
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
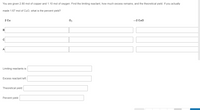
Transcribed Image Text:You are given 2.80 mol of copper and 1.10 mol of oxygen. Find the limiting reactant, how much excess remains, and the theoretical yield. If you actually
made 1.67 mol of Cuo, what is the percent yield?
2 Cu
O2
-2 Cuo
B
A
Limiting reactants is:
Excess reactant left:
Theoretical yield:
Percent yield:
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Combining 0.244 mol Fe, O, with excess carbon produced 16.0 g Fe. Fe,0, + 3 C 2 Fe + 3 CO What is the actual yield of iron in moles? actual yield: mol What is the theoretical yield of iron in moles? theoretical yield: mol What is the percent yield? percent yield: contact us helparrow_forward0 A reaction of 36.9 g of Na and 46.9 g of Br₂ yields 51.9 g of NaBr. What is the percent yield? 2 Na(s) + Br₂(g) - ->> 2 NaBr(s) percent yield:arrow_forwardCombining 0.333 mol Fe, O, with excess carbon produced 12.7 g Fe. Fe,0, + 3C → 2 Fe + 3 CO What is the actual yield of iron in moles? actual yield: mol What is the theoretical yield of iron in moles? theoretical yield: mol What is the percent yield? percent yield: %arrow_forward
- Part A Give the percent yield when 28.16 g of CO, are formed from the reaction of 4.000 moles of C3H18 with 4.000 moles of O2. 2 C3H18 + 25 O2→ 16 CO2 + 18 H20arrow_forwardCombining 0.376 mol Fe₂O3 with excess carbon produced 20.0 g Fe. Fe₂O3 + 3C2Fe + 3 CO What is the actual yield of iron in moles? actual yield: What is the theoretical yield of iron in moles? theoretical yield: What is the percent yield? percent yield: mol mol %arrow_forwardFor the following reaction, 5.68 grams of chlorine gas are mixed with excess phosphorus (P4) . The reaction yields 5.34 grams of phosphorus trichloride .phosphorus (P4) ( s ) + chlorine ( g ) phosphorus trichloride ( l ) What is the theoretical yield of phosphorus trichloride ? grams What is the percent yield for this reaction ? %arrow_forward
- 8. The combustion of glucose is represented by the following balanced equation: C H12O +6 0 6 H0+ 6 CO2. The reaction uses 1 gram of both CgH12Og and O2. What is the percent yield if 0.45 g of H,0 is produced? O a. 0.31% b. 0.558% c. 100% O d. 80% AM9 Litarrow_forwardIron oxide reacts with carbon to produce elemental iron and carbon monoxide according the the equation shown below. Consider the reaction of 51.4 grams of Fe2O3 with 24.98 grams of C to produce 19.20 grams of Fe. Fe2O3(s)+3c(s)-------2Fe(s)+3CO(g) a. actual yield b. theoretical yield c. percent yieldarrow_forwardIn the reaction below, 7.0 mol of NO and 5.0 mol of O2 are reacted together. The reaction generates 3.0 mol of NO2. What is the percent yield for the reaction? 2NO (g) +O2 (g)2NO2 (g)arrow_forward
- Combining 0.349 mol Fe,O, with excess carbon produced 17.9 g Fe. Fe, 0, + 3C 2 Fe + 3 CO What is the actual yield of iron in moles? actual yield: mol What is the theoretical yield of iron in moles?arrow_forwardSodium and chlorine react to form sodium chloride: What is the theoretical yield of sodium chloride for the reaction of 32.0 g Na with 107.2 g Cl2? A. 1.40 x 104 g NaCl B. 35.4 g NaCl C. 122 g NaCl D. 81.2 g NaClarrow_forwardMass of product (g) 3.516 Theoretical yield (g) Product percent yieldarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY