
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
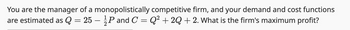
Transcribed Image Text:You are the manager of a monopolistically competitive firm, and your demand and cost functions
are estimated as Q = 25 - P and C = Q² +2Q + 2. What is the firm's maximum profit?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Hand written solutions are strictly prohibitedarrow_forwardPick the correct answer and explain in stepsarrow_forwardLe Jouet is a French firm, and it is the only seller of toy trains in France and Russia. Suppose that when the price of toy trains increases, Russian children more readily replace them with toy airplanes than French children. Thus, the demand for toy trains in Russia is more elastic than in France. The following graphs show the demand curves for toy trains in France (Dr) and Russia (DR) and marginal revenue curves in France (MRF) and Russia (MRR). Le Jouet's marginal cost of production (MC), depicted as the grey horizontal line in both graphs, is $12, and the resale of toy trains from Russia to France is prohibited. Assume there are no fixed costs in production, so marginal cost equals average total cost (ATC). PRICE (Dollars per toy train) 40 36 32 28 Total 24 20 16 12 8 4 0 Country France Russia France MR Price (Dollars per toy train) 20 20 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 QUANTITY (Millions of toy trains) N/A O True MC-ATC OF O False N/A (?) Single Price Quantity Sold (Millions of toy…arrow_forward
- A shoe store in a monopolistically competitive market has a demand curve for their shoes given by P = 81-0.5Q. The variable costs of producing a shoe are given by the equation VC = Q2 + 3Q and so the marginal costs are MC = 20 +3. a) What is the shoe store's profit - maximizing output and price? If the shoe store is in a long-run equilibrium, what must its fixed costs be?arrow_forwarda) Suppose that the two firms engage in Cournot competition. Find the equilibrium price PNE in the industry, the equilibrium outputs QANE and QBNE, as well as the profits πANE and πBNE, for each firm. b) Suppose the marginal cost for firm B increases from $20 to $140, while everything else remains unchanged. Find the new equilibrium price PNE in the industry, the new equilibrium outputs QANE and QBNE, as well as the new profits πANE and πBNE for each firm. c) Suppose that, in addition to the marginal cost increase from $20 to $140 from sub question b), firm B also has a fixed cost of $2500, out of which $2100 may be recouped if it shuts down; everything else remains unchanged. In this case, what will firm B’s optimal output be? (Justify your answer.) What will firm A’s profit be?arrow_forwardThere are two ice-cream parols on a beach. The dayly demand for ice-creams is given by Q = 3079 - 3p. The average variable cost of an ice-cream is 70, while the rent of the place is 966. How many ice-creams is the 'Leader' company selling if the two ice-cream stands operate as Stackelberg duopolists? (Please use 2 decimals in your answer.)arrow_forward
- Suppose that firm Alphabet is the only company that sells all-inclusive vacation packages in the UK. It faces two markets with demand curves given by P₁ = 200 - Q₁ and P₂ = 100-Q2. Assume that Alphabet's total cost function is C = 400 + 200 1) What is the market structure of the all-inclusive vacation packages in the UK? Is firm Alphabet a price taker or price maker? Explain. 2) If Alphabet can price discriminate and could tell which consumer belongs to which market before the purchase happens, what is the type of price discrimination that Alphabet is practising? Explain. Give another example of the same type of price discrimination. 3) If Alphabet can charge different prices at those two markets, what price should it charge in each market in order to maximise profits? What are the quantities it should produce in each market? 4) What if he cannot price discriminate? Then what price should he charge? What is the quantity produced?arrow_forwardThere are only two driveway paving companies in a small town, Asphalt, Inc. and Blacktop Bros. The inverse demand curve for paving services is ?= 2040 ―20? where quantity is measured in pave jobs per month and price is measured in dollars per job. Assume Asphalt, Inc. has a marginal cost of $100 per driveway and Blacktop Bros. has a marginal cost of $150. Answer the following questions: Determine each firm’s reaction curve and graph it. How many paving jobs will each firm produce in Cournot equilibrium? What will the market price of a pave job be? How much profit does each firm earn?arrow_forwardA firm in a monopolistically competitive market faces the following demand curve: Q(P)=2,223-57P Its total cost function is: TC(Q) = $ 15(Q) + $1208 Calculate the profit maximizing quantityarrow_forward
- please helparrow_forwardEric owns a plot of land in the desert that isn't worth much. One day, a giant meteorite falls on his property, making a large crater. The event attracts scientists and tourists, and Eric decides to sell nontransferable admission tickets to the meteor crater to both types of visitors: scientists (Market A) and tourists (Market B). The following graphs show daily demand (DD) curves and marginal revenue (MRMR) curves for the two markets. Eric's marginal cost of providing admission tickets is zero. PRICE (Dollars per ticket) 20 18 16 9 09 2 0 0 1 Market A MR 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 QUANTITY (Admission tickets) Pricing Policy Nondiscriminatory Discriminatory D 0 10 Total Revenue (Dollars) PRICE (Dollars per ticket) 20 18 18 14 12 10 8 4 2 0 0 1 low Market B Imagine that at first, Eric charges the same price of $8 per admission in both markets so that the total number of admissions demanded is Tickets. Imagine now that Eric decides to charge a different price in each market. To maximize revenue, Eric…arrow_forwardEconomics: Industrial Economics Question: In a market operating under quantity competition there are 2 firms (Cournot duopoly). The cost structure of firm 1 is given by C1(q1) = 675 + 60q1 + (q1)^2 and that of firm 2 is given by C2(q2) = 375 + 20 q2 + 5 (q2)^2. The inverse demand function is P = 300 - 2 Q1, where Q = q1 + q2. Define the profit maximization problem that every firm faces and solve for the respective best response functions. Use these (or the first order condition directly) to answer the following: 1. The Nash Equilibrium quantity produced by firm 1 q1* is Choices: A. 33.3 B. 38.3 C. 40 D. 35 2. The Nash Equilibrium quantity produced by firm 2 q2* is Choices: A. 15 B. 53.3 C. 20 D. 21.7 3. The Nash Equilibrium price is Choices: A. 126.7 B. 180 C. 200 D. 190 4. The Lerner Index for the market is closest to Choices: A. 0.29 B. 0.66 C. 0.43 D. 0.57 Thank you for your help and support Instructor Agent!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education