
Essential University Physics
4th Edition
ISBN: 9780134988559
Author: Wolfson, Richard
Publisher: Pearson Education,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 10, Problem 10FTD
A ball starts from rest and rolls without slipping down a slope, then starts up a frictionless slope (Fig. 10.26). Compare its maximum height on the frictionless slope with its starting height on the first slope.
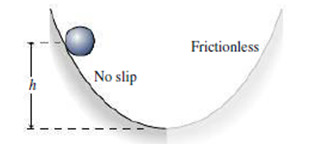
FIGURE 10.26 For Thought and Discussion 12, Problem 64
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
suggest a reason ultrasound cleaning is better than cleaning by hand?
Checkpoint 4
The figure shows four orientations of an electric di-
pole in an external electric field. Rank the orienta-
tions according to (a) the magnitude of the torque
on the dipole and (b) the potential energy of the di-
pole, greatest first.
(1)
(2)
E
(4)
What is integrated science.
What is fractional distillation
What is simple distillation
Chapter 10 Solutions
Essential University Physics
Ch. 10.1 - A wheel undergoes constant angular acceleration,...Ch. 10.2 - The forces in Figs. 10.5 and 10.6 all have the...Ch. 10.3 - Would the rotational inertia of the two-mass...Ch. 10.3 - Explain why the rotational inertia of the solid...Ch. 10.3 - The figure shows two identical masses m connected...Ch. 10.4 - A wheel is rotating at 100 rpm. To spin it up to...Ch. 10.5 - The wheels of trains, subway cars, and other rail...Ch. 10 - Do all points on a rigid, rotating object have the...Ch. 10 - A point on the rim of a rotating wheel has nonzero...Ch. 10 - Two forces act on an object, but the net force is...
Ch. 10 - Is it possible to apply a counterclockwise torque...Ch. 10 - A solid sphere and a hollow sphere of the same...Ch. 10 - A solid cylinder and a hollow cylinder of the same...Ch. 10 - A circular saw lakes a long time to stop rotating...Ch. 10 - The lower part of a horses leg contains...Ch. 10 - Given a fixed amount of a material, what shape...Ch. 10 - A ball starts from rest and rolls without slipping...Ch. 10 - Exercises and Problems Exercises Section 10.1...Ch. 10 - Whats the linear speed of a point (a) on Earths...Ch. 10 -
Express each of the following in radium per...Ch. 10 - A 25-cm-diameter circular saw blade spins at 3500...Ch. 10 - A compact discs rotation varies from about 200 rpm...Ch. 10 - During startup, a power plants turbine accelerates...Ch. 10 - A merry-go-round starts front rest and accelerates...Ch. 10 - Section 10.2 Torque A 320-N frictional force acts...Ch. 10 - Prob. 19ECh. 10 - A car tune-up manual calls for tightening the...Ch. 10 - A 55-g mouse runs out to the end of the 17-cm-long...Ch. 10 - You have your bicycle upside down for repairs. The...Ch. 10 - Section 10.3 Rotational Inertia and the Analog of...Ch. 10 - The shaft connecting a power plants turbine and...Ch. 10 - The chamber of a rock-tumbling machine is a hollow...Ch. 10 - A wheels diameter is 92 cm, and its rotational...Ch. 10 - (a) Estimate Earths rotational inertia, assuming...Ch. 10 - A 108-g Frisbee is 24 cm in diameter and has half...Ch. 10 - At the MIT Magnet Laboratory, energy is stored in...Ch. 10 - Section 10.4 Rotational Energy A 25-cm-diameter...Ch. 10 - Humankind uses energy at the rate of about 16 TW....Ch. 10 - A 150-g baseball is pitched at 33 m/s spinning at...Ch. 10 - (a) Find the energy stored in the flywheel of...Ch. 10 - A solid 2.4-kg sphere is rolling at 5.0 m/s. Find...Ch. 10 - What fraction of a solid disks kinetic energy is...Ch. 10 - A rolling ball has total kinetic energy 100 J, 40...Ch. 10 - Prob. 37ECh. 10 - Example 10.5: The rotational inertia of a thin rod...Ch. 10 - Prob. 39ECh. 10 - Prob. 40ECh. 10 - Prob. 41ECh. 10 - Prob. 42ECh. 10 - Example 10.12: A 29.5-kg wheel with radius 40.6 cm...Ch. 10 - Prob. 44ECh. 10 - A wheel turns through 2.0 revolutions while...Ch. 10 - Youre an engineer designing kitchen appliances,...Ch. 10 - You rev your cars engine and watch the tachometer...Ch. 10 - A circular saw spins at 5800 rpm, and its...Ch. 10 - Full-circle rotation is common in mechanical...Ch. 10 - A square frame is made from four thin rods, each...Ch. 10 - A thick ring has inner radius 12R, outer radius R,...Ch. 10 - A uniform rectangular flat plate has mass M and...Ch. 10 - The cellular motor driving the flagellum in E....Ch. 10 - Verify by direct integration Table 10.2s entry for...Ch. 10 - Prob. 55PCh. 10 - Prob. 56PCh. 10 - A 2.4-kg block rests on a slope and is attached by...Ch. 10 - Youve got your bicycle upside down for repairs,...Ch. 10 - A potters wheel is a stone disk 90 cm in diameter...Ch. 10 - A ships anchor weighs 5.0kN. Its cable passes over...Ch. 10 - Starting from rest, a hollow ball rolls down a...Ch. 10 - A hollow ball rolls along a horizontal surface at...Ch. 10 - As an automotive engineer, youre charged with...Ch. 10 - A solid ball of mass M and radius R starts at rest...Ch. 10 - A disk of radius R has an initial mass M. Then a...Ch. 10 - A 50-kg mass is tied to a massless rope wrapped...Ch. 10 - Each wheel of a 320-kg motorcycle is 52 cm in...Ch. 10 - A solid marble starts from rest and rolls without...Ch. 10 - A disk of radius R and thickness w has a mass...Ch. 10 - The disk in Fig. 10.29 is rotating freely about a...Ch. 10 - Prob. 71PCh. 10 - A lighter car requires less power for a given...Ch. 10 - Calculate the rotational inertia of a solid,...Ch. 10 - A thick ring of mass M has inner radius R1 and...Ch. 10 - Prob. 75PCh. 10 - The local historical society has asked your...Ch. 10 - Youre skeptical about a new hybrid car that stores...Ch. 10 - Figure 10.31 shows an object of mass M with one...Ch. 10 - Figure 10.32 shows an apparatus used to measure...Ch. 10 - Centrifuges are widely used in biology and...Ch. 10 - Centrifuges are widely used in biology and...Ch. 10 - Centrifuges are widely used in biology and...Ch. 10 - Centrifuges are widely used in biology and...Ch. 10 - Centrifuges are widely used in biology and...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Compare and contrast the carbon, sulfur, and nitrogen cycles in terms of the physiologies of the organisms that...
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
All of the following terms can appropriately describe humans except: a. primary consumer b. autotroph c. hetero...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Level 2: Application/Analysis 4. Nitrifying bactcria participatc in the nitrogen cycle mainly by (A) converting...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
You microscopically examine scrapings from a case of Acan-thamoeba keratitis. You expect to see a. nothing. b. ...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Q1. Which wavelength of light has the highest frequency?
a) 10 nm
b) 10 mm
c) 1 nm
d) 1 mm
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
Where is transitional epithelium found and what is its importance at those sites?
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 19:39 · C Chegg 1 69% ✓ The compound beam is fixed at Ę and supported by rollers at A and B. There are pins at C and D. Take F=1700 lb. (Figure 1) Figure 800 lb ||-5- F 600 lb بتا D E C BO 10 ft 5 ft 4 ft-—— 6 ft — 5 ft- Solved Part A The compound beam is fixed at E and... Hình ảnh có thể có bản quyền. Tìm hiểu thêm Problem A-12 % Chia sẻ kip 800 lb Truy cập ) D Lưu of C 600 lb |-sa+ 10ft 5ft 4ft6ft D E 5 ft- Trying Cheaa Những kết quả này có hữu ích không? There are pins at C and D To F-1200 Egue!) Chegg Solved The compound b... Có Không ☑ ||| Chegg 10 וחarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardair is pushed steadily though a forced air pipe at a steady speed of 4.0 m/s. the pipe measures 56 cm by 22 cm. how fast will air move though a narrower portion of the pipe that is also rectangular and measures 32 cm by 22 cmarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- 13.87 ... Interplanetary Navigation. The most efficient way to send a spacecraft from the earth to another planet is by using a Hohmann transfer orbit (Fig. P13.87). If the orbits of the departure and destination planets are circular, the Hohmann transfer orbit is an elliptical orbit whose perihelion and aphelion are tangent to the orbits of the two planets. The rockets are fired briefly at the depar- ture planet to put the spacecraft into the transfer orbit; the spacecraft then coasts until it reaches the destination planet. The rockets are then fired again to put the spacecraft into the same orbit about the sun as the destination planet. (a) For a flight from earth to Mars, in what direction must the rockets be fired at the earth and at Mars: in the direction of motion, or opposite the direction of motion? What about for a flight from Mars to the earth? (b) How long does a one- way trip from the the earth to Mars take, between the firings of the rockets? (c) To reach Mars from the…arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwarda cubic foot of argon at 20 degrees celsius is isentropically compressed from 1 atm to 425 KPa. What is the new temperature and density?arrow_forward
- Calculate the variance of the calculated accelerations. The free fall height was 1753 mm. The measured release and catch times were: 222.22 800.00 61.11 641.67 0.00 588.89 11.11 588.89 8.33 588.89 11.11 588.89 5.56 586.11 2.78 583.33 Give in the answer window the calculated repeated experiment variance in m/s2.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardCan you help me solve the questions pleasearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Rotational Kinetic Energy; Author: AK LECTURES;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=s5P3DGdyimI;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY