
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Given Lewis structure is to be drawn using condensed formula.
Concept introduction:
The condensed formula indicates how the atoms should be connected in a given molecule. To arrive at a total charge of zero, each carbon should have a maximum of four bonds while each oxygen should have a maximum of two bonds and two lone pairs. A parenthesis in the condensed formula represents that the repetitive unit is attached to the previous carbon atom. The CO2 notation denotes a carbon atom that is doubly bonded to one oxygen atom and singly bonded to another. Rings are generally now shown in their condensed formulas, but they are commonly shown in their partially condensed form.
Answer to Problem 1.61P
The condensed formula for the first Lewis structure is: CH3(CH2)2CH3
Explanation of Solution
The given Lewis structure is:
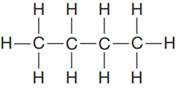
In the given Lewis structure, there are two CH2 units in the middle. In this case, the similar units are shown by using the notation (CH2)n, where ‘n’ is the number of CH2 units. Thus, the condensed formula for this is written as: CH3(CH2)2CH3
The condensed formula for the first Lewis structure is shown as: CH3(CH2)2CH3
(b)
Interpretation:
Given Lewis structure is to be drawn using condensed formula.
Concept introduction:
The condensed formula indicates how the atoms should be connected in a given molecule. To arrive at a total charge of zero, each carbon should have a maximum of four bonds while each oxygen should have a maximum of two bonds and two lone pairs. A parenthesis in the condensed formula represents that the repetitive unit is attached to the previous carbon atom. The CO2 notation denotes a carbon atom that is doubly bonded to one oxygen atom and singly bonded to another. Rings are generally now shown in their condensed formulas, but they are commonly shown in their partially condensed form.
Answer to Problem 1.61P
The condensed structure for the given Lewis structure is: CH3CHCHCH3
Explanation of Solution
The given Lewis structure is:
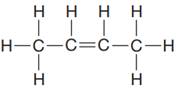
In the structure above, there are two CH3 groups on the terminal position. The middle carbon atoms have a double bond between them. Thus, the condensed formula for the given Lewis structure is: CH3CHCHCH3
The condensed formula for the given Lewis structure is shown as: CH3CHCHCH3
(c)
Interpretation:
Given Lewis structure is to be drawn using condensed formula.
Concept introduction:
The condensed formula indicates how the atoms should be connected in a given molecule. To arrive at a total charge of zero, each carbon should have a maximum of four bonds while each oxygen should have a maximum of two bonds and two lone pairs. A parenthesis in the condensed formula represents that the repetitive unit is attached to the previous carbon atom. The CO2 notation denotes a carbon atom that is doubly bonded to one oxygen atom and singly bonded to another. Rings are generally now shown in their condensed formulas, but they are commonly shown in their partially condensed form. Parentheses are also used to clarify when two or three groups are attached to the same carbon atom.
Answer to Problem 1.61P
The condensed structure for the given Lewis structure is: (CH3)2CCHCH3
Explanation of Solution
The given Lewis structure is:
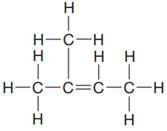
In the structure above, there are two CH3 groups attached directly to one of the doubly bonded carbon atom. Thus, a parenthesis has to be used to represent the two CH3 groups attached to one of the doubly bonded carbon atoms. The other doubly bonded carbon atom has one CH3 group attached to it. Thus, the condensed formula for the given Lewis structure is: (CH3)2CCHCH3
The condensed formula for the given Lewis structure is shown as: (CH3)2CCHCH3
(d)
Interpretation:
Given Lewis structure is to be drawn using condensed formula.
Concept introduction:
The condensed formula indicates how the atoms should be connected in a given molecule. To arrive at a total charge of zero, each carbon should have a maximum of four bonds while each oxygen should have a maximum of two bonds and two lone pairs. A parenthesis in the condensed formula represents that the repetitive unit is attached to the previous carbon atom. The CO2 notation denotes a carbon atom that is doubly bonded to one oxygen atom and singly bonded to another. Rings are generally now shown in their condensed formulas, but they are commonly shown in their partially condensed form. Parentheses are also used to clarify when two or three groups are attached to the same carbon atom.
Answer to Problem 1.61P
The condensed structure for the given Lewis structure is: (CH3)2CCHCH3
Explanation of Solution
The given Lewis structure is:
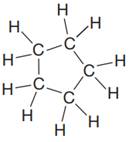
The structure above is a five carbon ring structure. Rings are generally now shown in their condensed formulas, but they are commonly shown in their partially condensed form. Thus, the condensed formula for the given Lewis structure is:
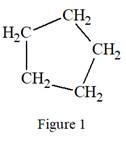
The condensed formula for the given Lewis structure is shown in Figure 1.
(e)
Interpretation:
Given Lewis structure is to be drawn using condensed formula.
Concept introduction:
The condensed formula indicates how the atoms should be connected in a given molecule. To arrive at a total charge of zero, each carbon should have a maximum of four bonds while each oxygen should have a maximum of two bonds and two lone pairs. A parenthesis in the condensed formula represents that the repetitive unit is attached to the previous carbon atom. The CO2 notation denotes a carbon atom that is doubly bonded to one oxygen atom and singly bonded to another. Rings are generally now shown in their condensed formulas, but they are commonly shown in their partially condensed form. Parentheses are also used to clarify when two or three groups are attached to the same carbon atom.
Answer to Problem 1.61P
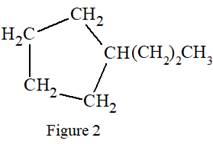
The condensed structure for the given Lewis structure is:
Explanation of Solution
The given Lewis structure is:
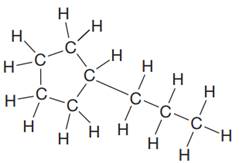
In the structure above, there is a five membered ring on the left side and a branch of three carbon atoms. Rings are generally now shown in their condensed formulas, but they are commonly shown in their partially condensed form. On one of the carbon atoms in the five membered ring, two CH2 units are attached with the terminal CH3 group.
Thus, the condensed formula for the given Lewis structure is:

The condensed formula for the given Lewis structure is shown in Figure 2.
(f)
Interpretation:
Given Lewis structure is to be drawn using condensed formula.
Concept introduction:
The condensed formula indicates how the atoms should be connected in a given molecule. To arrive at a total charge of zero, each carbon should have a maximum of four bonds while each oxygen should have a maximum of two bonds and two lone pairs. A parenthesis in the condensed formula represents that the repetitive unit is attached to the previous carbon atom. The CO2 notation denotes a carbon atom that is doubly bonded to one oxygen atom and singly bonded to another. Rings are generally now shown in their condensed formulas, but they are commonly shown in their partially condensed form. Parentheses are also used to clarify when two or three groups are attached to the same carbon atom.
Answer to Problem 1.61P
The condensed structure for the given Lewis structure is: CH3OCHCH3
Explanation of Solution
The given Lewis structure is:
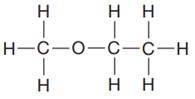
In the structure above, a CH3 unit is attached to the oxygen atom on one side. On the other side of the oxygen, there is an ethyl fragment, -CH2CH3. Thus, the condensed formula for the given Lewis structure is: CH3OCHCH3
The condensed formula for the given Lewis structure is CH3OCHCH3
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEM PRINC & MECH (BUNDLE)
- Synthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIf possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forwardWe mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardQuestion 3 (4 points), Draw a full arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reaction Please draw all structures clearly. Note that this intramolecular cyclization is analogous to the mechanism for halohydrin formation. COH Br + HBr Brarrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
