
Concept explainers
a.
To find how much wax is used in each candle
a.
Answer to Problem 15E
1809 ft3
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Diameter( d ) of the red candle is 3 inches
Height( h ) of the red candle is 6 inches
Diameter( d ) of the blue candle is 3 inches
Height( h ) of the blue candle is 9 inches
Diameter( d ) of the green candle is 4 inches
Height( h ) of the green candle is 4 inches
Formula used:
Volume( V ) of the cylinder = 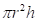
Calculation:
Diameter of the base, d=2r
Then Radius,
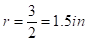 for red candle
for red candle
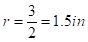 for blue candle
for blue candle
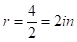 for green candle
for green candle
Substituting value of Radius ( r ) and Height( h ) of respective candle in formula,
For red candle:
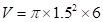 Square of 1.5 is 2.25
Square of 1.5 is 2.25
Value of pi upto 2 decimal points is 3.14
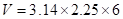
On solving,
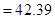 in3
in3
For blue candle:
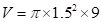
Square of 1.5 is 2.25
Value of pi upto 2 decimal points is 3.14
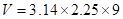
On solving,
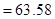 in3
in3
For green candle:
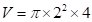
Square of 2 is 4
Value of pi upto 2 decimal points is 3.14
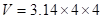
On solving,
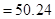 in3
in3
Hence, wax used in red, blue and green candle is 42.39 in3 , 63.58 in3 and 50.24 in3 in respective candle.
b.
To find ratio of cost of candle to volume of wax used in candle
b.
Answer to Problem 15E
For red candle- 1:6
For blue candle- 1:8
For green candle- 1:5
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The cost of red candle is $7.05
The cost of blue candle is $7.80
The cost of green candle is $10.55
Calculated volume
=42.39 in3 For red candle
=63.58 in3 For blue candle
=50.24 in3 For green candle
Calculation:
Cost to volume ratio for red candle,
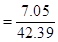
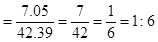
Cost to volume ratio for blue candle,
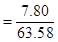
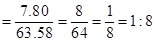
Cost to volume ratio for green candle,
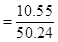
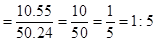
c.
To find which candle is the best buy
c.
Answer to Problem 15E
Blue Candle
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The cost to volume ratio,
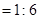 For red candle
For red candle
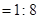 For blue candle
For blue candle
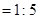 For green candle
For green candle
Calculation:
Blue candle is best buy because cost to volume ratio is
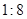 which mean in 1$ person can buy 8 in3 wax.
which mean in 1$ person can buy 8 in3 wax.
Chapter 10 Solutions
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition 2012
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
- 3. Let M = (a) - (b) 2 −1 1 -1 2 7 4 -22 Find a basis for Col(M). Find a basis for Null(M).arrow_forwardSchoology X 1. IXL-Write a system of X Project Check #5 | Schx Thomas Edison essay, x Untitled presentation ixl.com/math/algebra-1/write-a-system-of-equations-given-a-graph d.net bookmarks Play Gimkit! - Enter... Imported Imported (1) Thomas Edison Inv... ◄›) What system of equations does the graph show? -8 -6 -4 -2 y 8 LO 6 4 2 -2 -4 -6 -8. 2 4 6 8 Write the equations in slope-intercept form. Simplify any fractions. y = y = = 00 S olo 20arrow_forwardEXERCICE 2: 6.5 points Le plan complexe est rapporté à un repère orthonormé (O, u, v ).Soit [0,[. 1/a. Résoudre dans l'équation (E₁): z2-2z+2 = 0. Ecrire les solutions sous forme exponentielle. I b. En déduire les solutions de l'équation (E2): z6-2 z³ + 2 = 0. 1-2 2/ Résoudre dans C l'équation (E): z² - 2z+1+e2i0 = 0. Ecrire les solutions sous forme exponentielle. 3/ On considère les points A, B et C d'affixes respectives: ZA = 1 + ie 10, zB = 1-ie 10 et zc = 2. a. Déterminer l'ensemble EA décrit par le point A lorsque e varie sur [0, 1. b. Calculer l'affixe du milieu K du segment [AB]. C. Déduire l'ensemble EB décrit par le point B lorsque varie sur [0,¹ [. d. Montrer que OACB est un parallelogramme. e. Donner une mesure de l'angle orienté (OA, OB) puis déterminer pour que OACB soit un carré.arrow_forward
- 2 Use grouping to factor: 10x + 13x + 3 = 0 Identify A B and C in the chart below feach responce inarrow_forward2 Use grouping to factor: 10x² + 13x + 3 = 0 Identify A, B, and C in the chart below. (each rearrow_forward2 Use grouping to factor: 10x + 13x + 3 = 0 Identify A B and C in the chart below feach responce inarrow_forward
- Use grouping to fully factor: x³ + 3x² - 16x - 48 = 0 3 2arrow_forwardName: Tay Jones Level Two Date: Algebra 3 Unit 3: Functions and Equations Practice Assessment Class: #7-OneNote 1. The function f(x) = x² is transformed in the following functions. List the vertex for each function, circle whether the function opens up or down, and why. All three parts must be correct to receive Level 2 points. You can receive points for a, b, and c. a) g(x) = -2(x+5)² Vertex: Opens Up Opens Down Why? ais negative -2 Vertex: b) g(x) = (x + 2)² - 3 c) g(x) = -4(x + 2)² + 2 Opens Up Opens Down Vertex: Opens Up Opens Down Why? 4 Ca is negative) Why? his positive 2. The graph of the function f(x) is shown below. Find the domain, range, and end behavior. Then list the values of x for which the function values are increasing and decreasing. f(x) Domain: End Behavior: As x → ∞o, f(x) -> -6 As x, f(x) -> Range: Where is it Increasing? (002] Where is it Decreasing? (1,00)arrow_forwardShow what to do on the graph visually please!arrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





