
Concept introduction:
Budget Line: It is defined as the combination of all goods that a consumer can buy exhausting his all income. Formula for the budget line is:
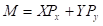
Here,
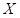 is the quantity of good X.
is the quantity of good X. 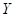 is the quantity of good Y.
is the quantity of good Y. 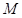 is the total income.
is the total income. 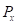 is the price of good X.
is the price of good X. 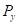 is the price of good Y.
is the price of good Y.
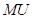 is the marginal utility.
is the marginal utility. 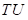 is the total utility.
is the total utility. - X is the quantity of any good.
- N is the number of goods.
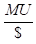 is the marginal utility per dollar.
is the marginal utility per dollar. 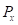 is the price of good X.
is the price of good X. 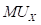 is the marginal utility of good X.
is the marginal utility of good X. 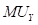 is the marginal utility of good Y.
is the marginal utility of good Y. 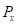 is the price of good X.
is the price of good X. 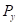 is the price of good Y.
is the price of good Y.
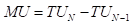 Or
Or
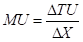
Here,
Marginal Utility per dollar: It is the ratio of marginal utility to that of the price of a good. The formula to calculate the marginal utility per dollar is:

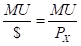
Here,
Maximizing utility in the case of two goods: It states that the equilibrium level of consumption of two goods for a consumer is achieved when the marginal utility per dollar of the two goods are equal. This means that the following conditions must be fulfilled:
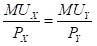
Here,
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
Economics

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





