
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:X
101 Chem 101
bAnswered: Write a balanced X
G how many kilograms are in X
(71) Tyler DeWitt - YouTube
(71) Converting Between Gr
G how many grams are in a lit X
X
x
app.101edu.co
Submit
Question 1 of 47
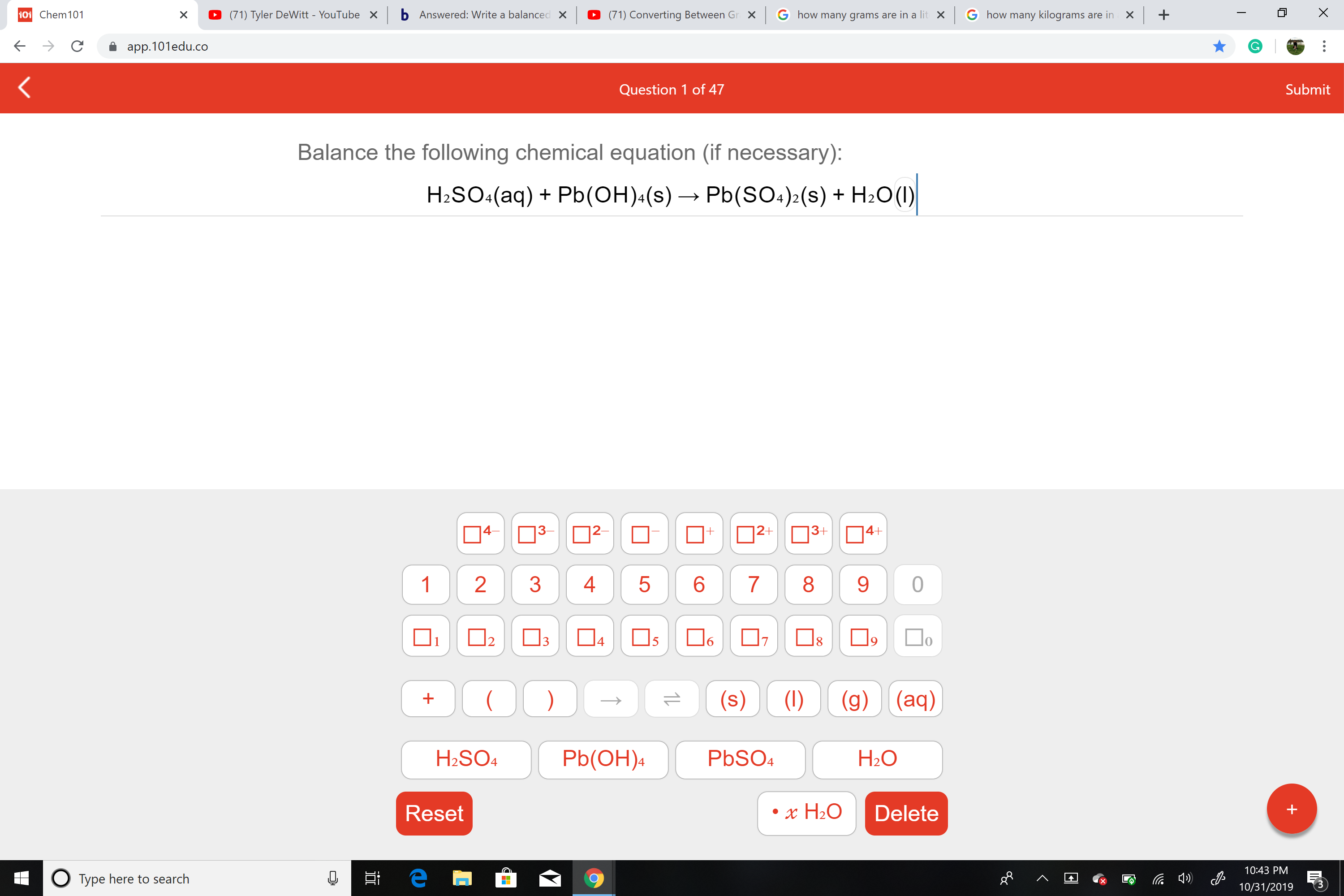
Balance the following chemical equation (if necessary):
-
Pb(SO4)2(s) H2O(I)
H2SO4(aq)Pb(OH)(s)
3
4-
|2+
|3+
|4+
1
2
5
6
7
8
9
0
19
17
2
4
6
(s)
(g) (aq)
(1)
PbSO4
H2SO4
Н.О
РЫ(ОН).
Reset
Delete
x H20
10:43 PM
е
OTYPE here to search
10/31/2019
LO
3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 8, The coefficients in the balanced equation below are respectfully:_____NO3-(aq) + _____In+(aq) +_______H+(aq) => ______NO(g) + ______In3+(aq) + _____H2O(l)NO3-(aq), NO(g) [ Select ] ["8", "2", "3", "1", "4"] In+(aq) , In3+(aq) [ Select ] ["3", "5", "1", "2", "4"] H+(aq) [ Select ] ["2", "8", "4", "12", "6"] H2O(l) [ Select ] ["2", "8", "6", "1", "4"]arrow_forwardBacl 2 + CuSo4 》〉》 BaSo4 + CuCl2 find net ionic equationarrow_forwardRemaining Time: 1 hour, 01 minute, 47 seconds. * Question Completion Status: QUESTION 2 The number of water molecules in 2.3 mg of water is O 6.02 x 1023 O 77.0 x 1023 O 7.7 x 1023 O 7.7 x 1019 none of the above QUESTION 3 A ctudent makes a colution bu discolvina 254a ofNDOH int0 450 gof water Wh. Click Save and Submit to save and submit. Click Save All Answers to save all answer ere to search DELLarrow_forward
- What would be the correct products to complete the total ionic equation given below: Zn2+ (aq) + 2CIO (aq) + 2H* (aq) + S²- (aq) --> ? The following notation is used in the answers given: Chemical Answer symbol notation Zn2+ Zn^2+ CIO CIO^- H* H^+ S2- S^2- ZnS (s) + 2CIO^- (aq) + 2H^+ (aq) Zn^2+ (aq) + 2HCIO (s) + S^2- (aq) Zn^2+ (aq) + 2CIO^- (aq) + 2H^+ (aq) + S^2- (aq) Zn(CIO)2 (aq) + H2S (aq)arrow_forwardplease answer questionarrow_forwardWhat is the molarity of the H4C10H12N2O8 (aq) sample? Round to correct sig figs.arrow_forward
- Consider the following (fictional) reaction: 2A (s) + B2(g) 2AB (s) AH=-350.0 k) Given: Compound: Formula Mass (g/mol) 25.00 B2 75.00 AB 62.50 What is AH (in k) when 1.00 g A reacts with excess B2? Upload a pictarrow_forwardvo Chem101 Question 1 of 10 Balance the following chemical equation (if necessary): Ca(C:H,O2)2(aq) + Na:CO:(aq) → Ca CO.(s) + NaC2H.O>(aq) 04 1 4 6. 7 8 Os (s) (1) (g) (aq) CaCO, NaC:H.O2 Ca(C.H.O:) Na:COs x H:O Delete Resetarrow_forwardHow will the following sitations affect the final calculation of the molarity of HC2H3O2? An air bubble was present in the tip of the buret when making the intial volume reading, but not when making the final volume reading. After the standardization of the NaOH solution using solid H2C2O4 * 2H2O, the molar mass of anhydrous oxalic acid was used to calculate the molarity of the NaOH solution.arrow_forward
- Need thesearrow_forwardHow many liters of a 2.00 M solution of sodium chloride are needed to have 1.00 g of radium chloride if the GFW is 58.44 g ? We must first convert 1.00 g into moles so that we can use the concentration To calculate the moles we cancel out liters Blank 1. Fill in the blank, read surrounding text. mol ( Blank 2. Fill in the blank, read surrounding text. g)(–––––––––––––––––––––––) = Blank 3. Fill in the blank, read surrounding text. mol Blank 4. Fill in the blank, read surrounding text. g Then we convert moles into liters using Blank 5. Fill in the blank, read surrounding text. as a conversion factor Blank 6. Fill in the blank, read surrounding text. L ( Blank 7. Fill in the blank, read surrounding text. mol)(–––––––––––––––––––––––) = Blank 8. Fill in the blank, read surrounding text. L…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY