
As depicted in Fig. P1.24, the downward deflection
where
If
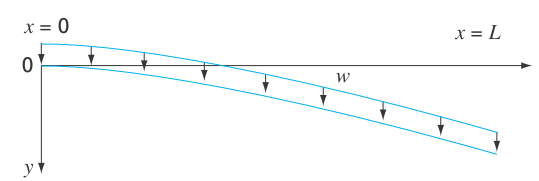
FIGURE P1.24
A cantilever beam.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 1 Solutions
EBK NUMERICAL METHODS FOR ENGINEERS
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Basic Technical Mathematics
Fundamentals of Differential Equations (9th Edition)
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Calculus: Single And Multivariable
- A long steel rod is placed horizontally between two supports, one at each end. The rod bends a little in the center. Which property of this rod can be used to estimate how much the rod should bend at the center? 1. Its Shear Modulus 2. Its Young's Modulus 3. All of these Moduli can be used to compute how much it bends. 4. Its Bulk Modulus.arrow_forwardIn. 10:03 こ Eと A docs.google.com It is desired to remove the spike from the timber by applying force along its horizontal axis. An obstruction A prevents direct access, so that two forces, one 1.6 kN and the other P, are applied by cables as shown. Compute the magnitude of P necessary to ensure a resultant T directed alo the spike. Also, find T. * 200 mm 100 mm A 150 mm 1.6 kN 1 Add file Submit Never submit passwords through Google Forms. This form was created inside of lla. Report Abuse Google Formsarrow_forward1.75m 1.5 m 2.75m Given: G/0 Find: 2.25m Đ B h 2.0m • h = 0.35 meters Tension = 65 Newtons E 1.5m W Magnitude of internal shear force (Newtons) Axial Force AJO Bending moment V Shear forcearrow_forward
- A rectangular tube of outer width w = 7.5 m, outer height h = 5 m and thickness t = 0.17 m experiences bending through the x axis. What is the moment of inertia of the cross-sectional area In? y -- X MATLAB input variables: format shortEng W = 7.5; h = 5; t = 0.17; moment of inertia I, = m4arrow_forward1.75m 1.5 m 2.75m Given: G/0 Find: 2.25m 6 o B 2.0m . h = 2.05 meters • Tension = 85 Newtons 26 1.5m W Magnitude of internal axial force (Newtons) Axial Force Bending moment V Shear forcearrow_forward1. Consider a right pyramid whose base is an equilateral triangle of side 4cm each, each slant edge is 5 cm long. what will be the volume of the pyramid? a) (4√61)/(3) cm^3 b)(4√59)/(3) cm^3 c)(4√71)/(3) cm^3 d)(4√8)/(3) cm^3 2. Find the value of k such that lines 3kx+8y=5 and 6y-4kx=-1 are perpendicular and 3kx+8y=5 has a positive slope a) 0 b) -2 c) 4 d) 2 3. what is the equation of the line passing through the origin and perpendicular to the line 2x-5y+6=0 a) 2y-5x+0 b) 2y+5x=0 c) 5y+2x=0 d) 5y-2x=0arrow_forward
- c) Calculate the equations of internal shear force V(x) and bending moment M(x). Type the mathematical expressions or constants, following the defined sign convection. Section AB: Internal shear force equation: V(x) = Internal bending moment equation: M(x) : Section BC: Internal shear force equation: V(x) Internal bending moment equation: M(x) = = N N N*mm N*mmarrow_forwardQ1 The stiffness matrix for a Timoshenko beam-column element in its local coordinate system (where x is along the beam length) is: L²A L²A ī(1+$) -7 (1+ 4) 12 6L -12 6L E I 6L L²(4 + ¤) -6L L(2 – 4) [K'] = L²A (1 + 4) L³ (1 + Ø) L²A (1+ ø) I -12 -6L 12 -6L 6L L²(2 – $) -6L L2(4+ ¢)] 12EI GAŞL? a) Derive the transformation matrix [T] for this element, such that the stiffness matrix of the element can be transformed to the global coordinate system using the following relation: [K«] = [T<]*[K¢°][Te]arrow_forwardull JAWWAL ? 6:20 PM @ 50% A moodle.najah.edu МOODLE Recent - For the following system, answer the following assuming each tension in cable = 10 kN 1) Express tensions in Cartesian coordinate system 2) Find moment due to both cables and weight of door= 1 kN about point A 3) Find moment due to both cables and weight of door= 1 kN about z-axis 960 mm 450 mm 90 mm 675 mm B 90 mm 690 mm 270 mm Fig. P4.113 IIarrow_forward
- upper leg muscle 9 cm in radius). 2) Don't ever try the acorn diet, its nuts. In the tree diagrammed here, a force of 800 N is exerted at the tip of the limb (equivalent to the weight of "800 apples). The limb is circular in cross-section and 2 m long with a tip radius of 3 cm a base radius of 10 cm. The radius increases linearly from the tip to the base. Plot the tensile stress at the top of the limb along its length. Where along the length would you expect the limb to break? M. X. Lo Yarrow_forwardThe graph shown below shows the Modulus of Elasticity (E) of different materials with respect to temperature (°C). 240 210 170 140 100 -Carbon Steel, C < 0.3% -Nickel Steels, Ni 2% - 9% 70 Cr-Mo Steels, Cr 2%-3% Copper -Leaded Ni-Bronze -Nickel Alloys - Monel 400 35 -Titanium rengineeringtoolbox.com -Aluminium -300 -200 -100 100 300 400 500 600 700 800 Temperature (degc) a) Which material is the most ductile with increasing temperature? b) Which material is the least ductile with increasing temperature? c) Discuss the change in ductility (brittle / ductile behavior) occurring for different materials. Also, comment on why Young's modulus changes with temperature. E-modulus of elasticity (GPa)arrow_forwardSy Step-by-Step Calculator - Syn x b Change in length of strut DC X b The displacements at points I x A WebAssign - ENGR 2331 Su2 x -> A webassign.net/web/Student/Assignment-Responses/last?dep=26956849#Q6 W 24 Statically Indeterminate S x E Apps M Gmail D YouTube Maps O Reading list A rigid bar of weight W= 810 N hangs from three equally spaced vertical wires (length L- 150 mm, spacing a= S0 mm): two of steel and one of aluminum. The wires also support a load Pacting on the bar. The diameter of the steel wires is d-2 mm, and the diameter of the wire is d,=4 mm. Assume E, - 210 GPa and E, = 70 GPa. Rigid bar of weight W (a) L. Rigid bar of weight W (b) (a) What load P (in N) can be supported at the midpoint of the bar (x = a) if the allowable stress in the steel wires is 200 MPa and in the aluminum wire is 65 MPa? (Se figure part (a).) (b) What is P (in N) if the load is positioned at x = a/2? N (c) Repeat part (b) if the second and third wires are switched as shown in the figure part…arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





