
Calculus: Early Transcendentals
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781285741550
Author: James Stewart
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
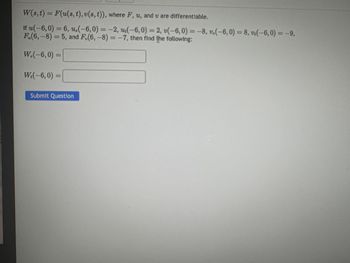
Transcribed Image Text:W(s, t) = F(u(s, t), v(s, t)), where F, u, and u are differentiable.
If u(-6,0) = 6, u,(-6,0) = -2, u(-6,0) = 2, v(-6,0) = -8, v.(-6,0) = 8, v(-6,0) = -9,
F.(6,-8)= 5, and F.(6,-8)= -7, then find the following:
W.(-6,0) =
W₁(-6,0) =
Submit Question
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- W(s, t) = F(u(s, t), v(s, t)), where F. u. and v are differentiable. If u (6,-6)= -2, u,(6, −6) = 3, ut(6, −6) = 6, v(6, −6) = −7. v,(6, −6) = −4, vr(6, −6) = −6, Fu(-2,-7)=8, and F(-2,-7)=-5, then find the following: W,(6,-6) W₂(6, -6)arrow_forwardLet R(s, t) = G(u(s, t), v(s, t)), where G, u, and v are differentiable, and the following applies. u(-9, 5) = -2 v(-9, 5) Vs(-9, 5) V(-9, 5) G,(-2, 3) : 3 Us(-9, 5) = 6 -4 = -1 = 4 G,(-2, 3) (s '6–)'n = -6 = -7 Find R,(-9, 5) and R,(-9, 5). R(-9, 5) R;(-9, 5) Need Heln? Read Itarrow_forwardLet W(s, t) = F(u(s, t), v(s, t)), where F, u, and v are differentiable, and the following applies. u(3,-2) = -6 us(3,-2) = 4 u(3,-2) = -7 Fu(-6, -4) = 0 v(3,-2) = -4 Vs(3,-2) = 9 v(3,-2) = 1 F(-6, -4) = 7 Find We(3,-2) and We(3,-2). Ws(3,-2) = W+(3,-2) =arrow_forward
- Find the value of fr and fy at (1, -1) when 4 f(x,y) +5x² + 3y². ry - f= = 9, f (1,-1) 3. 2. fa f- _ = - 6, f fa | fa | ,-1) 5. f = -7 = : 2 ,-1) 1 = 14, fv -1 = 4. : 1- = - 6,1 ,-1) 1,-1) = -10 = -10 = 14, 1 5 -1 = 2arrow_forwardIf u=(2,4)�=(2,4) and v=(3,−4)�=(3,−4) then proju(v)≈arrow_forwardVx (-y +2,22 +323, 2233) =? 0 (3y -3222, 223, -2 + 2) 0 (-3y +3X372, -332, 1 + 2x) 0 (2y +2224-423,1 + 22) 0 (-34-3222, 42,1 +22) 0 (-3y +322y2, -3'2, 1 + 2)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:9781285741550
Author:James Stewart
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:9780134438986
Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:9780134763644
Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:9781319050740
Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert Franzosa
Publisher:W. H. Freeman


Calculus: Early Transcendental Functions
Calculus
ISBN:9781337552516
Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. Edwards
Publisher:Cengage Learning