
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
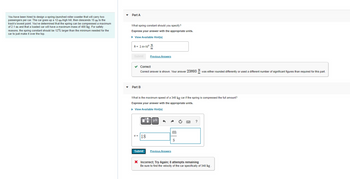
Transcribed Image Text:You have been hired to design a spring-launched roller coaster that will carry two
passengers per car. The car goes up a 12-m-high hill, then descends 15 m to the
track's lowest point. You've determined that the spring can be compressed a maximum
of 2.1 m and that a loaded car will have a maximum mass of 400 kg. For safety
reasons, the spring constant should be 12% larger than the minimum needed for the
car to just make it over the top.
Part A
What spring constant should you specify?
Express your answer with the appropriate units.
► View Available Hint(s)
k = 2.4x104 N
Submit
✓ Correct
Correct answer shown. Your answer 23893 was either rounded differently
Part B
v=
Previous Answers
What is the maximum speed of a 340 kg car if the spring is compressed the full amount?
Express your answer with the appropriate units.
▸ View Available Hint(s)
18
Submit
Previous Answers
m
m
X Incorrect; Try Again; 8 attempts remaining
Be sure to find the velocity of the car specifically of 340 kg.
used a different number of significant figures than required for this part.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A box is pressed against a horizontal spring, compressing the spring from its relaxed length. The box is then released and the spring launches the box horizontally along a track that ends in a ramp, as shown above. The box has enough speed to leave the ramp, and the box reaches a maximum vertical height above the floor. Assume there is negligible friction between the box and the track and air resistance is negligible. K = spring constant of spring X = distance the spring is compressed M = mass box Theta = angle of ramp from horizontal H = maximum height reached by box The scenario is repeated using a different box with a greater mass. The spring is compressed the same distance x. Indicate how h in this second scenario compares to h in the original scenario, and explain why without mathematically deriving a relation for h. Students derive an equation for h in the original scenario, h= (sin2theta)kx2/2Mg, which may or may not be correct. Is this equation consistent with your claim…arrow_forwardYou have been hired to design a spring-launched roller coaster that will carry two passengers per car. The car goes up a 10-m-high hill, then descends 17 m to the track's lowest point. You've determined that the spring can be compressed a maximum of 2.5 m and that a loaded car will have a maximum mass of 400 kg. For safety reasons, the spring constant should be 13% larger than the minimum needed for the car to just make it over the top. k = 1.4x104 Submit Part B m Previous Answers Correct Correct answer is shown. Your answer 14174 significant figures than required for this part. V = What is the maximum speed of a 360 kg car if the spring is compressed the full amount? Express your answer with the appropriate units. ► View Available Hint(s) μÅ m ? was either rounded differently or us Value Units ! You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again.arrow_forwardAn m = 12.0kg block is released from rest on a frictionless incline that makes an angle of 0 = 27.0°, as shown in the figure. Below the block is a spring that has a spring constant of 1.55 × 10¹ N/m. The block momentarily stops when it compresses the spring by 5.50 cm. How far I does the block move down the incline from its release point to the stopping point? Answer in units of centimeters. m eeeeeee 0arrow_forward
- How far the block will compress the spring after fall back from its maximum height?arrow_forwardA block of mass m = 2.80 kg is dropped from height h = 46.0 cm onto a spring of spring constant k = 986 N/m (see the figure). Find the maximum distance the spring is compressed. WI peeeeeeeearrow_forwardThe elastic energy stored in your tendons can contribute up to 35% of your energy needs when running. Sports scientists find that (on average) the knee extensor tendons in sprinters stretch 42 mm while those of nonathletes stretch only 35 mm. The spring constant of the tendon is the same for both groups, 33 N/mm. What is the difference in maximum stored energy between the sprinters and the nonathletes? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. ► View Available Hint(s) AU = μA Value N marrow_forward
- A spring loaded toy dart gun shoots a dart straight up in the air and the dart reaches a maximum height of 22.90 m. The same dart is shot straight up a second time but this time the spring is compressed only half as far. How far up in meters does the dart go this time neglecting friction? Write your answer to 2 decimals. Your Answer: Answerarrow_forwardIt's your birthday, and to celebrate you're going to make your first bungee jump. You stand on a bridge 105 m above a raging river and attach a 30-m-long bungee cord to your harness. A bungee cord, for practical purposes, is just a long spring, and this cord has a spring constant of 48 N/m. Assume that your mass is 70 kg. After a long hesitation, you step off the bridge.How far are you above the water when the cord reaches its maximum elongation?arrow_forwarda cannonball with a mass of 6.95 kg is placed in a vertical, spring-loaded cannon bearing a spring with a spring constant of 5.6 newtons/meter. The spring is compressed by a distance of 4.54 meters and released. Please use g=9.80 m/s2. The max height reached by the cannonball in meters is?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON