
Concept explainers
Prepare comparative income statement and comparative schedule of cost of goods sold for each month under (1) absorption costing method and (2) variable costing method.
Explanation of Solution
Absorption costing: It refers to the method of product costing in which the price of the product is calculated considering all fixed as well as the variable or direct costs. The
Variable costing: It refers to the method of product costing in which the price of the product is calculated considering only the variable or direct costs or the cost that happened to occurred due to the product only. It also called as marginal costing as it takes marginal costs while calculating the product cost.
Prepare comparative income statement and comparative schedule of cost of goods sold for each month under (1) absorption costing method and (2) variable costing method as follows:
Comparative schedule of cost of goods sold for each month:
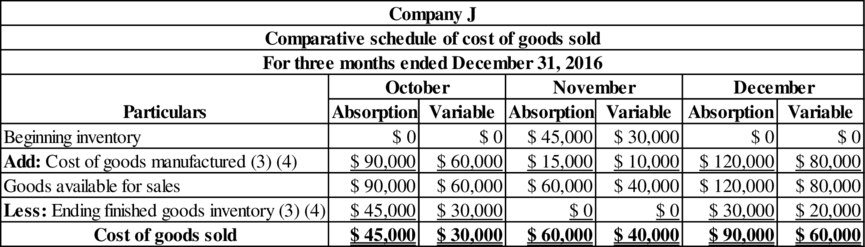
Table (1)
Comparative income statement for each month:
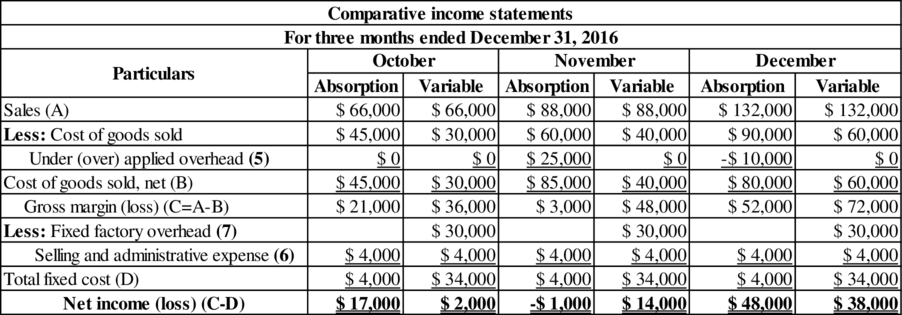
Table (2)
Working note (1):
Calculate the absorption costing per unit.
Working note (2):
Calculate the ending inventory units for each month.
| Particulars | October | November | December |
| Beginning inventory | 0 | 3,000 | 0 |
| Add: Number of units produced | 6,000 | 1,000 | 8,000 |
| Less: Number of units sold | 3,000 | 4,000 | 6,000 |
| Ending inventory | 3,000 | 0 | 2,000 |
Table (3)
Working note (3):
Calculate the cost of goods sold and ending inventory under absorption costing for each month.
| Particulars | October | November | December |
| Number of units produced (A) | 6,000 | 1,000 | 8,000 |
| Absorption cost per unit (B) (1) | $ 15 | $ 15 | $ 15 |
| Cost of goods manufactured | $ 90,000 | $ 15,000 | $ 120,000 |
| Ending inventories units (C) (2) | 3000 | 0 | 2000 |
| Absorption cost per unit (D) | $ 15 | $ 15 | $ 15 |
| Ending inventory | $ 45,000 | $ 0 | $ 30,000 |
| Beginning inventory units (E) (2) | 0 | 3,000 | 0 |
| Absorption cost per unit (F) | $ 15 | $ 15 | $ 15 |
| Beginning inventory | $ 0 | $ 45,000 | $ 0 |
Table (4)
Working note (4):
Calculate the cost of goods sold and ending inventory under variable costing for each month.
| Particulars | October | November | December |
| Number of units produced (A) | 6,000 | 1,000 | 8,000 |
| Variable cost per unit (B) | $ 10 | $ 10 | $ 10 |
| Cost of goods sold | $ 60,000 | $ 10,000 | $ 80,000 |
| Ending inventories units (C) (2) | 3000 | 0 | 2000 |
| Variable cost per unit (D) | $ 10 | $ 10 | $ 10 |
| Ending inventory | $ 30,000 | $ 0 | $ 20,000 |
| Beginning inventory units (E) (2) | 0 | 3,000 | 0 |
| Variable cost per unit (F) | $ 10 | $ 10 | $ 10 |
| Beginning inventory | $ 0 | $ 30,000 | $ 0 |
Table (5)
Working note (5):
Calculate the under or over applied fixed
October:
November:
December:
Working note (6):
Calculate the fixed selling and administrative expense per month.
Working note (7):
Calculate the fixed factory overhead per month.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Principles of Cost Accounting
- How do I prepare an income statement based on variable costing?arrow_forwardLukin Corporation reports the following first-year production cost information:arrow_forwardWolsey Industries Inc. expects to maintain the same inventories at the end of 20Y8 as at the beginning of the year. The total of all production costs for the year is therefore assumed to be equal to the cost of goods sold. With this in mind, the various department heads were asked to submit estimates of the costs for their departments during the year. A summary report of these estimates is as follows: 1 Estimated Fixed Cost Estimated Variable Cost (per unit sold)2 Production costs:3 Direct materials — $50.004 Direct labor — 32.005 Factory overhead $190,000.00 20.006 Selling expenses:7 Sales salaries and commissions 101,000.00 12.008 Advertising 36,000.00 —9 Travel 14,000.00…arrow_forward
- Wolsey Industries Inc. expects to maintain the same inventories at the end of 20Y8 as at the beginning of the year. The total of all production costs for the year is therefore assumed to be equal to the cost of goods sold. With this in mind, the various department heads were asked to submit estimates of the costs for their departments during the year. A summary report of these estimates is as follows: 1 Estimated Fixed Cost Estimated Variable Cost (per unit sold) 2 Production costs: 3 Direct materials — $46.00 4 Direct labor — 40.00 5 Factory overhead $200,000.00 20.00 6 Selling expenses: 7 Sales salaries and commissions 110,000.00 8.00 8 Advertising 40,000.00 — 9 Travel 12,000.00 — 10 Miscellaneous selling expense 7,600.00 1.00 11 Administrative expenses: 12 Office and officers’ salaries 132,000.00 — 13 Supplies 10,000.00 4.00 14…arrow_forwardWolsey Industries Inc. expects to maintain the same inventories at the end of 20Y8 as at the beginning of the year. The total of all production costs for the year is therefore assumed to be equal to the cost of goods sold. With this in mind, the various department heads were asked to submit estimates of the costs for their departments during the year A summary report of these estimates is as follows: Estimated Fixed Cost Estimated Variable Cost (per unit sold) 2 Production costs: 3 Direct materials 4 Direct labor 5 Factory overhead $56.00 36.00 $194,000.00 20.00 6 Selling expenses: 7 Sales salaries and commissions 110,000.00 8.00 8 Advertising 42,000.00 9 Travel 13,000.00 10 Miscellaneous selling expense 7,000.00 1.00 11 Administrative expenses: 12 Office and officers' salaries 13 Supplies 124,600.00 8,000.00 6.00arrow_forwardBrindle Arts uses Variable Costing for internal purposes, but uses Absorption Costing for their financial reports. The following information is for Quarter 4, 2021 and Quarter 1, 2022. Calculate unit product costs for Quarters 4 and 1 for Variable and Absorption Costing. Prepare an income statement for each method, then show why there is a difference between the two. Selling price per unit $ 150 Quarter 4 Quarter 1 Variable costs per unit Units in beginning inventory - 1,750 Direct materials $ 45.00 Production (in units) 15,000 10,750 Direct labor $ 20.00 Sales (in units) 13,250 12,500 Variable overhead $ 15.00 Ending inventory 1,750 - Variable S&A $ 10.00 Fixed Costs in total per quarter Fixed manufacturing overhead…arrow_forward
- Huge Company’s traditional format income statement for the month of May was as follows: Using the space provided below, please prepare an income statement for the month in contribution margin format b. By how much would net income increase if sales increased by $30,000?arrow_forward2. What is the expected contribution margin ratio? Round to the nearest whole percent. 3. Determine the break-even sales in units and dollars. Units units Dollars 4. Construct a cost-volume-profit chart on your own paper. What is the break-even sales? 2$ 5. What is the expected margin of safety in dollars and as a percentage of sales? Dollars: Percentage: (Round to the nearest whole percent.) % 6. Determine the operating leverage. Round to one decimal place.arrow_forwardOn October 31, the end of the first month of operations, Maryville Equipment Company pre- pared the following income statement, based on the variable costing concept: Maryville Equipment Company Variable Costing Income Statement For the Month Ended October 31 Sales (220,000 units).... $ 7,920,000 Variable cost of goods sold: Variable cost of goods manufactured . Inventory, October 31 (45,000 units) .. Total variable cost of goods sold... Manufacturing margin....... Variable selling and administrative expenses $ 6,360,000 (1,080,000) (5,280,000) $ 2,640,000 (330,000) $ 2,310,000 Contribution margin... Fixed costs: Fixed manufacturing costs ... Fixed selling and administrative expenses.. $ 530,000 100,000 Total fixed costs.... (630,000) $ 1,680,000 Operating income... Prepare an income statement under absorption costing.arrow_forward
- The following production data came from the records of Olympic Enterprises for the year ended December 31, 2016: During the year, 40,000 units were manufactured but only 35,000 units were sold. Determine the effect on inventory valuation by computing the following: 1. Total inventoriable costs and the cost of the 35,000 units sold and of the 5,000 units in the ending inventory, using variable costing. 2. Total inventoriable costs and the cost of the 35,000 units sold and of the 5,000 units in the ending inventory, using absorption costing.arrow_forwardWhen prices are falling (deflation), which costing method would produce the highest gross margin for the following? Choose first-in, first-out (FIFO); last-in, first-out (LIFO); or weighted average, assuming that B62 Company had the following transactions for the month. Calculate the gross margin for each of the following cost allocation methods, assuming B62 sold just one unit of these goods for $400. Provide your calculations. A. first-in, first-out (FIFO) B. last-in, first-out (LIFO) C. weighted average (AVG)arrow_forwardIncome Statements under Absorption and Variable Costing In the coming year, Kalling Company expects to sell 28,700 units at 32 each. Kallings controller provided the following information for the coming year: Required: 1. Calculate the cost of one unit of product under absorption costing. 2. Calculate the cost of one unit of product under variable costing. 3. Calculate operating income under absorption costing for next year. 4. Calculate operating income under variable costing for next year.arrow_forward
 Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College





