
Conceptual Physical Science (6th Edition)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780134060491
Author: Paul G. Hewitt, John A. Suchocki, Leslie A. Hewitt
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 1, Problem 97DQ
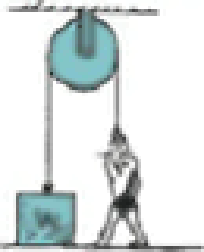
For the pulley system shown, what is the upper limit of the weight the strong man can lift?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Checkpoint 4
The figure shows four orientations of an electric di-
pole in an external electric field. Rank the orienta-
tions according to (a) the magnitude of the torque
on the dipole and (b) the potential energy of the di-
pole, greatest first.
(1)
(2)
E
(4)
What is integrated science.
What is fractional distillation
What is simple distillation
19:39 ·
C
Chegg
1 69%
✓
The compound beam is fixed at Ę and supported by rollers at A and B. There are pins at C and D. Take
F=1700 lb. (Figure 1)
Figure
800 lb
||-5-
F
600 lb
بتا
D
E
C
BO
10 ft 5 ft 4 ft-—— 6 ft — 5 ft-
Solved Part A The compound
beam is fixed at E and...
Hình ảnh có thể có bản quyền. Tìm hiểu thêm
Problem
A-12
% Chia sẻ
kip
800 lb
Truy cập )
D Lưu
of
C
600 lb
|-sa+ 10ft 5ft 4ft6ft
D
E
5 ft-
Trying
Cheaa
Những kết quả này có
hữu ích không?
There are pins at C and D To F-1200 Egue!)
Chegg
Solved The compound b...
Có Không ☑
|||
Chegg
10
וח
Chapter 1 Solutions
Conceptual Physical Science (6th Edition)
Ch. 1 - Aristotle on Motion 1. What did Aristotle believe...Ch. 1 - Did Aristotle believe that forces are necessary to...Ch. 1 - Galileos Concept of Inertia 3. What idea of...Ch. 1 - Which dominated Galileos way of extending...Ch. 1 - What name is given to the property by which...Ch. 1 - MassA Measure of Inertia 6. Which depends on...Ch. 1 - Where is your weight greater, on Earth or on the...Ch. 1 - What are the unit of measurement for weight and...Ch. 1 - A 1-kg object weight nearly 10 N on Earth. Would...Ch. 1 - Net Force 10. What is the net force on a box that...
Ch. 1 - What two properties are necessary for a vector...Ch. 1 - The Equilibrium Rule 12. Name the force that...Ch. 1 - How much tension is in a vertical rope that holds...Ch. 1 - Prob. 14RCQCh. 1 - One bowling ball sits at rest, and another bowling...Ch. 1 - Support Force 16. Why is the support force on an...Ch. 1 - When you weigh yourself, how does the support...Ch. 1 - The Force of Friction 18. How does the direction...Ch. 1 - If you push to the right on a heavy piece of...Ch. 1 - Suppose you push to the right on a heavy piece of...Ch. 1 - If you push a heavy piece of furniture and it...Ch. 1 - Speed and Velocity 22. Distinguish between speed...Ch. 1 - Why do we say that velocity is a vector and speed...Ch. 1 - Does the speedometer on a vehicle show average...Ch. 1 - How can you be both at rest and moving at 100,000...Ch. 1 - Acceleration 26. Distinguish between velocity and...Ch. 1 - What is the acceleration of an object that moves...Ch. 1 - What is the acceleration of an object in free fall...Ch. 1 - Show that the average speed of a rabbit that runs...Ch. 1 - Calculate your average walking speed when you step...Ch. 1 - Show that the acceleration of a car that can go...Ch. 1 - Show that the acceleration of a hamster is 5 m/s2...Ch. 1 - Show that the hamster in Exercise 37 travels a...Ch. 1 - Show that a freely falling rock drops a distance...Ch. 1 - Find the strength of the net force produced by a...Ch. 1 - Lucy Lightfoot stands with one foot on one...Ch. 1 - Henry Heavyweight weighs 1200 N and stands on a...Ch. 1 - The sketch shows a painters scaffold in mechanical...Ch. 1 - A different scaffold that weighs 400 N supports...Ch. 1 - A horizontal force of 120 N is required to push a...Ch. 1 - Driving along the toad at 88 km/h, Reckless Rick...Ch. 1 - An airplane with an airspeed of 90 km/h lands on a...Ch. 1 - (a) Show that the average speed of a tennis ball...Ch. 1 - (a) Show that Leslies average speed is 10 km/h...Ch. 1 - (a) Show that the acceleration is 7.5 m/s2 for a...Ch. 1 - Lillian rides her bicycle along a straight road at...Ch. 1 - Extend Table 1.2 (which gives values from 0 to 5...Ch. 1 - A car races on a circular track of radius r. (a)...Ch. 1 - A ball is thrown straight up with an animal speed...Ch. 1 - A ball is thrown straight up with enough speed so...Ch. 1 - A school bus slows to a stop with an average...Ch. 1 - An airplane starting from rest, at one end of a...Ch. 1 - The weights of Burl, Paul and the scaffold produce...Ch. 1 - Rank, from greatest to least, the net force on the...Ch. 1 - Different materials. A, B, C, and D, rest on a...Ch. 1 - Three pucks, A, B, and C, are sliding across ice...Ch. 1 - EXERCISES (SYNTHESIS) 1.1. Aristotle on Motion 62....Ch. 1 - Which of Aristotle's ideas did Galileo discredit...Ch. 1 - Galileo's Concept of Inertia 64. A bawling ball...Ch. 1 - A space probe is carried by a rocket into outer...Ch. 1 - When a ball rolls down an incline, it gains speed...Ch. 1 - MassA Measure of Inertia 67. What physical...Ch. 1 - Which has more mass: a 2-kg fluffy pillow or a...Ch. 1 - Is a person on a diet more accurately said to lose...Ch. 1 - Personally, what is your mass in kilograms? Your...Ch. 1 - Gravitational force on the Moon is merely 1/6 the...Ch. 1 - Net Force 72. A monkey harp stationary at the end...Ch. 1 - Suppose the monkey weighs 100 N and the vine...Ch. 1 - If the vine that supports the monkey breaks, what...Ch. 1 - The Equilibrium Rule 75. Can an object be in...Ch. 1 - When you push downward on a book that it at rest...Ch. 1 - Nellie Newton hangs at rest from the ends of the...Ch. 1 - A hockey puck at rest is in equilibrium. Is it in...Ch. 1 - Support Force 79. An empty jug of weight W is at...Ch. 1 - Place a heavy book on a table, and the table...Ch. 1 - The Force of Friction 81. In order to slide a...Ch. 1 - Consider your desk at rest on your bedroom floor....Ch. 1 - In Figure 1.15 we see Marie pushing horizontally...Ch. 1 - Speed and Velocity 84. One ultralight aircraft...Ch. 1 - What is the impact speed when a car moving at 100...Ch. 1 - You're in a car traveling on a highway at some...Ch. 1 - Emily Easy go can paddle a canoe in still water at...Ch. 1 - Acceleration 88. Grade says acceleration is how...Ch. 1 - What is the acceleration of a Tesla automobile...Ch. 1 - What is the acceleration of a car that moves at a...Ch. 1 - Correct your friend who says, "Japan's bullet...Ch. 1 - Suppose that a freely falling object were somehow...Ch. 1 - Consider a freely falling object dropped from...Ch. 1 - Asteroids have been moving through space for...Ch. 1 - In answer to the question "What keeps Earth moving...Ch. 1 - Harry the painter swings year after year from his...Ch. 1 - For the pulley system shown, what is the upper...Ch. 1 - When the strong man in Exercise 97 exerts a...Ch. 1 - In tearing a paper towel or plastic bag from a...Ch. 1 - Someone standing at the edge of a cliff (as in...Ch. 1 - When a ball is tossed straight up, it momentarily...Ch. 1 - Suppose that a freely falling object falls from a...Ch. 1 - In the absence of air resistance, a ballplayer...Ch. 1 - On which of these hills does the ball roll down...Ch. 1 - Because Earth routes once every 24 hours, the west...Ch. 1 - If you toss a coin straight upward while riding in...Ch. 1 - Two balls, A and B, are released simultaneously...Ch. 1 - Refer to the tracks in Exercise 107. (a) Does ball...Ch. 1 - Choose the BEST way to complete the statement. 1....Ch. 1 - According to Galileo, inertia is a (a) force like...Ch. 1 - When a 10-kg block is simultaneously pushed...Ch. 1 - Tension is actually a force that tends to (a)...Ch. 1 - The equilibrium rule, F = 0, applies to (a)...Ch. 1 - When you stand on two bathroom scales, one fool on...Ch. 1 - Your Average speed in skateboarding to your...Ch. 1 - If an object moves with constant acceleration, its...Ch. 1 - If a falling object gains 10 m/s each second it...Ch. 1 - A freely falling object his a speed of 30 m/s at...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Distinguish between microevolution, speciation, and macroevolution.
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
What name is given to the zone of greatest seismic activity?
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
1. Define and distinguish incomplete penetrance and variable expressivity.
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Where is transitional epithelium found and what is its importance at those sites?
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
27. Consider the reaction.
Express the rate of the reaction in terms of the change in concentration of each of...
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Modified True/False 6. __________ Halophiles inhabit extremely saline habitats, such as the Great Salt Lake.
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- air is pushed steadily though a forced air pipe at a steady speed of 4.0 m/s. the pipe measures 56 cm by 22 cm. how fast will air move though a narrower portion of the pipe that is also rectangular and measures 32 cm by 22 cmarrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward13.87 ... Interplanetary Navigation. The most efficient way to send a spacecraft from the earth to another planet is by using a Hohmann transfer orbit (Fig. P13.87). If the orbits of the departure and destination planets are circular, the Hohmann transfer orbit is an elliptical orbit whose perihelion and aphelion are tangent to the orbits of the two planets. The rockets are fired briefly at the depar- ture planet to put the spacecraft into the transfer orbit; the spacecraft then coasts until it reaches the destination planet. The rockets are then fired again to put the spacecraft into the same orbit about the sun as the destination planet. (a) For a flight from earth to Mars, in what direction must the rockets be fired at the earth and at Mars: in the direction of motion, or opposite the direction of motion? What about for a flight from Mars to the earth? (b) How long does a one- way trip from the the earth to Mars take, between the firings of the rockets? (c) To reach Mars from the…arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwarda cubic foot of argon at 20 degrees celsius is isentropically compressed from 1 atm to 425 KPa. What is the new temperature and density?arrow_forwardCalculate the variance of the calculated accelerations. The free fall height was 1753 mm. The measured release and catch times were: 222.22 800.00 61.11 641.67 0.00 588.89 11.11 588.89 8.33 588.89 11.11 588.89 5.56 586.11 2.78 583.33 Give in the answer window the calculated repeated experiment variance in m/s2.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Work-Energy Theorem | Physics Animation; Author: EarthPen;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GSTW7Mlaoas;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY