
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
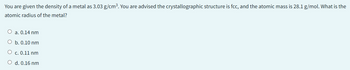
Transcribed Image Text:You are given the density of a metal as 3.03 g/cm³. You are advised the crystallographic structure is fcc, and the atomic mass is 28.1 g/mol. What is the
atomic radius of the metal?
O a. 0.14 nm
O b. 0.10 nm
O c. 0.11 nm
O d. 0.16 nm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 5- Question 5. Some hypothetical alloy is composed of 42.5 wt% of metal A and 57.5 wt% of metal B. If the densities of metals A and B are 4.35 and 6.27 g/cm3, respectively, whereas their respective atomic weights are 91.4 and 105.3 g/mol, determine whether the crystal structure for this alloy is simple cubic, face-centered cubic, or body-centered cubic. Assume a unit cell edge length of 0.395 nm.arrow_forwardI need help with the question in the picture below. the book refrenced is Materials Science and Engineering: An Introduction, 9e Thank you in advancearrow_forwardYou are given the density of a metal as 2.07 g/cm³. You are advised the crystallographic structure is fcc, and the atomic mass is 25.5 g/mol. What is the atomic radius of the metal? a. 0.15 nm b. 0.12 nm c. 0.11 nm d. 0.18 nmarrow_forward
- Copper is a typical face-centered-cubic metal. In its pure state, it has extremely high electrical conductivity. Oxygen in copper causes a major reduction of conductivity. To investigate this issue further, I want to you to tell me whether oxygen atoms substitute for copper atoms, or if they enter interstitial sites.arrow_forwardIron (Fe) has the Body-Centered Cubic (BCC) crystal structure. The edge length is a = 0.2864 nm. What is the linear density in (atoms/nm) along direction [011]? Select one: O a. 6.98 O b.7.48 Oc494 Od.349 O e 2.47arrow_forwardThe random arrangement of atoms in a structure is known as amorphous structure. Select one: True Falsearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY