
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
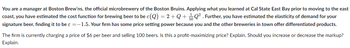
Transcribed Image Text:You are a manager at Boston Brew'ns, the official microbrewery of the Boston Bruins. Applying what you learned at Cal State East Bay prior to moving to the east
coast, you have estimated the cost function for brewing beer to be c(Q) = 2+Q+Q². Further, you have estimated the elasticity of demand for your
signature beer, finding it to be ε =-1.5. Your firm has some price setting power because you and the other breweries in town offer differentiated products.
The firm is currently charging a price of $6 per beer and selling 100 beers. Is this a profit-maximizing price? Explain. Should you increase or decrease the markup?
Explain.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A noncompetitive firm has the following total cost function: TC = 3Q³ – 40Q² + 250Q + 900 If the demand function for the firm's product is P = 2000 – 40Q. Find the firm's profit maximizing level of output and profit.arrow_forwardA firm's demand and total cost function are given by the expression: P = 20 - Q/2 (1) TC = 0.5Q2 + 36 (2) Where P is price per unit in £ TC = total cost in £ Q is quantity demanded and produced. Find the profit-maximising level of output using the profit function and calculate how much profit is made at this output level.arrow_forwardConsider the following cost function: Total Cost = 50+5Q^3 and demand curve Price= 5000-275*Q Given these functions, what would be the profit maximizing output?arrow_forward
- A fried chicken franchise finds that the demand equation for its new roast chicken product, "Roasted Rooster," is given by 40 p0.6 where p is the price (in dollars) per quarter-chicken serving and q is the number of quarter-chicken servings that can be sold per hour at this price. Find E(p) E(p) = q= X Find the price elasticity of demand when the price is set at $3.70 per serving. At a price of $3.70, a 1% increase in price leads to a Interpret the result. At a price of $3.70, the demand is elastic They should raise X% decrease in demand. ✓X the price per serving in order to increase revenue.arrow_forwardSuppose that the inverse demand for aloe juice in Greece is given by P = 100 – 2Q, where P is the price per bottle (1000ml) of aloe juice and Q is the total quantity, i.e., number of bottles, supplied in the market. There are two aloe juice manufacturers in Greece, Aloe Health and Aloe Wealth, operating under similar cost conditions. Each manufacturer's cost function is C(q) = 4qi, i =1,2, where q¡ is the manufacturer's individual quantity produced and Q = qı + q2. (a) Based on demand conditions every year, they decide, independently of each other, the quantity of aloe juice that will be supplied, letting the market determine the price per bottle. Find the equilibrium price and each firm's profit in this market. %3D (b) Consider that the above two manufacturers form a cartel, agreeing to fix their total quantity in such a way that the market maintains a collusive price. For simplicity, the eventual cartel directory will determine the target total-quantity and price pair, and each firm…arrow_forwardPlease solve this problem? THANK YOUarrow_forward
- The Poster Bed Company believes that its industry can best be classified as monopolistically competitive. An analysis of the demand for its canopy bed has resulted in the following estimated demand function for the bed: P = 1,265-9Q The cost analysis department has estimated the total cost function for the poster bed as TC = -15Q3 +5Q +24,000 Short-run profits are maximized when the level of output is The total profit at this price-output level is The point price elasticity of demand at the profit-maximizing level of output is The level of fixed costs the firm is experiencing on its bed production is What is the impact of a $5,000 increase in the level of fixed costs on the price charged, output produced, and profit generated? Price Charged Output Produced Profits Generated Increase No change Decrease O O and the price is $ O Oarrow_forwardTasty Inc. sells table salt to both retail grocery chains and commercial users (e.g., bakeries, snack food makers, etc.). The demand function for each of these markets is: Retail grocery chains: P1 = 180 − 8Q1 Commercial users: P2 = 100 − 4Q2 where P1 and P2 are the prices charged and Q1 and Q2 are the quantities sold in the respective markets. Tasty's total cost function (which includes a "normal" return to the owners) for salt is: TC = 50 + 20(Q1 + Q2) (a) Determine Tasty's total profit function. (b) Assuming that Tasty Inc. is effectively able to charge different prices in the two markets, what are the profit-maximizing price and output levels for the product in the two markets? What is Tasty's total profit under this condition?arrow_forwardSuppose a manager is faced with the following demand curve for a new software application in a monopoly market, Q = 200 - 50P and the short run total cost function is TC = 2Q + Q2 / 30 If the manager is able to maximize the firms' profit in this monopoly market, what is the total profit value?arrow_forward
- Firms in a competitive market can sell as much as they like at a market price of $16. The cost function for each firm is TC = 50 + 4Q +2Q². The associated marginal cost function is MC = 4 + 4Q and the point of minimum average cost is Q = 5. How much profit is each firm earning?arrow_forwardIf the inverse demand function is P=10-Q and total cost is C=2Q, what is the optimal fixed cost to be charged in a two part pricing ?arrow_forwardA firm produces two substitute goods . Their demand curves and total cost function are given below : P1 = 130 - 4Q1-Q 2 P2 = 160-2Q1-5Q2 TC = 2Q1 +2Q1Q2 + 4Q 2 ( a ) Determine the profit maximizing outputs of both goods . ( Restrict your answers to 2 decimal points ) ( b ) Find the price elasticity of demand . ( c ) Evaluate the second order " Hessian " required for profit to be maximized .arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education