
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781133939146
Author: Katz, Debora M.
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Please circle answer and this is for homework
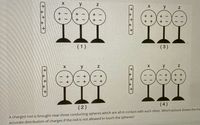
Transcribed Image Text:y
+ +
+ +
III
(1)
(3)
X
y
+ +
+ +
III
III
(2)
(4)
A charged rod is brought near three conducting spheres which are all in contact with each other. Which picture shows the mc
accurate distribution of charges if the rod is not allowed to touch the spheres?
(++ ++ +
+
+ +
+ + + + +
+ + + + +)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A sphere has a net charge of 8.05 nC, and a negatively charged rod has a charge of 6.03 nC. The sphere and rod undergo a process such that 5.00 109 electrons are transferred from the rod to the sphere. What are the charges of the sphere and the rod after this process?arrow_forwardThree identical conducting spheres are fixed along a single line. The middle sphere is equidistant from the other two so that the center-to-center distance between the middle sphere and either of the other two is 0.125 m. Initially, only the middle sphere is charged, with qmiddle = +35.6 nC. The middle sphere is later connected by a conducting wire to the sphere on the left. The wire is removed and then used to connect the middle sphere to the sphere on the right. The wire is again removed. a. C What is the charge on each sphere? b. C Which sphere experiences the greatest electrostatic force? c. N What is the magnitude of that force?arrow_forward(a) Calculate the number of electrons in a small, electrically neutral silver pin that has a mass of 10.0 g. Silver has 47 electrons per atom, and its molar mass is 107.87 g/mol. (b) Imagine adding electrons to the pin until the negative charge has the very large value 1.00 mC. How many electrons are added for every 109 electrons already present?arrow_forward
- Review. Two insulating spheres have radii 0.300 cm and 0.500 cm, masses 0.100 kg and 0.700 kg, and uniformly distributed charges 2.00 C and 3.00 C. They are released from rest when their centers are separated by 1.00 m. (a) How fast will each be moving when they collide? (b) What If? If the spheres were conductors, would the speeds be greater or less than those calculated in part (a)? Explain.arrow_forward(i) A metallic sphere A of radius 1.00 cm is several centimeters away from a metallic spherical shell B of radius 2.00 cm. Charge 450 nC is placed on A, with no charge on B or anywhere nearby. Next, the two objects are joined by a long, thin, metallic wire (as shown in Fig. 25.19), and finally the wire is removed. How is the charge shared between A and B? (a) 0 on A. 450 nC on B (b) 90.0 nC on A and 360 nC on B, with equal surface charge densities (c) 150 nC on A and 300 nC on B (d) 225 nC on A and 225 nC on B (e) 450 nC on A and 0 on B (ii) A metallic sphere A of radius 1 cm with charge 450 nC hangs on an insulating thread inside an uncharged thin metallic spherical shell B of radius 2 cm. Next, A is made temporarily to touch the inner surface of B. How is the charge then shared between them? Choose from the same possibilities. Arnold Arons, the only physics teacher yet to have his picture on the cover ol Time magazine, suggested the idea for this question.arrow_forwardProblems 72, 73, and 74 are grouped. 72. A Figure P26.72 shows a source consisting of two identical parallel disks of radius R. The x axis runs through the center of each disk. Each disk carries an excess charge uniformly distributed on its surface. The disk on the left has a total positive charge Q, and the disk on the right has a total negative charge Q. The distance between the disks is 3R, and point A is 2R from the positively charged disk. Find an expression for the electric potential at point A between the disks on the x axis. Approximate any square roots to three significant figures. FIGURE P26.72 Problems 72, 73, and 74.arrow_forward
- Figure 18.47 shows the electric field lines near two charges q j and g2. What is the ratio of their magnitudes? (b) Sketch the electric field lines a long distance from the charges shown in the figure.arrow_forwardA proton is fired from very far away directly at a fixed particle with charge q = 1.28 1018 C. If the initial speed of the proton is 2.4 105 m/s, what is its distance of closest approach to the fixed particle? The mass of a proton is 1.67 1027 kg.arrow_forwardA proton and an alpha particle (charge = 2e, mass = 6.64 1027 kg) are initially at rest, separated by 4.00 1015 m. (a) If they are both released simultaneously, explain why you cant find their velocities at infinity using only conservation of energy. (b) What other conservation law can be applied in this case? (c) Find the speeds of the proton and alpha particle, respectively, at infinity.arrow_forward
- a. In Figure 23.8, why are there three plus signs on the red rod and three minus signs on the red cloth? b. Which object in Figure 23.8 has the greatest positive charge? How do you know?arrow_forward(a) Find the magnitude and direction of the electric field at the position of the 2.00 C charge in Figure P13.13. (b) How would the electric field at that point be affected if the charge there were doubled? Would the magnitude of the electric force be affected?arrow_forwardAn electron with a speed of 3.00 106 m/s moves into a uniform electric field of magnitude 1.00 103 N/C. The field lines are parallel to the electrons velocity and pointing in the same direction as the velocity. How far does the electron travel before it is brought to rest? (a) 2.56 cm (b) 5.12 cm (c) 11.2 cm (d) 3.34 m (e) 4.24 marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College