
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:hysics.com/myct/itemView?assignment ProblemID=189028777
2
W
S
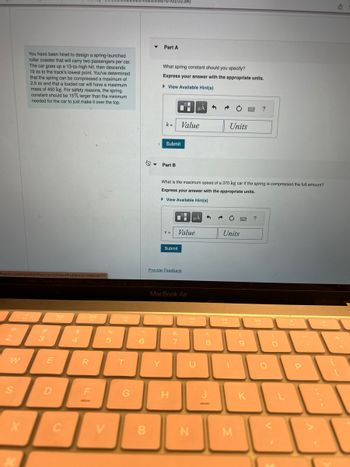
You have been hired to design a spring-launched
roller coaster that will carry two passengers per car.
The car goes up a 13-m-high hill, then descends
19 m to the track's lowest point. You've determined
that the spring can be compressed a maximum of
2.5 m and that a loaded car will have a maximum
mass of 450 kg. For safety reasons, the spring
constant should be 15% larger than the minimum
needed for the car to just make it over the top.
X
3
E
D
80
F3
C
$
4
888
F4
ק|ר|
R
F
%
5
V
F5
T
G
6
B
▼
162023#/
Part A
Y
What spring constant should you specify?
Express your answer with the appropriate units.
View Available Hint(s)
k= Value
Submit
Part B
V =
Submit
Provide Feedback
H
What is the maximum speed of a 370 kg car if the spring is compressed the full amount?
Express your answer with the appropriate units.
► View Available Hint(s)
%
MacBook Air
Value
&
7
μÃ
μA 3
A4
F7
U
N
3
**
8
Units
Units
DII
FB
1
M
(
9
www.
K
?
?
DD
FO
CO
O
F10
P
F11
U
[
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Full solution for this question. Answer is 0.919marrow_forwardA block of mass 2.80 kg is placed against a horizontal spring of constant k = 745 N/m and pushed so the spring compresses by 0.0550 m. HINT (a) What is the elastic potential energy of the block-spring system (in J)? When a spring is compressed or stretched, the spring potential energy, PEs = 1 2 kx2, is always positive. Gravitational potential energy, PEg = mgy, can be positive or negative depending on whether an object is above or below the y = 0 reference height. J (b) If the block is now released and the surface is frictionless, calculate the block's speed (in m/s) after leaving the spring. m/sarrow_forwardYou have been hired to design a spring-launched roller coaster that will carry two passengers per car. The car goes up a 12-m-high hill, then descends 15 m to the track's lowest point. You've determined that the spring can be compressed a maximum of 2.1 m and that a loaded car will have a maximum mass of 400 kg. For safety reasons, the spring constant should be 12% larger than the minimum needed for the car to just make it over the top. Part A What spring constant should you specify? Express your answer with the appropriate units. ► View Available Hint(s) k = 2.4x104 N Submit ✓ Correct Correct answer shown. Your answer 23893 was either rounded differently Part B v= Previous Answers What is the maximum speed of a 340 kg car if the spring is compressed the full amount? Express your answer with the appropriate units. ▸ View Available Hint(s) 18 Submit Previous Answers m m X Incorrect; Try Again; 8 attempts remaining Be sure to find the velocity of the car specifically of 340 kg. used a…arrow_forward
- The fair is in town and one of the attractions is a bungee jump. They are trying to determine the safety restrictions to prevent an accident. The length of the cord is 6.3m. The maximum distance of the fall is H=31 m, and the spring constant is K=145N/m. Given this information, what is the largest mass of jumper this attraction can allow?arrow_forwardYou have been hired to design a spring-launched roller coaster that will carry two passengers per car. The car goes up a 12-m-high hill, then descends 15 m to the track's lowest point. You've determined that the spring can be compressed a maximum of 2.1 m and that a loaded car will have a maximum mass of 400 kg. For safety reasons, the spring constant should be 12% larger than the minimum needed for the car to just make it over the top. Part A Part B What is the maximum speed of a 340 kg car if the spring is compressed the full amount? Express your answer with the appropriate units. ► View Available Hint(s) V = O Value Submit Units ?arrow_forwardA 250 gram block is dropped from rest at a height of 1.2m onto a relaxed vertical spring that has a spring constant of k =2.5 N/cm. The block continues downward, compressing the spring until it reaches its lowest point. At the lowest point, how much has the spring been compressed? Please answer in units of meters.arrow_forward
- A block of mass 0.259 kg is placed on top of a light, vertical spring of force constant 4 800 N/m and pushed downward so that the spring is compressed by 0.108 m. After the block is released from rest, it travels upward and then leaves the spring. To what maximum height above the point of release does it rise? (Round your answer to two decimal places.)arrow_forwardA 150 g particle at x = 0 is moving at 2.00 m/s in the +x-direction. As it moves, it experiences a force given by Fx =(0.350N)sin(x/2.00m). What is the particle's speed when it reaches x = 3.14 m? Note:- Consider "/" as a division symbol.arrow_forwardA glider that is 180 kg is pushed by a spring with constant 3.2*10^5 N/m down a water slide track from a height of 35m in a zig zag path. Once the slide reaches the floor level track, it will be eventually stop due to friction. Friction only exists on the ground level, and the coefficient of kinetic friction here is 0.8. If 70 meters is the max distance that the glider move on this ground level track, what is the safest maximum distance that the spring can be compressed if a 20 kg person is also on the glider.arrow_forward
- In the Back to the Future movies, a DeLorean car of mass 1,230 kg travels at 88 miles per hour to venture back to the future. (a) What is the kinetic energy (in kJ) of the DeLorean? kJ (b) What spring constant (in N/m) would be needed to stop this DeLorean in a distance of 0.82 m? N/marrow_forwardWillow is testing a spring. The spring has a natural length of 5 m, and it takes 71 J for Willow to stretch the spring to a length of 6 m. What is the spring constant? Round to 3 decimal places Type your answer...arrow_forwardIn the figure, a spring with spring constant k = 180 N/m is at the top of a frictionless incline of angle e = 38°. The lower end of the incline is distance D = 0.92 m from the end of the spring, which is at its relaxed length. A 1.5 kg canister is pushed against the spring until the spring is compressed 0.22 m and released from rest. (a) What is the speed of the canister at the instant the spring returns to its relaxed length (which is when the canister loses contact with the spring)? (b) What is the speed of the canister when it reaches the lower end of the incline? (a) Number UnitšTm/s (b) Number Unitsm/s Click if you would like to Show Work for this question: Open Show Work Question Attempts: Unlimited SAVE FOR LATER SUBMIT ANSWER 10:37 PM ENG e to search 4/4/2021 13) 19home & 7. LEGO 08. 9. E R. Yarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON