
(This serial problem begins in this chapter and continues through most Of the book. It is helpful, but not necessary, to use the Working papers that accompany the book.)
SP 1 Santana Rey, owner of Business Solutions, decides to diversify her business by also manufacturing computer workstation furniture.
Required
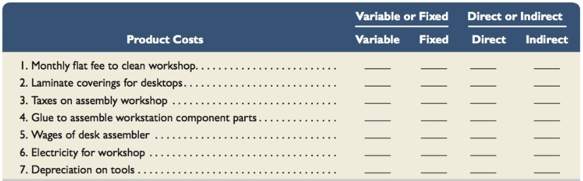
- Classify the following
manufacturing costs of Business Solutions as either (a) variable or fixed and (b) direct or indirect.
- Prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured for Business Solutions for the month ended January 31, 2016. Assume the following manufacturing costs:
Direct materials: $2,2000
Beginning work in process: none (December 31, 2015)
Ending work in process: $540 (January 31, 2016)
- Prepare the cost of goods sold section of a partial income statement for Business Solutions for the month ended January 31, 2016.
Concept introduction:
Variable cost:
The costs which are associated with the amount of goods produced or services provided. These vary directly with the production level i.e. company’s variable cost increases as the production increases and vice-a-versa.
Fixed cost:
These costs do not vary with the level of production. They do not change with the amount of goods or services a company produces. They remain same even if the company does not produce any product or provide any service during an accounting period.
Direct cost:
These costs, as the name specifies, are traceable to the production of specific product or service. These are connected to specific cost object which can be a product, department or project.
Indirect cost:
These costs are necessary for production but not traceable to act of production. These costs are necessary to keep business operational. They go beyond the costs associated with creating a product to include the costs of maintaining the entire company.
Requirement 1:
Classification of manufacturing costs of Business Solutions as (a) variable or fixed and (b) direct or indirect.
Answer to Problem 1SP
Classification of manufacturing costs of Business Solutions:
| Particulars | Variable or Fixed cost | Direct or Indirect cost |
| Monthly flat fee to clean workshop | Fixed | Indirect |
| Laminate coverings for desktops | Variable | Direct |
| Taxes on assembly workshops | Fixed | Indirect |
| Glue to assemble workstation component parts | Variable | Indirect |
| Wages of desk assembler | Variable | Direct |
| Electricity for workshop | Variable | Indirect |
| Depreciation on tools | Fixed | Indirect |
Explanation of Solution
The manufacturing costs of Business Solutions can be classified into variable or fixed and direct or indirect costs based on their nature i.e. on the basis of their behavior and traceability as explained below:
Variable costs vary directly with the production level i.e. company’s variable cost increases as the production increases and vice-a-versa. Therefore, following costs would be classified as Variable:
- Laminate coverings for desktops: The number of desktops held by Business Solutions would determine the costs for their laminate coverings which would vary
- Glue to assemble workstation component parts: Component parts held by Business Solutions at its workstation would determine the costs for glue required for their assembly
- Wages of desk assembler: Number of desk assembler may vary at different periods, thereby leading to variation in their wages
- Electricity for workshop: Electricity cost for workshop would vary in proportion of number of units consumed
Fixed costs do not vary with the level of production. They do not change with the amount of goods or services a company produces. Therefore, those costs which are fixed in nature would be covered under fixed costs as given below:
- Monthly flat fee to clean workshop: The cost that would be incurred for cleaning of workshop monthly is fixed in nature
- Taxes on assembly workshops: Taxes incurred on assembly workshops are fixed irrespective of the level of production
