
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
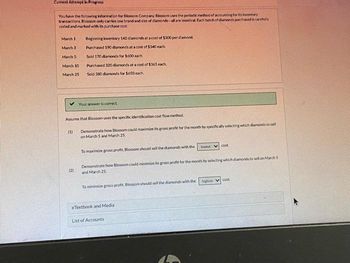
Transcribed Image Text:Current Attempt in Progress
You have the following information for Blossom Company Blossom uses the periodic method of accounting for its inventory
transactions, Blossom only carries one brand and size of diamonds-all are identical Each hatch of diamonds purchased is carefully
coded and marked with its purchase cost
March 1
March 3
March 5
March 10
March 25
✓ Your answer is correct
Beginning inventory 140 diamonds at a cost of $300 perdiamond
Purchased 190 diamonds at a cost of $340 each
Sold 170 diamonds for $600 each.
Purchased 320 diamonds at a cost of $365 each
Sold 300 damonds for $650 each.
Assume that Blossom uses the specific identification cost flow method.
Demonstrate how Blossom could maximize its gross profit for the month by specifically selecting which diamonds to sell
on March 5 and March 25
(1)
(2)
To maximize gross profit, Blossom should sell the diamonds with the
lowest cost
Demonstrate how Blossom could minimize its gross profit for the month by selecting which diamonds to sell on March 5
and March 25
To minimize gross profit, Blosson should sell the diamonds with the
eTextbook and Media
List of Accounts
highest cost
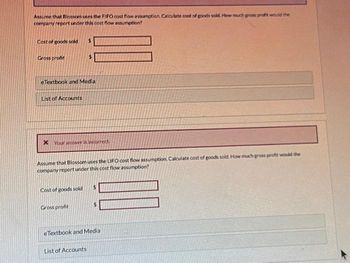
Transcribed Image Text:Assume that Blossom uses the FIFO cost flow assumption. Calculate cost of goods sold. How much gross profit would the
company report under this cost flow assumption?
Cost of goods sold
Gross profit
eTextbook and Media
List of Accounts
Your answer is incorrect
Assume that Blossom uses the LIFO cost flow assumption. Calculate cost of goods sold. How much gross profit would the
company report under this cost flow assumption?
Cost of goods sold
Gross profit
$
eTextbook and Media
List of Accounts
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales data for tennis rackets are as follows: April 3 Inventory 19 units @ $18 11 Purchase 16 units @ $16 14 Sale 20 units 21 Purchase 12 units @ $21 25 Sale 14 units Complete the inventory cost card assuming the business maintains a perpetual inventory system and determine the cost of goods sold and ending inventory using LIFO. Cost of Goods Sold Inventory Purchases Qty. Unit Cost Total Cost Qty. Unit Cost Total Cost Date Qty. Unit Cost Total Cost April 3 11 $ 14 $ 21 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24arrow_forwarddont uplode images in answerarrow_forwardPlease help with this solutionarrow_forward
- Waterway Inc. is a retailer operating in British Columbia. Waterway uses the perpetual inventory system. All sales returns from customers result in the goods being returned to inventory; the inventory is not damaged. Assume that there are no credit transactions; all amounts are settled in cash. You are provided with the following information for Waterway Inc. for the month of January 2022. Date Description Quantity Unit Cost or Selling Price January 1 Beginning inventory 100 $21 January 5 Purchase 148 24 January 8 Sale 114 36 January 10 Sale return 10 36 January 15 Purchase 55 26 January 16 Purchase return 5 26 January 20 Sale 94 41 January 25 Purchase 26 28 Calculate the Moving-average cost per unit at January 1, 5, 8, 10, 15, 16, 20, & 25 For each of the following cost flow assumptions, calculate cost of goods sold,…arrow_forwardBeginning inventory, purchases, and sales data for tennis rackets are as follows: April 3 Inventory 18 units @ $12 11 Purchase 17 units @ $19 14 Sale 22 units 21 Purchase 12 units @ $17 25 Sale 19 units Complete the inventory cost card assuming the business maintains a perpetual inventory system and determine the cost of goods sold and ending inventory using FIFO. Cost of Inventory Purchases Goods Sold Date Qty. Unit Cost Total Cost Qty. Unit Cost Total Cost Qty. Unit Cost Total Cost April 3 11 14 21 25 Total Cost of goods sold Ending inventory valuearrow_forwardBeginning inventory, purchases, and sales data for tennis rackets are as follows: April 3 Inventory 18 units @ $14 11 Purchase 12 units @ $18 14 Sale 25 units 21 Purchase 13 units @ $19 25 Sale 8 units Complete the inventory cost card assuming the business maintains a perpetual inventory system and determine the cost of goods sold and ending inventory using FIFO. Cost of Purchases Goods Sold Inventory Date Qty. Unit Cost Total Cost Qty. Unit Cost Total Cost Qty. Unit Cost Total Cost April 3 %$4 11 $4 $ 14 21 $4 25 $4 $4 $4 Total Cost of goods sold $4 Ending inventory value %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24 %24arrow_forward
- Kingbird Company sells discounted shoes to the fashion-oriented consumer. The following schedule relates to the company's inventory for the month of March: March 1 (a) 7 8 15 i. 20 ii. 25 27 Beginning inventory Purchase Purchase Sale Sale Purchase Sale * Your answer is incorrect. Kingbird Company uses the periodic inventory system. FIFO 3,780 units 1,260 units Weighted-average 1,890 units $ 4,410 units $ 882 units 630 units 1,512 units Cost $115,290 Calculate Kingbird Company's cost of goods sold, gross margin, and ending inventory using: 50,400 i. FIFO ii. Weighted-average (Round calculations for cost per unit to 2 decimal places, e.g. 10.52.) Cost of Goods Sold 94,500 19,530 250,110 248,724 Sales $ $396,900 66,150 $ 90,720 Gross Margin 303,660 305,046 $ $ tA Ending Inventory 25,074 26,460arrow_forwardeBook Show Me How I Print Item Journal Entries-Periodic Inventory Instructions Chart of Accounts General Journal Instructions Amy Douglas owns a business called Douglas Distributors. The following transactions took place during January of the current year. January Transactions: Jan. Purchased merchandise on account from Elite Warehouse, $3,950. 8 Paid freight charge on merchandise purchased, $250. 12 Sold merchandise on account to Memories Unlimited, $4,650. 15 Received a credit memo from Elite Warehouse for merchandise returned, $680. 22 Issued a credit memo to Memories Unlimited for merchandise returned, $440. Required: Journalize the transactions in a general journal using the periodic inventory method.arrow_forwardhelp please answer in text form with proper workings and explanation for each and every part and steps with concept and introduction no AI no copy paste remember answer must be in proper format with all workingarrow_forward
- Current Attempt in Progress Bramble Ltd. had beginning inventory of 54 units that cost $105 each. During September, the company purchased 206 units on account at $105 each, returned 6 units for credit, and sold on account 153 units at $201 each. Prepare journal entries for the September transactions, assuming that Bramble uses a periodic inventory system. (Credit account titles are automatically indented when the amount is entered. Do not indent manually. If no entry is required, select "No Entry" for the account titles and enter o for the amounts. List all debit entries before credit entries.) Account Titles and Explanation Debit Credit (To record purchase on account) (To record purchase return) Preparjalneries for the Sopomber tramming that perdicimentary titles are automatically indented whes the amount is entered De not indest manually. If ne entry is required, Entry for the account ctles and enter O for the amounts List el dret estr les defane crentes) Account Titles and…arrow_forwardk t K nt ences Peterson Furniture Designs is preparing the annual financial statements dated December 31. Ending inventory information about the five major items stocked for regular sale follows: Required: 1-a. Complete the table column "Write-Down per Item" and then sum the final column. 1-b. Compute the amount of the total write-down when the LCM/NRV rule is applied to each item. 2. Prepare the journal entry Peterson Furniture Designs would record on December 31 to write down its inventory to LCM/NRV. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. h Req 1A Req 1B Item Alligator Armoires Bear Bureaus Cougar Credenzas Dingo Cribs Elephant Dressers Complete the table column "Write-Down per Item" and then sum the final column. NRV per Item Write-down per Item Req 2 Unit Cost (FIFO) $ 60 55 53 55 22 $ 56 55 59 55 14 Req 1A Quantity on Hand 50 30 80 70 50 Total Write- down Req 1B >arrow_forwardBeginning inventory, purchases and sales data for T-shirts are as follows: April 3 Inventory 24 units @ $10 11 Purchase 26 units @ $12 14 Sale 36 units 21 Purchase 18 units @ $15 25 Sale 20 units Assuming the business maintains a periodic inventory system; calculate the cost of merchandise sold and ending inventory under the following assumptions: FIFO LIFO Average cost In your computations, round the average cost per unit to two decimal places and round your final answers to the nearest dollar.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education