
Concept explainers
The beam AB is pin supported at A and supported by a cable BC. A separate cable CG is used to hold up the frame. If AB weighs 120 lb/ft and the column FC has a weight of 180 lb/ft, determine the resultant internal loadings acting on cross sections located at points D and E.
Answer to Problem 1.1RP
The resultant internal loadings at cross section at D are ND=−2.16 kip, VD=0_, and MD=2.16 kip⋅ft_.
The resultant internal loadings at cross section at E are NE=4.32 kip, VE=0.54 kip_, and ME=2.16 kip⋅ft_.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The beam AB is pin supported at A and supported by a cable BC.
The weight of the beam AB is 120 lb/ft.
The weight of the column FC is 180 lb/ft.
Calculation:
Find the loading at the center of the beam AB (PAB):
PAB=Weight of beam AB×Length of beam AB
Substitute 120 lb/ft for the weight of beam AB and 12 ft for the length of beam AB.
PAB=120×12=1,440 lb
Convert the unit from lb to kip.
PAB=1,440 lb×1 kip1,000 lb=1.44 kip
Sketch the Free Body Diagram of the beam AB shown in Figure 1.
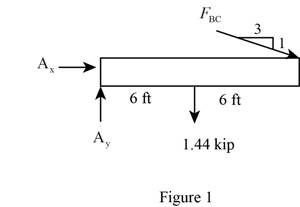
Refer to Figure 1.
Find the angle of cable BC to the horizontal (θ):
sinθ=1√12+32sinθ=13.1623θ=sin−1(0.3162)θ=18.43°
Find the tension in cable BC as shown below.
Take moment about A is Equal to zero.
∑MA=0(FBCsin18.43°×12)+1.44×6=03.794FBC+8.64=03.794FBC=−8.64
FBC=−2.277 kip
Find the support reaction at A as shown below.
Apply the Equations of Equilibrium as shown below.
Summation of forces along horizontal direction is Equal to zero.
∑Fx=0Ax−2.277cos18.43°=0Ax−2.16=0Ax=2.16 kip
Summation of forces along vertical direction is Equal to zero.
∑Fy=0Ay−1.44+2.277sin18.43°=0Ay−0.72=0Ay=0.72 kip
Find the loading at the center of the beam AD (PAD):
PAD=Weight of beam AD×Length of beam AD
Substitute 120 lb/ft for the weight of beam AD and 6 ft for the length of beam AD.
PAD=120×6=720 lb
Convert the unit from lb to kip.
PAD=720 lb×1 kip1,000 lb=0.72 kip
Sketch the Free Body Diagram of the section for point D as shown in Figure 2.
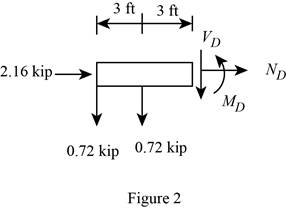
Refer to Figure 2.
Find the internal loadings as shown below.
Apply the Equations of Equilibrium as shown below.
Summation of forces along horizontal direction is Equal to zero.
∑Fx=0ND+2.16=0ND=−2.16 kip
Summation of forces along vertical direction is Equal to zero.
∑Fy=0VD+0.72−0.72−=0VD=0
Take moment about D is Equal to zero.
∑MD=0MD−0.72×3=0MD−2.16=0MD=2.16 kip⋅ft
Hence, the resultant internal loadings at cross section at D are ND=−2.16 kip, VD=0_, and MD=2.16 kip⋅ft_.
Find the loading at the center of the column FC (PFC):
PFC=Weight of column FC×Length of column FC
Substitute 180 lb/ft for the weight of column FC and 16 ft for the length of column FC.
PFC=180×16=2,880 lb
Convert the unit from lb to kip.
PFC=2,880 lb×1 kip1,000 lb=2.88 kip
Sketch the Free Body Diagram of the beam FC shown in Figure 3.
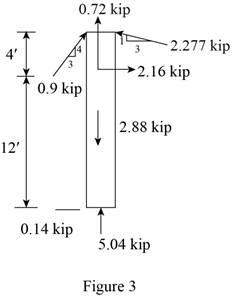
Refer to Figure 3.
Find the angle of cable CG to the horizontal.
sinθ=3√42+32sinθ=35θ=sin−1(0.6)θ=36.87°
Find the tension in cable CG as shown below.
Summation of forces along horizontal direction is Equal to zero.
∑Fx=0FCGcos36.87°−2.277sin18.43°=00.8FCG−0.72=00.8FCG=0.72
FCG=0.9 kip
Find the loading at the center of the column FE (PFE):
PFE=Weight of column FE×Length of column FE
Substitute 180 lb/ft for the weight of column FE and 4 ft for the length of column FC.
PFE=180×4=720 lb
Convert the unit from lb to kip.
PFE=720 lb×1 kip1,000 lb=0.72 kip
Sketch the Free Body Diagram of the section for point E as shown in Figure 4.
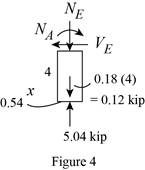
Refer to Figure 4.
Find the internal loadings as shown below.
Apply the Equations of Equilibrium as shown below.
Summation of forces along horizontal direction is Equal to zero.
∑Fx=0VE−0.54=0VE=0.54 kip
Summation of forces along vertical direction is Equal to zero.
∑Fy=0NE+0.72−5.04=0NE−4.32=0NE=4.32 kip
Take moment about E is Equal to zero.
∑ME=0−ME+0.54×4=0−ME+2.16=0ME=2.16 kip⋅ft
Therefore, the resultant internal loadings at cross section at E are NE=4.32 kip, VE=0.54 kip_, and ME=2.16 kip⋅ft_.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
MECHANICS OF MATERIAL IN SI UNITS
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Degarmo's Materials And Processes In Manufacturing
Starting Out with C++: Early Objects (9th Edition)
Computer Science: An Overview (13th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Introduction To Programming Using Visual Basic (11th Edition)
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
- Solve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forwardSolve this problem and show all of the workarrow_forwarddraw the pneumatic circuit to operate a double-acting cylinder with: 1. Extension: Any of two manual conditions plus cylinder fully retracted, → Extension has both meter-in and meter-out, 2. Retraction: one manual conditions plus cylinder fully extended, → Retraction is very fast using quick exhaust valve.arrow_forward
- Correct answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you. Expert solution plsarrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forward
- Correct answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only with fbd. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forward
- Correct answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution with fbd only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forwardCorrect answer is written below. Detailed and complete solution only. I will upvote, thank you.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





