
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
You were tasked with modifying an audio amplifier circuit. Amplifier circuits are responsible for increasing the current sent to the speakers, avoiding damaging the sound device. The original design is shown in the figure. You want to increase the current I1 by a factor of 10 (10 times). The conditions of the design area are: Both font values must be increased. None of the values can be equal to 0. What are the new values that you propose for the design of the amplifier?
** Argue your answer by analyzing the results obtained through calculations.
(Check image 4 for the circuit)
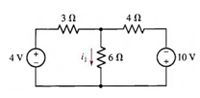
Transcribed Image Text:4 N
4 V
10 V
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Do not copy from other websites Correct and detailed answer will be Upvoted else downvoted. Thank you!arrow_forwardAnswer for #'s 4 and 5 please.arrow_forwardOften it is useful to model complex chips as simple linear equivalent models to determine the effects of the current draw and to ensure safe operation of the circuit. Consider the circuit shown in figure 5, it is a model of a digital microprocessor circuit. Each current source represent the current drawn by a portion of a digital circuits in the microprocessor. The resistors represent the power distribution network from the supply to that portion of the processor. Each current source can only have the following values: either be off i.e. 0 or have a value of I.. The reason being digital circuits when they are not performing a computation consume zero power and when operational they consume an average current (in this case I). In our model all portions consume the same current when they are operational. Power Supply V (+ Linear Model of a Digital Microprocessor V₁ ww R₁ 1 I₁ mm R₂ 2 1₂ V₂ → ни R3 Figure 5: Linear Model of the microprocessor 13 3 (a) Given the possible values for I1, I2…arrow_forward
- (Asterisked problems are associated with optional sections.) 1. Determine the output of each of the following circuits, assuming that the upper input is 1 and the lower input is 0. What would be the output when the upper input is 0 and the lower input is 1? a. b. C. D D nia 00arrow_forwardQuestion 3 The 555 timer is connected in the following circuit. The resistance of the extra resistor is 102, the capacitance of the extra capacitor is 0.1F. The voltage input at Pin2 is Vcc. What is the output state at Pin3? 1) 2) Decide the voltage input value at Pin 6 when the condition is stable. 3) Decide the output state at Pin3 when a trigger input is applied at Pin2 (voltage input at Pin2 changes from Vcc to 0, and return back to Vcc immediately). 4) After the trigger input is applied at Pin2, how long would the output maintain at the unstable state. Vc R O Output Vo 555 Vc 0.01µF Trigger Inputarrow_forwardWhat is the peak positive output voltage to the load resistor? (Units are in Volts.) What is the peak negative output voltage to the load resistor? (Units are in Volts.) Please in typing format please ASAP forarrow_forward
- As we know that opamps working on a dual power supply and both power supply should be in the same polarity. If the power supply is not similar in both the polarity the dc output will drift to either side depending on the higher amplitude of polarity and sometimes the case is like this offset nulling will become difficult to achieve So what is "offset nulling" ? Please explainarrow_forwardFirst,Calculate the input resistance Rin defined as Vin/Iin . Hint: Assuming you know the variable Vin, find Iin in terms of Vin. Substitute Iin into Vin/Iin, then variables Vin will cancel each other on the numerator and denominator. You will get a number that represents Rin. Second,Construct the resistive network in figure 5 with Vin = 5V from the Arduino POWER section. Measure Vin. Then, measure Iin by inserting the DMM between node n1 and n2. Divide these two values to get Rin. Report Vin, Iin, and Rin. Then, Are the measured input resistance values the same when you use Vin = 3.3V and when you use Vin = 5V? Is Rin independent from Vin and Iin? Explain it. Also, include a photo of your circuit!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,