridge supplied with a 10 Vdc. The bridge was initially balanced. After the bar is put under tension, the bridge output voltage is 0.0008 Vdc. Draw the schematic of the bridge (setup). Calculate the force on the bar.arrow_forwardBasic force sensor. The ceiling of a large building is supported by 16 vertical steel tubes, each with an inner diameter of 100 mm and an outer diameter of 140 mm. Each tube is equipped with a 240 2 strain gauge (nominal, unstressed resistance at 20°C), prestressed to 2.5% strain. The Young's modulus for steel is 200 GPa. The strain gauge has a gauge factor of 2.2. 6.6 a. If the maximum strain mneasured is 2% in each tube, what is the maximum weight of the roof? b. What is the change in the resistance of the strain gauge and what is the actual resistance reading for maximum allowable weight? C. If the expected temperature range is 0°C-50°C, what is the error in reading of the maximum weight, assuming the sensor is not temperature compensated and it is made of constantan?arrow_forwardStrain gauges are a standard sensor to convert deformation into an electrical signal and are used in many applications. Describe how train gauges could be used to measure (i) acceleration; (ii) fluid pressure. Use a sketch for each case to illustrate how they are used.arrow_forward
- 9.11 A strain gauge, diaphragm pressure transducer (accuracy: <0.1% reading) is subjected to a pressure differential of 10 kPa. If the output is measured using a voltmeter having a resolution of 10 mV and accuracy of better than 0.1% of the reading, estimate the uncertainty in pressure at the design stage. How does this change at 100 and 1,000 kPa?arrow_forward3. Compare the resistance change produced by a strain of 150 microstrain if a strain gauge of nominal resistance of 120 N is used (i) when made of wire resistance having a gauge factor of 2.13 and (ii) when made of a semiconducting material having a gauge factor of 151. 4. A metallic strain gauge has a resistance of 120 Q and a gauge factor of 2. It is installed on an aluminium structure which has a yield point stress of 0.2 GN/m² and young's modulus of 68.7 GN/m?, determine the change in resistance of the gauge that would be caused by loading the material to yield point.arrow_forwardMeasurement & metrology- Q-3 ) A resistance wire strain gauge uses a soft iron wire of small diameter. The gauge factor is +5.4 Neglecting the piezoresistive effects, calculate the Poisson's ratio.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





