
Concept explainers
a.
Find the sample proportions and test statistic for equal proportions.
Find the p-value.
a.
Answer to Problem 22SE
Sample proportions:
The test statistic is 1.4825.
The conclusion is that, there is no significant difference in the proportion of dissatisfied workers in two companies.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The given information is that,
State the hypotheses:
Null hypothesis:
That is, there is no significant difference in the proportion of dissatisfied workers in two companies.
Alternative hypothesis:
That is, there is a significant difference in the proportion of dissatisfied workers in two companies.
Sample proportions:
First sample:
Second sample:
Pooled proportion:
Thus, the pooled proportion is 0.35.
Test statistic:
Thus, the test statistic is 1.4825.
p-value:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the p-value using EXCEL software is as follows:
- Open an EXCEL file.
- In cell A1, enter the formula “=NORM.S.DIST(1.4825)”
- Output using Excel software is given below:
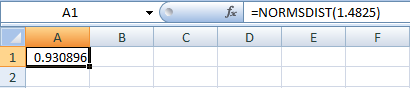
The p-value is,
Thus, the p-value is 0.1382.
Decision rule:
If
Conclusion:
Here, the p-value is greater than the level of significance.
That is,
Therefore, the null hypothesis is not rejected.
Thus, it can be concluded that there is no significant difference in the proportion of dissatisfied workers in two companies.
b.
Find the sample proportions and test statistic for equal proportions.
Find the p-value.
b.
Answer to Problem 22SE
Sample proportions:
The test statistic is –2.16.
The conclusion is that, the proportion of rooms rented at least a week in advance at the 2nd hotel is not less than the 1st hotel.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The given information is that,
State the hypotheses:
Null hypothesis:
That is, the proportion of rooms rented at least a week in advance at the 2nd hotel is not less than the 1st hotel.
Alternative hypothesis:
That is, the proportion of rooms rented at least a week in advance at the 2nd hotel is less than the 1st hotel.
Sample proportions:
First sample:
Second sample:
Pooled proportion:
Thus, the pooled proportion is 0.144.
Test statistic:
Thus, the test statistic is –2.16.
p-value:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the p-value using EXCEL software is as follows:
- Open an EXCEL file.
- In cell A1, enter the formula “=NORM.S.DIST(–2.16)”
- Output using Excel software is given below:
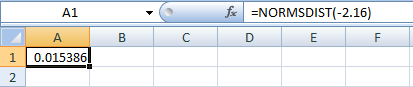
Thus, the p-value is 0.0154.
Decision rule:
If
Conclusion:
Here, the p-value is greater than the level of significance.
That is,
Therefore, the null hypothesis is not rejected.
Thus, it can be concluded that the proportion of rooms rented at least a week in advance at the 2nd hotel is not less than the 1st hotel.
c.
Find the sample proportions and test statistic for equal proportions.
Find the p-value.
c.
Answer to Problem 22SE
Sample proportions:
The test statistic is 1.6379.
The conclusion is that, the proportion of home equity loan default rates for first bank is not greater than the second bank.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
The given information is that,
State the hypotheses:
Null hypothesis:
That is, the proportion of home equity loan default rates for first bank is not greater than the second bank.
Alternative hypothesis:
That is, the proportion of home equity loan default rates for first bank is greater than the second bank.
Sample proportions:
First sample:
Second sample:
Pooled proportion:
Thus, the pooled proportion is 0.062.
Test statistic:
Thus, the test statistic is 1.6379.
p-value:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the p-value using EXCEL software is as follows:
- Open an EXCEL file.
- In cell A1, enter the formula “=NORM.S.DIST(1.6379)”
- Output using Excel software is given below:
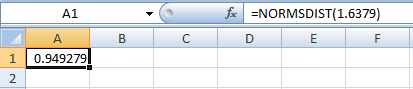
The p-value is,
Thus, the p-value is 0.0507.
Decision rule:
If
Conclusion:
Here, the p-value is greater than the level of significance.
That is,
Therefore, the null hypothesis is not rejected.
Thus, it can be concluded that the proportion of home equity loan default rates for first bank is not greater than the second bank.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Applied Statistics in Business and Economics
- AP1.2 A child is 40 inches tall, which places her at the 90th percentile of all children of similar age. The heights for children of this age form an approximately Normal distribution with a mean of 38 inches. Based on this information, what is the standard deviation of the heights of all children of this age? 0.20 inches (c) 0.65 inches (e) 1.56 inches 0.31 inches (d) 1.21 inchesarrow_forwardAP1.1 You look at real estate ads for houses in Sarasota, Florida. Many houses range from $200,000 to $400,000 in price. The few houses on the water, however, have prices up to $15 million. Which of the following statements best describes the distribution of home prices in Sarasota? The distribution is most likely skewed to the left, and the mean is greater than the median. The distribution is most likely skewed to the left, and the mean is less than the median. The distribution is roughly symmetric with a few high outliers, and the mean is approximately equal to the median. The distribution is most likely skewed to the right, and the mean is greater than the median. The distribution is most likely skewed to the right, and the mean is less than the median.arrow_forwardDuring busy political seasons, many opinion polls are conducted. In apresidential race, how do you think the participants in polls are generally selected?Discuss any issues regarding simple random, stratified, systematic, cluster, andconvenience sampling in these polls. What about other types of polls, besides political?arrow_forward
- Please could you explain why 0.5 was added to each upper limpit of the intervals.Thanksarrow_forward28. (a) Under what conditions do we say that two random variables X and Y are independent? (b) Demonstrate that if X and Y are independent, then it follows that E(XY) = E(X)E(Y); (e) Show by a counter example that the converse of (ii) is not necessarily true.arrow_forward1. Let X and Y be random variables and suppose that A = F. Prove that Z XI(A)+YI(A) is a random variable.arrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt



