
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Determine the radius of gyration kx of the paraboloid. The density of the material is ρ = 5 Mg/m3.
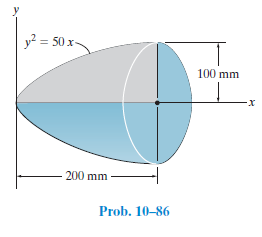
Transcribed Image Text:y? = 50 x-
100 mm
200 mm
Prob. 10-86
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Describe the basic properties of Montmorillonite.arrow_forwardDescribe the basic properties of Halloysite.arrow_forwardIf it is constrained between two supports A and B and is stress-free at 20 ℃, what would be the stress in the two materials when it is heated to 70 ℃, For Steel: Es = 210 GPa, Coefficient of expansion = 12x10^6/℃. For Brass: Eb = 105 GPa, Coefficient of expansion = 19x10^-6/℃arrow_forward
- Determine the exact total hardness in units of mg/L as CaC03.Ba2+ contributes to hardness as wellarrow_forwardA uniform edge load of w₁ = 540 lb/in. and W2 = 400 lb/in. is applied to the polystyrene specimen. Ep = 597 (10³) psi and vp = 0.25. (Figure 1) Figure T W₂ b - < 1 of 1arrow_forwardQuestion 3 For a 40 wt% Sn-60 wt% Pb alloy at 150 °C and taking the densities of Pb and Sn at 150 °C to be 11.23 and 7.24 g/cm?, respectively. Composition Cats Sn) 20 60 100 327C 600 300 Liquid 500 232'C 200 400 183°C 18.3 61.9 97.8 300 100 200 100 60 80 100 (Pb) Composition (wt% Sn) (Sn) The lead-tin phase diagram a) AN6 marks b) W c) calculate raction. CROmarks d) calculate the relative amount of each phase present in terms of mass fraction volume fraction Temperature ("C) Temperature (F)arrow_forward
- i need the answer quicklyarrow_forwardQ1/ Consider the brass alloy for which the stress-strain behavior is shown in the figure below. A cylindrical specimen of this material 10.0 mm in diameter and 101.6 mm long is pulled in tension with a force of 10,000 N. If it is known that this alloy has a value for Poisson's ratio of 0.35, compute (a) the specimen elongation, and (b) the reduction in specimen diameter. 500 70 Tensile strength 450 MPa (65,000 psi) 60 400 50 10 psi 300 MPa 40 40 30 200 Yield strength 30 200 250 MPa (36,000 psi) 20 100 20 10 100 10 0.005 0.10 0.20 0.30 0.40 Strain Stress (MPa) Stress (10 psi)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning