
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
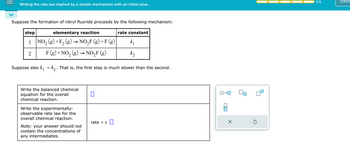
Transcribed Image Text:Writing the rate law implied by a simple mechanism with an initial slow...
Suppose the formation of nitryl fluoride proceeds by the following mechanism:
step
elementary reaction
1 NO₂(g) + F₂ (g) → NO₂F (g) + F(g)
2
2
F (g) + NO₂ (g) → NO₂F (g)
Suppose also k₁ « k₂ . That is, the first step is much slower than the se nd.
Write the balanced chemical
equation for the overall
chemical reaction.
Write the experimentally-
observable rate law for the
overall chemical reaction.
Note: your answer should not
contain the concentrations of
any intermediates.
0
rate = k
rate constant
k₁
k₂
ロ→ロ
00
X
Ś
0/5
Izabe
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose the decomposition of dinitrogen monoxide proceeds by the following mechanism: step elementary reaction rate constant N,0 (g) → N, (g) +0 (g) k1 1 2 N,0 (g)+0 (g) → N, (g) + 0, (g) k2 Suppose also k, « k,. That is, the first step is much slower than the second. Write the balanced chemical ローロ equation for the overall chemical reaction. Write the experimentally- observable rate law for the overall chemical reaction. rate = k ] Note: your answer should not contain the concentrations of any intermediates. Continue ©2021 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rightsarrow_forwardThe rate constant for this first‑order reaction is 0.0130 s−1 at 400 ∘C. A⟶products After how many seconds will 11.1% of the reactant remain?arrow_forwardGiven a reaction vessel of 0.361 M C4H8(g) which obeys first order kinetics and has a half-life of 1842.9 seconds, What is the concentration of C4H8(g) after 1542.0 seconds. Enter your answer here: Marrow_forward
- Suppose the reduction of nitric oxide proceeds by the following mechanism: step elementary reaction rate constant 1 H, (g) + 2NO (g) → N,0 (g)+ H,0 (g) k1 H, (g) + N,0 (g) → N2 (g) + H20 (g) k2 Suppose also k, « k,. That is, the first step is much slower than the second. Write the balanced chemical equation for the overall chemical reaction. Write the experimentally- observable rate law for the overall chemical reaction. rate = k|| Note: your answer should not contain the concentrations of any intermediates.arrow_forwardThe rate constant for this second‑order reaction is 0.630 M−1⋅s−1at 300 ∘C. A⟶products How long, in seconds, would it take for the concentration of A to decrease from 0.920 M to 0.290 M? t= ? sarrow_forwardX, + Y2 - X,Y2 rate = K[X,] A reaction and its experimentally determined rate law are represented above. A chemist proposes two different possible mechanisms for the reaction, which are given below. Mechanism 1 X, - 2 X (slow) X + Y, - XY, (fast) Mechanism 2 X, -- 2 X (slow) X + Y2 + XY + Y (fast) X + XY, - X,Y, (fast) X+ XY -- X,Y (fast) X,Y + Y → X,Y, (fast) Based on the information above, which of the following is true? Both mechanism 1 and mechanism 2 are consistent with the rate law. Only mechanism 2 is consistent with the rate law. Only mechanism 1 is consistent with the rate law. Neither mechanism 1 nor mechanism 2 is consistent with the rate law.arrow_forward
- Suppose the formation of iodine proceeds by the following mechanism: step elementary reaction 1 H₂(g) + IC1 (g) → HI(g) + HC1 (g) k₁ 2 HI (g) + IC1 (g) → I₂ (g) + HCl (g) k₂ Suppose also k₁ « k₂. That is, the first step is much slower than the second. Write the balanced chemical equation for the overall chemical reaction. Write the experimentally- observable rate law for the overall chemical reaction. Note: your answer should not contain the concentrations of any intermediates. 0 rate = k rate constantarrow_forwardThe generic reaction 2 A → products follows zero-order kinetics with a rate constant of 0.00628 M/s. What is the half-life of substance A if its original concentration is 2.23 M? Be sure to enter a unit with the answer.arrow_forwardInitialte data a centain empera - fat rafe tuse is given in He table forr the the fable for the followingreactim. Determine the pate constont, Ko नाप the value and emits ofarrow_forward
- The rate constant for this first‑order reaction is 0.0210 s−1 at 400 ∘C. A⟶products After how many seconds will 22.9% of the reactant remain?arrow_forwardDirection:Express the rate of the following chemical reactions in terms of the change in concentration of the reactants or products. 1.2NO2(g)→N2 (g)+ 202 (g) 2.N2 (g)+ 3H2 (g)→2NH3 (g) 3.2C4H10 (g)+ 1302 (g)→8CO2 (g)+ 10H2O(g)arrow_forwardAt a certain temperature the rate of this reaction is second order in ClCH2CH2Cl with a rate constant of ·0.0543M−1s−1: →ClCH2CH2Clg+CH2CHClgHClg Suppose a vessel contains ClCH2CH2Cl at a concentration of 0.710M. Calculate the concentration of ClCH2CH2Cl in the vessel 210. seconds later. You may assume no other reaction is important. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. =___Marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY