
You wish to react acetylene (C2H2) and hydrogen chloride (HCl) to produce
vinylchloride (C2H3Cl), which is used to manufacture polyvinylchloride:
C2H2 + HCl = C2H3Cl (Desired)
You wish to minimize the side reaction of vinylchloride to dicloroethane:
C2H3Cl + HCl = C2H4Cl2 (Undesired)
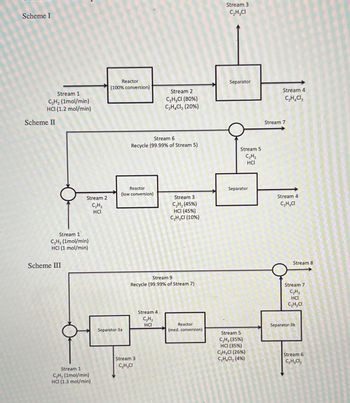
Consider the three process schemes shown below. All compositions are mol percent.
without doing any calculations, answer the following questions,
a) Which scheme has the highest rate of production of desired product, C2H3Cl?
Explain
b) Which scheme has the highest rate of production of undesired by-product,
C2H4Cl2? Explain
c) Which scheme has the largest reactor, as measured by the total mol/min through the
reactor? Explain
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 10 images

- Balance the following equation according to the half-reaction method: H2S (g) + Hg22+ (aq) -> Hg (l) + S (s) *in acid The answer the book gives is: H2S + Hg22+ + 2H20 -> 2Hg + S + 2H3O+arrow_forwardConsider the following reaction: 10 KNO3(s) +8 C(s) +3 S(s) 2 K2CO3(s) + 3 K,SO,(s) + 6 CO2(g) + 5 N2(g) you mix 0.75 kg of KNO3 with 0.75 kg of sulfur in the presence of excess carbon and the reaction proceeds with 55% yield, what mass of gas-phase products (i.e., CO2 plus N2) will leave the reaction mixture? Show complete work including all calculations, units, appropriate significant figures, and 1-5 key words of explanation at each step of your calculation. Ifarrow_forwardSolve please,typed ans need. And need both parts solution,plz don't reject ques. I will rate your answer if correctarrow_forward
- 2. Combustion of fuels with air at high temperatures can produce nitrogen/oxygen compounds (NOx) as unwanted by products. Because these compounds are pollutants, they must be removed, and one process for doing so is called selective catalytic reduction (SCR). A researcher claims to have developed a new SCR catalyst that uses ammonia (NH3) as a reactant to convert NO into nitrogen and water via the reaction: 6NO(g) + 4NH3(g) ---> 5N₂(g) + 6H₂O(g) We are working on the design for a process using this reaction in which 120 mol/hr of an equimolar mixture of NO and NH3 (i.e., 60 mol/hr NO and 60 mol/hr NH3) at 450°C is fed to the reactor. We may assume that the reaction goes to completion in the limiting reactant. The reactor is jacketed to maintain the temperature at 450°C, and we may assume that the pressure is held constant at 1 Atm. Use the following constant heat capacities for the gases: (a) (b) I (c) [ Species NO (g) NH3(g) N₂ (g) H₂O (g) Cp (J/mol K) 30.5 37.0 29.1 34.2 Determine…arrow_forward2. Combustion of fuels with air at high temperatures can produce nitrogen/oxygen compounds (NOx) as unwanted by products. Because these compounds are pollutants, they must be removed, and one process for doing so is called selective catalytic reduction (SCR). A researcher claims to have developed a new SCR catalyst that uses ammonia (NH3) as a reactant to convert NO into nitrogen and water via the reaction: 6NO(g) + 4NH3(g) ---> 5N2(g) + 6H₂O(g) We are working on the design for a process using this reaction in which 120 mol/hr of an equimolar mixture of NO and NH3 (i.e., 60 mol/hr NO and 60 mol/hr NH3) at 450°C is fed to the reactor. We may assume that the reaction goes to completion in the limiting reactant. The reactor is jacketed to maintain the temperature at 450°C, and we may assume that the pressure is held constant at 1 Atm. Use the following constant heat capacities for the (a) (b) | (c) [ Species NO (g) NH3(g) N₂ (g) H₂O (g) gases: C₂ (J/mol K) 30.5 37.0 29.1 34.2 Determine…arrow_forwardExample 2: A hydrocarbon fuel, which has the general form (CnH2n+2) is mixed with pure - Oxygen with two different equivalence ratios as the two reactions below: 1) CxHy + 502→bCO2 + dH2O + f02 2) CxHya02 →cCO + dH20 (Lean condition) at Ocut (Rich condition) For reaction1, the total moles of products are 6.5moles. For reaction 2, the mole fraction of CO in products is, Find: 1) Type of fuel 2) equivalence ratio for both above reactions.arrow_forward
- Balance the following redox reaction in an acidic solution: UO22+(aq)+Zn(s)->U4+(aq)+Zn2+(aq)arrow_forwardAs reported in US Patent 4203923, cyclohexanone is an important chemical raw material in the production of nylon intermediates. The separation and purification section for cyclohexanone production usually done through a series of distillation units. Liquid mixture of cyclohexanone (1) and phenol (2) was reported to exist in equilibrium with its vapor at 144 °C (417.15K). The system conforms closely to Modified Raoult’s Law. The mixture forms azeotrope at composition of 0.695. (Refer Table) (a) Provide a sketch that clearly shows that the system exhibits azeotrope(α12)x1=0 = P1sat eA / P2sat and (α12)x1=1 = P1sat / P2sat eA (b) State Paz and sketch a P-xy diagram of the systemarrow_forward1. An impure sample of compound A is contaminated with two impurities B and C. The sample is to be purified by recrystallization using ethanol as the solvent. The solubility properties of the three components are summarized below. Solubility in Solubility in ethanol Solubility in 50 mL Solubility in 50 mL ethanol at -78 °C at - 0°C ethanol at -78 °C ethanol at - 0°C (g) (g) Compound A 0.12 g/mL 0.02 g/mL Impurity B 0.58 g/mL 0.04 g/mL Impurity C 0.005 g/mL 0.0003 g/mL The impure (7.5 g) sample contains 5.0 g of compound A, 1.5 g of B and 1.0 g of C and is recrystallized using 50 mL of ethanol. The sample is boiled with 50 mL of ethanol, filtered by gravity and then cooled in ice and filtered by suction. a) How much compound A should be obtained as the final product? Will the sample be contaminated with any of the impurities? Explain (using calculations to support your answer-fill in the missing masses in the table above). Hint: For this question you should calculate the mass of each…arrow_forward
- Predict the product when the two substances mix. If the reaction occurs, write the balanced chemical equation. If the reaction does not happen, write "NA" A solution of nickel(III) nitrate is mixed with a solution of sodium hydroxide.arrow_forwardNaOH (Caustic soda) may be produced in a process from the following reactions: CaCO3 = CaO + CO2 CaO+H2O = Ca(OH)2 2NaCl + CaCO3 = Na2CO3 + CaCl2 Na2CO3+ Ca(OH)2 = 2 NaOH + CaCO3 1. Write the overall reaction for NaOH production using salt (NaCl), limestone (CaCO3) and water (H2O) as raw materials 2. What are the required feed rates of salt (NaCl), limestone (CaCO3) and water (H2O) required to produce 1000 lbm/day of NaOH as a 10% wt solution.arrow_forwardTable Q4 shows the solubility of liquid trichlorohexane in toluene (also liquid) at equilibrium at different temperatures, where species 1 is trichlorohexane and species 2 is toluene. These data are obtained at 1 atm. X1 0.037 0.050 0.085 0.135 0.199 0.288 0.364 0.482 0.500 0.585 Table Q4 Temperature (°C) 92.18 100.00 107.11 111.96 113.84 112.87 109.63 101.91 100.00 90.05 (a) Plot a properly labeled T-x₁ diagram of this binary mixture at 1 atm. (b) Estimate the composition of each phase at 110°C for this binary mixture. (c) At 110°C and 1 atm, trichlorohexane is added dropwise into an initially pure toluene until the mole fraction of trichlorohexane reaches 0.5. Assuming equilibrium is preserved during every addition of trichlorohexane, describe what you would see if the whole process is conducted in a transparent beaker. (d) At 100°C, determine the A12 and A21 in the two-constant Margules equation. Justify any assumptions that you make.arrow_forward
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The