- Depreciation on tools: The depreciation charge on tools would remain fixed and would not change with the level of production
Direct costs are traceable to the production of specific product or service. These are connected to specific cost object which can be a product, department or project. Following would be classified as direct costs:
- Laminate coverings for desktops: These costs are traceable to the production of specific product
- Wages of desk assembler: These costs are traceable to the production of specific product
Indirect costs are necessary for production but not traceable to act of production. These costs are necessary to keep business operational. They go beyond the costs associated with creating a product to include the costs of maintaining the entire company. Following are the indirect cost given in the problem:
- Monthly flat fee to clean workshop are associated with costs of maintenance
- Taxes on assembly workshops are not traceable to act of production
- Glue to assemble workstation component parts are not traceable to act of production
- Electricity for workshop are costs necessary to keep business operational
- Depreciation on tools are associated with costs of maintenance
Therefore, classification of manufacturing costs of Business Solution as asked in the given problem is shown below in the tabular manner:
Classification of manufacturing costs of Business Solutions:
| Particulars | Variable or Fixed cost | Direct or Indirect cost |
| Monthly flat fee to clean workshop | Fixed | Indirect |
| Laminate coverings for desktops | Variable | Direct |
| Taxes on assembly workshops | Fixed | Indirect |
| Glue to assemble workstation component parts | Variable | Indirect |
| Wages of desk assembler | Variable | Direct |
| Electricity for workshop | Variable | Indirect |
| Depreciation on tools | Fixed | Indirect |
Concept introduction:
Cost of goods manufactured:
Cost of goods manufactured, also known as cost of goods completed calculates the total value of inventory that was produced during the period and is ready for sale. It is the total amount of expenses incurred to turn work in process into finished goods. It includes total manufacturing costs including all direct materials, direct labor, factory overheads to the beginning work in process inventory and subtracting ending work in process inventory which can be seen below:
Requirement 2:
To calculate:
Cost of goods manufactured for Business Solutions for the month ended January 31, 2016.
Answer to Problem 1SP
Cost of goods manufactured = $3, 050
Explanation of Solution
To calculate cost of goods manufactured, following formula would be used:
In the given problem, following information is given:
Direct materials = $2, 200
Direct labor = $900
Factory overheads = $490
Beginning work in process inventory = Nil
Ending work in process inventory = $540
Therefore, schedule of cost of goods manufactured as asked in the given problem is given below:
Schedule of cost of goods manufactured of Business Solutions (Amount in $):
| Particulars | (Amount in $) | (Amount in $) |
| Direct materials | 2, 200 | |
| Add: Direct labor | 900 | |
| Add: Factory overheads | 490 | |
| Total manufacturing costs | 3, 590 | |
| Add: Beginning work in process inventory | 0 | |
| Less: Ending work in process inventory | (540) | |
| Cost of goods manufactured | 3, 050 |
Thus, cost of goods manufactured = $3, 050.
Concept introduction:
Cost of goods sold:
Cost of goods sold is the costs incurred for manufacturing or acquiring the products sold by a company in a given year. It includes all the direct costs incurred for the products sold. It can be calculated using the following formula:
Requirement 3:
Cost of goods sold section of partial income statement for the month ended January 31, 2016.
Answer to Problem 1SP
Cost of goods sold = $2, 700
Explanation of Solution
For calculating cost of goods sold, following formula would be used:
We have already calculated cost of goods manufactured as $3, 050. In the given problem, it is given that Beginning finished goods inventory is Nil and Ending finished goods inventory are $350.
Therefore, Cost of goods sold section of partial income statement for the month ended January 31, 2016 would be:
Cost of goods sold section of partial income statement for the month ended January 31, 2016 of Business Solutions (Amount in $):
| Particulars | (Amount in $) | (Amount in $) |
| Cost of goods manufactured | 3, 050 | |
| Add: Beginning finished goods inventory | 0 | |
| Total manufacturing costs | 3, 050 | |
| Less: Ending finished goods inventory | (350) | |
| Cost of goods sold | 2, 700 |
Thus, Cost of goods sold = $2, 700.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING FUND. W/CONNECT
- Ventana Window and Wall Treatments Company provides draperies, shades, and various window treatments. Ventana works with the customer to design the appropriate window treatment, places the order, and installs the finished product. Direct materials and direct labor costs are easy to trace to the jobs. Ventanas income statement for last year is as follows: Ventana wants to find a markup on cost of goods sold that will allow them to earn about the same amount of profit on each job as was earned last year. Required: 1. What is the markup on cost of goods sold (COGS) that will maintain the same profit as last year? (Round the percentage to two significant digits.) 2. A customer orders draperies and shades for a remodeling job. The job will have the following costs: What is the price that Ventana will quote given the markup percentage calculated in Requirement 1? (Round the price to the nearest dollar.) 3. What if Ventana wants to calculate a markup on direct materials cost, since it is the largest cost of doing business? What is the markup on direct materials cost that will maintain the same profit as last year? (Round the percentage to two significant digits.) What is the bid price Ventana will use for the job given in Requirement 2 if the markup percentage is calculated on the basis of direct materials cost? (Round to the nearest dollar.)arrow_forwardAssume you are the manager for the semi-trucks division at the Speedy Delivery Company. The semi-truck division is a cost center and you are reviewing the driver overtime costs for the previous year, shown here: A. Microsoft Excel or another spreadsheet application, create a line chart with markers showing the driver overtime expense. Describe your observations. B. Knowing that safety is important in your industry and weather plays a significant role in the safety of drivers, you decide to talk with the safety manager and obtained the following information: Using Microsoft Excel or another spreadsheet application, create individual line charts with markers showing the average snowfall and non-company highway accidents. Describe your observations and actions you might consider.arrow_forwardBumblebee Mobiles manufactures a line of cell phones. The management has identified the following overhead costs and related cost drivers for the coming year. The following were incurred in manufacturing two of their cell phones, Bubble and Burst, during the first quarter. REQUIREMENT Review the worksheet called ABC that follows these requirements. You have been asked to determine the cost of each product using an activity-based cost system. Note that the problem information is already entered into the Data Section of the ABC worksheet.arrow_forward
- Directions: Answer the following questions by the due date. Use numerical calculations (if needed) to support your argument. Submit your answers through uploading a Microsoft Word file, Excel file or PDF. Tread-Force Fitness, Inc. assembles and sells elliptical machines. All activity costs are related to labor. Management must remove $2.00 of activity cost from the product in order for it to remain competitive. Activity-based product information for each elliptical machine is as follows: (Hrs per unit) Activity Activity Based Usage x Activity rate / hr = Activity Cost Moving 0.20 $15 $3.00 Motor Assembly 1.50 $20 $30.00 Final Assembly…arrow_forwardValue chain and classification of costs, computer company. Dell Computer incurs the following costs:a. Utility costs for the plant assembling the Latitude computer line of productsb. Distribution costs for shipping the Latitude line of products to a retail chainc. Payment to David Newbury Designs for design of the XPS 2-in-1 laptopd. Salary of computer scientist working on the next generation of serverse. Cost of Dell employees’ visit to a major customer to demonstrate Dell’s ability to interconnect withother computersf. Purchase of competitors’ products for testing against potential Dell productsg. Payment to business magazine for running Dell advertisementsh. Cost of cartridges purchased from outside supplier to be used with Dell printersarrow_forwardClassify each cost as being either variable or fixed with respect to the number of units produced and sold. Also classify each cost as either a period or a product cost. Cost Item Predicting Cost Behavior Preparing Financial Statements 1.Hamburger buns in a Wendy’s restaurant. 2.Advertising by a dental office. 3.Apples processed and canned by Del Monte. 4.Shipping canned apples from a Del Monte plant to customers. 5.Insurance on a Bausch & Lomb factory producing contact lenses. 6.Insurance on IBM’s corporate headquarters. 7.Salary of a supervisor overseeing production of printers at Hewlett-Packard. 8.Commissions paid to automobile salespersons. 9.Depreciation of factory lunchroom facilities at a General Electric plant. 10.Steering wheels installed in BMWs.arrow_forward
- I need answers to all parts in this question. Cost Description Possible Measure of Activity 1. Salary of production manager at a surfboard manufacturer Surfboards produced 2. Cost of solder used in making computers Computers produced 3. Cost of dough used at a pizza shop Pizzas cooked 4. Janitorial wages at a surfboard manufacturer Surfboards produced 5. Salary of the controller at a hospital Number of patients 6. Cost of sales at an electronics store Dollar sales 7. Cost of testing materials used in a medical lab Tests run 8. Cost of heating an electronics store Dollar sales 9. Cost of electricity for production equipment at a surfboard manufacturer Surfboards produced 10. Depreciation on shelving at a book store Dollar sales Required:For each item above, indicate whether the cost is MAINLY fixed or variable with respect to the possible measure of activity listed next to it. Essay Toolbar navigation opens in a dialogarrow_forwardTechPro offers instructional courses in e-commerce website design. The company holds classes in a building that it owns. Identify each of TechPro’s costs below as (a) variable or fixed and (b) direct or indirect by selecting the appropriate dropdowns. Assume the cost object is an individual class. Variable or Fixed Direct or Indirect 1. Instructional manuals for students 2. Advertising Fixed Indirect 3. Salesperson salary 4. Sales commissions 5. Computer printer ink 6. Depreciation on classroom buildingarrow_forwardEthan Manufacturing Incorporated produces floor mats for automobiles. The owner, Joseph Ethan, has asked you to assist in estimating maintenance costs. Together, you and Joseph determine that the single best cost driver for maintenance costs is machine hours. These data are from the previous fiscal year for maintenance costs and machine hours: 1. What is the cost equation for maintenance costs using the high-low method? 2. Calculate the mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) for the cost equation you developed in requirement 1. Month Maintenance Costs Machine Hours 1 $ 2,660 1,750 2 2,820 1,830 3 2,970 1,910 4 3,080 1,930 5 3,160 1,960 6 3,130 1,940 7 3,070 1,920 8 2,910 1,900 9 2,680 1,760 10 2,280 1,160 11 2,290 1,360 12 2,510 1,650arrow_forward
- Below is a list of costs. Please identify each cost as either a product or period cost. Dragged and dropped options on the right-hand side will be automatically saved. For keyboard navigation... SHOW MORE ✓ Depreciation on office copier Depreciation on office building Insurance on office building Metal used in building a car Salary of CEO Salary of production manager Salary of assembly line workers Utilities of office building = = Product Period = Period = Period = Product = Product = = Period Periodarrow_forwardA new product Zico was recently introduced by Philadelphia Co., in order to complement its other products, Novo and Domo. The accountant used to allocate the indirect cost according to the units produced. With the recent addition of an expanded computer system, Sonata would like to investigate the possibility of implementing ABC. Before making a final decision, management has come to you for advice. You collected the following information regarding manufacturing overhead: Table (1) Mfg. Overhead Mfg. Overhead Costs Allocation bases Set-up $ 40,000 Number of set-ups Ordering materials $ 45,000 Number of material orders Handling materials $ 9,000 Number of times material was handled Inspection $ 21,000 Number of inspection hours $115,000 Table (2) Activity Products Zico Novo Domo Total Number of set-ups 5 20 55 Total…arrow_forwardA new product Zico was recently introduced by Philadelphia Co., in order to complement its other products, Novo and Domo. The accountant used to allocate the indirect cost according to the units produced. With the recent addition of an expanded computer system, Sonata would like to investigate the possibility of implementing ABC. Before making a final decision, management has come to you for advice. You collected the following information regarding manufacturing overhead: Table (1) Mfg. Overhead Mfg. Overhead Allocation bases Costs $ 40,000 $ 45,000 $ 9,000 $ 21,000 Number of set-ups Set-up Ordering materials Handling materials Inspection Number of material orders Number of times material was handled Number of inspection hours $115,000 Table (2) Products Activity Zico Novo Domo Total Number of set-ups 5 20 55 Total Number of material orders 1 2 7 Total Number of times material was handled 1 17 Total Number of inspection hours Number of units produced 3 10 6,000 3,000 1,000 Required: 1.…arrow_forward
 Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College


