
FUNDAMENTALS OF PHYSICS V.1
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781119573913
Author: Halliday
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 10, Problem 29P
Figure 10-32 shows an early method of measuring the
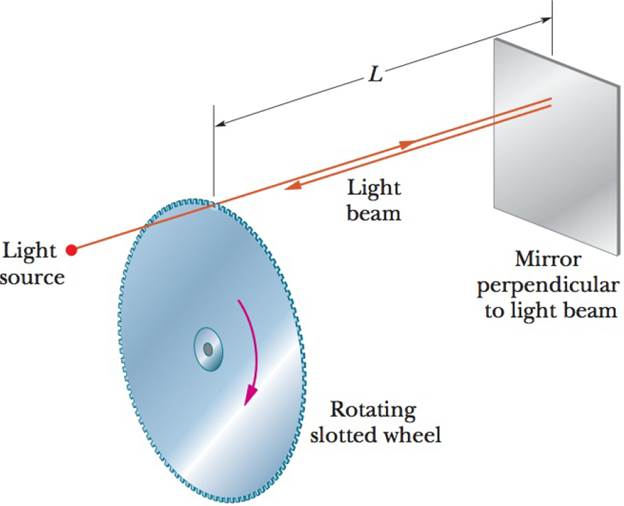
Figure 10-32 Problem 29.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
An early method of measuring the speed of light makes use of a rotating slotted wheel. A beam of light passes through a slot at the
outside edge of the wheel, as in the figure, travels to a distant mirror, and returns to the wheel just in time to pass through the next slot
in the wheel. One such slotted wheel has a radius of 3.5 cm and 150 slots at its edge. Measurements taken when the mirror is L= 250 m
from the wheel indicate a speed of light of 3.0 x 105 km/s. (a) What is the (constant) angular speed of the wheel? (b) What is the linear
speed of a point on the edge of the wheel?
Light
beam
Light
Mirror
SOurce
perpendicular
to light beam
Rotating
slotted wheel
(a) Number
i
Units
(b) Number
i
Units
An early method of measuring the speed of light makes use of a rotating slotted wheel. A beam of light passes through a slot at the outside edge of the wheel, as in the figure,
travels to a distant mirror, and returns to the wheel just in time to pass through the next slot in the wheel. One such slotted wheel has a radius of 2.9 cm and 120 slots at its edge.
Measurements taken when the mirror is L = 670 m from the wheel indicate a speed of light of 3.0 x 105 km/s. (a) What is the (constant) angular speed of the wheel? (b) What is
the linear speed of
point on the edge of the wheel?
Light
beam
Light
Mirror
Source
perpendicular
to light beam
Rotating
słotted wheel
(a) Number
Units
(b) Number
Units
Click if you would like to Show Work for this question: Open Show Work
An early method of measuring the speed of light makes use of a rotating slotted wheel. A beam of light passes through a slot at the
outside edge of the wheel, as in the figure, travels to a distant mirror, and returns to the wheel just in time to pass through the next slot
in the wheel. One such slotted wheel has a radius of 3.23 cm and 130 slots at its edge. Measurements taken when the mirror is L-
1090 m from the wheel indicate a speed of light of 3.00 x 105 km/s. (a) What is the (constant) angular speed of the wheel? (b) What is
the linear speed of a point on the edge of the wheel?
(a) Number
(b) Number i
Light
source
Units
Units
Light
beam
Rotating
slotted wheel
Mirror
perpendicular
to light beam
Chapter 10 Solutions
FUNDAMENTALS OF PHYSICS V.1
Ch. 10 - Figure 10-20 is a graph of the angular velocity...Ch. 10 - Figure 10-21 shows plots of angular position ...Ch. 10 - A force is applied to the rim of a disk that can...Ch. 10 - Figure 10-22b is a graph of the angular position...Ch. 10 - In Fig. 10-23, two forces F1 and F2 act on a disk...Ch. 10 - In the overhead view of Fig. 10-24, five forces of...Ch. 10 - Figure 10-25a is an overhead view of a horizontal...Ch. 10 - Figure l0-25b shows an overhead view of a...Ch. 10 - Figure 10-26 shows a uniform metal plate that had...Ch. 10 - Figure 10-27 shows three flat disks of the same...
Ch. 10 - Figure 10-28a shows a meter stick, hall wood and...Ch. 10 - Figure 10-29 shows three disks, each with a...Ch. 10 - A good baseball pitcher can throw a baseball...Ch. 10 - What is the angular speed of a the second hand, b...Ch. 10 - When a slice of buttered toast is accidentally...Ch. 10 - The angular position of a point on a rotating...Ch. 10 - ILW A diver makes 2.5 revolutions on the way from...Ch. 10 - The angular position of a point on the rim of a...Ch. 10 - The wheel in Fig. 10-30 has eight equally spaced...Ch. 10 - The angular acceleration of a wheel is = 6.0t4 ...Ch. 10 - A drum rotates around its central axis at an...Ch. 10 - Starting from rest, a disk rotates about its...Ch. 10 - A disk, initially rotating at 120 rad/s, is slowed...Ch. 10 - The angular speed of an automobile engine is...Ch. 10 - ILW A flywheel turns through 40 rev as it slows...Ch. 10 - GO A disk rotates about its central axis starling...Ch. 10 - SSM Starting from rest, a wheel has constant =...Ch. 10 - A merry-go-round rotates from rest with an angular...Ch. 10 - At t = 0, a flywheel has an angular velocity of...Ch. 10 - A pulsar is a rapidly rotating neutron star that...Ch. 10 - What are the magnitudes of a the angular velocity,...Ch. 10 - An object rotates about a fixed axis, and the...Ch. 10 - Between 1911 and 1990, the top of the leaning bell...Ch. 10 - An astronaut is tested in a centrifuge with radius...Ch. 10 - SSM WWW A flywheel with a diameter of 1.20 m is...Ch. 10 - A vinyl record is played by rotating the record so...Ch. 10 - SSM a What is the angular speed about the polar...Ch. 10 - The flywheel of a steam engine runs with a...Ch. 10 - A seed is on a turntable rotating at 3313 rev/min,...Ch. 10 - In Fig. 10-31, wheel A of radius rA = 10 cm is...Ch. 10 - Figure 10-32 shows an early method of measuring...Ch. 10 - A gyroscope flywheel of radius 2.83 cm is...Ch. 10 - GO A disk, with a radius of 0.25 m. is to be...Ch. 10 - A car starts from rest and moves around a circular...Ch. 10 - SSM Calculate the rotational inertia of a wheel...Ch. 10 - Figure 10-33 gives angular speed versus time for a...Ch. 10 - SSM Two uniform solid cylinders, each rotating...Ch. 10 - Figure 10-34a shows a disk that can rotate about...Ch. 10 - SSM Calculate the rotational inertia of a meter...Ch. 10 - Figure 10-35 shows three 0.0100 kg particles that...Ch. 10 - Trucks can be run on energy stored in a rotating...Ch. 10 - Figure 10-36 shows an arrangement of 15 identical...Ch. 10 - GO In Fig. 10-37, two particles, each with mass m...Ch. 10 - The masses and coordinates of four particles are...Ch. 10 - SSM WWW The uniform solid block in Fig. 10-38 has...Ch. 10 - Four identical particles of mass 0.50 kg each are...Ch. 10 - SSM ILW The body in Fig. 10-39 is pivoted at O,...Ch. 10 - The body in Fig. 10-40 is pivoted at O. Three...Ch. 10 - SSM A small ball of mass 0.75 kg is attached to...Ch. 10 - The length of a bicycle pedal arm is 0.152 m, and...Ch. 10 - SSM ILW During the launch from a board, a divers...Ch. 10 - If a 32.0 N m torque on a wheel causes angular...Ch. 10 - Prob. 51PCh. 10 - GO In Fig. 10-42, a cylinder having a mass of 2.0...Ch. 10 - GO Figure 10-43 shows a uniform disk that can...Ch. 10 - In a judo foot-sweep move, you sweep your...Ch. 10 - In Fig. 10-45a, an irregularly shaped plastic...Ch. 10 - Figure 10-46 shows particles 1 and 2, each of mass...Ch. 10 - GO A pulley, with a rotational inertia of 1.0 103...Ch. 10 - a IF R= 12 cm, M = 400 g, and m = 50 g in Fig....Ch. 10 - An automobile crankshaft transfers energy from the...Ch. 10 - A thin rod of length 0.75 m and mass 0.42 kg is...Ch. 10 - A 32.0 kg wheel, essentially a thin hoop with...Ch. 10 - In Fig. 10-35, three 0.0100 kg particles have been...Ch. 10 - SSM ILW A meter stick is held vertically with one...Ch. 10 - A uniform cylinder of radius 10 cm and mass 20 kg...Ch. 10 - GO A tall, cylindrical chimney fall;; over when...Ch. 10 - GO A uniform spherical shell of mass M = 4.5 kg...Ch. 10 - GO Figure 10-48 shows a rigid assembly of a thin...Ch. 10 - Prob. 68PCh. 10 - Prob. 69PCh. 10 - A wheel, starling from rest, rotates with a...Ch. 10 - SSM In Fig. 10-50, two 6.20 kg blocks are...Ch. 10 - Prob. 72PCh. 10 - A uniform helicopter rotor blade is 7.80 m long,...Ch. 10 - Prob. 74PCh. 10 - Prob. 75PCh. 10 - Starting from rest at t = 0, a wheel undergoes a...Ch. 10 - SSM A record turntable rotating at 3313 rev/min...Ch. 10 - Prob. 78PCh. 10 - Prob. 79PCh. 10 - A disk rotates al constant angular acceleration,...Ch. 10 - GO The thin uniform rod in Fig. 10-53 has length...Ch. 10 - Prob. 82PCh. 10 - Prob. 83PCh. 10 - At 7:14 A.M. on June 30, 1908, a huge explosion...Ch. 10 - A golf ball is launched at an angle of 20 to the...Ch. 10 - Prob. 86PCh. 10 - GO IN Fig. 10-55, a wheel of radius 0.20 m is...Ch. 10 - A thin spherical shell has a radius of 1.90 m. An...Ch. 10 - Prob. 89PCh. 10 - The flywheel of an engine is rotating at 25.0...Ch. 10 - SSM In Fig. 10-19a, a wheel of radius 0.20 m is...Ch. 10 - Our Sun is 23 104 ly light-years from the center...Ch. 10 - SSM A wheel of radius 0.20 m is mounted on a...Ch. 10 - If an airplane propeller rotates at 2000 rev/min...Ch. 10 - The rigid body shown in Fig. 10-57 consists of...Ch. 10 - Beverage engineering. The pull tab was a major...Ch. 10 - Figure 10-58 shows a propeller blade that rotates...Ch. 10 - A yo-yo-shaped device mounted on a horizontal...Ch. 10 - Prob. 99PCh. 10 - Two thin rods each of mass 0.20 kg are joined...Ch. 10 - In Fig. 10-61, four pulleys are connected by two...Ch. 10 - Prob. 102PCh. 10 - In Fig. 10-63, a thin uniform rod mass 3.0 kg,...Ch. 10 - Prob. 104PCh. 10 - Prob. 105PCh. 10 - A point on the rim of a 0.75-m-diameler grinding...Ch. 10 - A pulley wheel that is 8.0 cm in diameter has a...Ch. 10 - A vinyl record on a turntable rotates at 3313...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- An early method of measuring the speed of light makes use of a rotating slotted wheel. A beam of light passes through a slot at the outside edge of the wheel, as in the figure, travels to a distant mirror, and returns to the wheel just in time to pass through the next slot in the wheel. One such slotted wheel has a radius of 7.3 cm and 190 slots at its edge. Measurements taken when the mirror is L = 1100 m from the wheel indicate a speed of light of 3.0 x 105 km/s. (a) What is the (constant) angular speed of the wheel? (b) What is the linear speed of a point on the edge of the wheel? (a) Number (b) Number Mi Light Source Units Units Light beam Rotating slotted wheel Mirror perpendicular to light beamarrow_forwardDistances in space are often quoted in units of light years, the distance light travels in one year (365.25 days). How many meters is a light year? Provide the solution: x 1015 marrow_forwardAsap.arrow_forward
- In 1926, Albert Michelson measured the speed of light with a technique similar to that used by Fizeau. Michelson used an eight-sided mirror rotating at 528 rev/s in place of the toothed wheel, as illustrated in the figure. The distance from the rotating mirror to a distant reflector was 35.5 km. If the light completed the 71.0-km round trip in the time it took the mirror to complete one-eighth of a revolution, what is the speed of light?arrow_forwardbeen having some trouble with this problem: Michelson used rotating mirrors, similar to those shown below, to calculate the speed of light. Light is emitted from the light source, reflects from mirror surface X to the plane mirror, and then to the position of surface Z. By the time the light moves from the X to Z position, mirror surface X will have moved to the position of mirror surface Z. The light then continues to the observer. The distances from the light source and the observer to the rotating mirrors are negligible. The distance from the rotating mirrors to the plane mirror is 35.0 km.If the mirrors are rotating at 480 rev/s, the speed of light calculated from the given information isarrow_forwardThe speed of light is c = 3.0 x 10^8 m/s. If the distance between the Earth and the moon is d = 2.39 x 10^5 mi (1.0 mi = 1.61 km). You send a laser from the Earth to the moon and back. How long does this take?arrow_forward
- (a) The distance to a star is approximately 4.97 × 10¹8 m. If this star were to burn out today, in how many years would we see it disappear? years (b) How long does it take sunlight to reach Earth? minutes (c) How long does it take for a microwave radar signal to travel from Earth to the Moon and back? (The distance from Earth to the Moon is 3.84 x 105 km.) Sarrow_forwardYour answer is partially correct. A distant galaxy emits light that has a wavelength of 634.5 nm. On earth, the wavelength of this light is measured to be 639.0 nm. (a) Decide whether this galaxy is approaching or receding from the earth. (b) Find the speed of the galaxy relative to the earth. (Give your answer to 4 significant digits. Use 2.998 x 108 m/s as the speed of light.) (a) The galaxy is (b) Number receding 2126000 from the earth. Units m/sarrow_forwardThe speed of light in (m/s) in diamond (u = 2.42) is: 2.14 x 108 2.30 x 108 1.24 x 108 3.00 x 108arrow_forward
- The light year (ly) is a unit of distance commonly used in astronomy. It is defined as the distance traveled by light in a vacuum in one year. Express 1 ly in km.arrow_forwardHow far does light travel in one year? [This distance is known as a light-year (ly) and is used in measuring astronomical distances.] I think the answer might have to be in scientific notationn formarrow_forwardJ33arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Moment of Inertia; Author: Physics with Professor Matt Anderson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZrGhUTeIlWs;License: Standard Youtube License