
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The radicals, in order of theirs decreasing stability, are to be listed.
Concept introduction:
A molecule that contains at least one unpaired electron is known as a radical.
The relative stability of radicals is the same as that of carbocations.
The stability of radicals is as follows:
Answer to Problem 1PP
Solution:
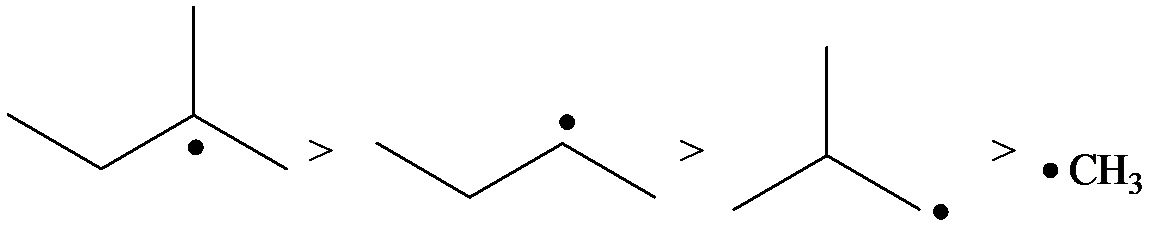
Explanation of Solution

The radical is a methyl radical. So, it is the least stable.
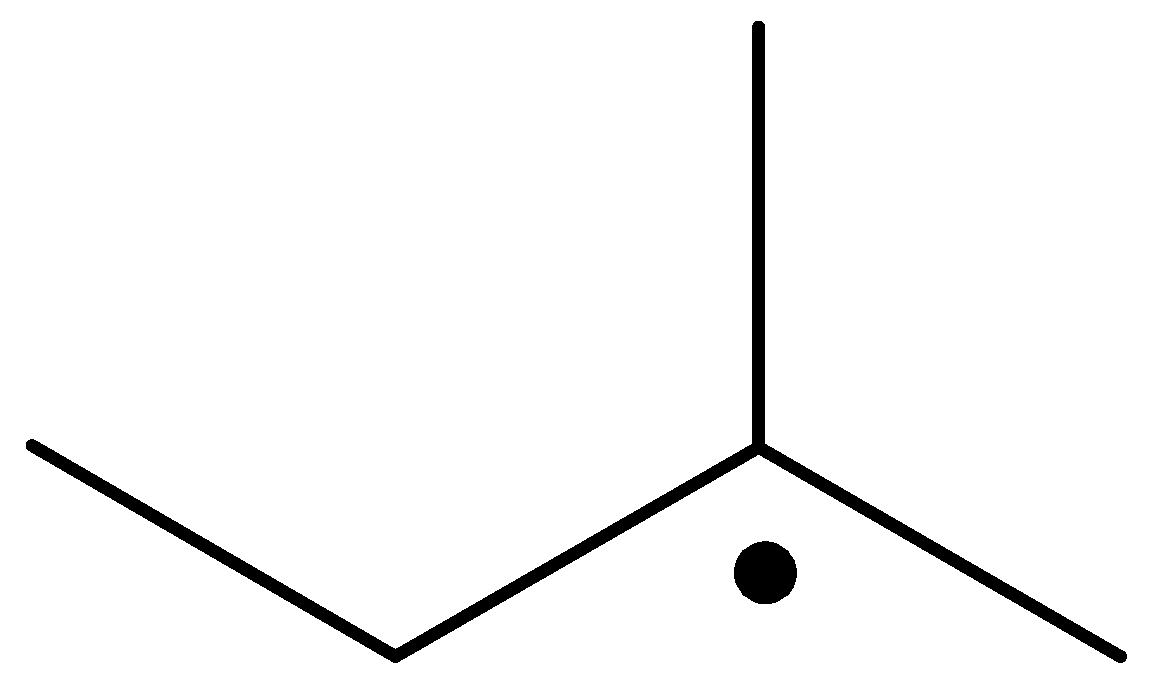
The radical is given as follows:
The carbon containing the unpaired electron is primary. Thus, the radical is a primary radical.
The radical is given as follows:
The carbon containing the unpaired electron is tertiary. Thus, the radical is a tertiary radical.
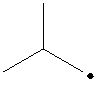
The radical is given as follows:
The carbon containing the unpaired electron is secondary. Thus, the radical is a secondary radical.
Therefore, the tertiary radical is the most stable and the methyl radical is the least stable.
Hence, the decreasing order of the stability of the radical is as follows:
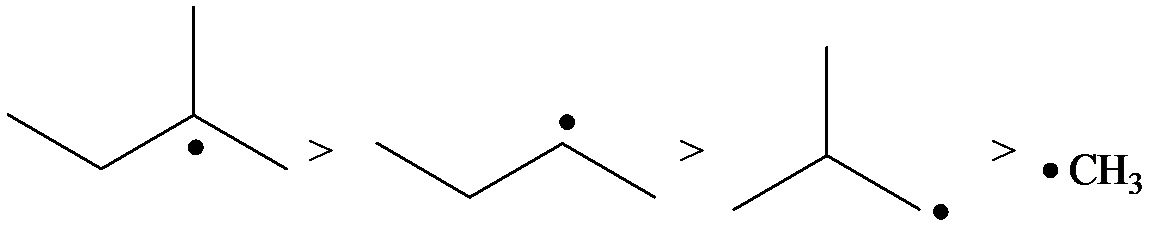
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardIndicate the correct option.a) Graphite conducts electricity, being an isotropic materialb) Graphite is not a conductor of electricityc) Both are falsearrow_forward(f) SO: Best Lewis Structure 3 e group geometry:_ shape/molecular geometry:, (g) CF2CF2 Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement:_ shape/molecular geometry: (h) (NH4)2SO4 Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forward
- 1. Problem Set 3b Chem 141 For each of the following compounds draw the BEST Lewis Structure then sketch the molecule (showing bond angles). Identify (i) electron group geometry (ii) shape around EACH central atom (iii) whether the molecule is polar or non-polar (iv) (a) SeF4 Best Lewis Structure e group arrangement:_ shape/molecular geometry: polarity: (b) AsOBr3 Best Lewis Structure e group arrangement:_ shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forward(c) SOCI Best Lewis Structure 2 e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry:_ (d) PCls Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group geometry:_ shape/molecular geometry:_ (e) Ba(BrO2): Best Lewis Structure polarity: e group arrangement: shape/molecular geometry: polarity: Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles): Sketch (with angles):arrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

