
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
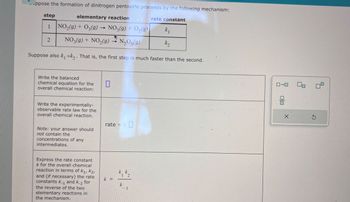
Transcribed Image Text:-ppose the formation of dinitrogen pentoxide proceeds by the following mechanism:
elementary reaction
NO2(g) + O3(g) → NO3(g) + O2(9)
step
1
2
NO3(g) + NO2(9)
N2O5(9)
rate constant
k₁
k₂
Suppose also k₁ »k. That is, the first step is much faster than the second.
Write the balanced
chemical equation for the
overall chemical reaction:
Write the experimentally-
observable rate law for the
overall chemical reaction.
Note: your answer should
not contain the
concentrations of any
intermediates.
☐
rate = k ☐
Express the rate constant
k for the overall chemical
reaction in terms of K1, K2,
and (if necessary) the rate
constants k-1 and k-2 for
the reverse of the two
elementary reactions in
the mechanism.
k =
k₁k₁₂
12
k
1
ローロ
G
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 13 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Nitrogen and hydrogen react to form ammonia, like this: N,(9)+3H,(0) 2 NH,(9) Imagine 117. mmol of NH, are added to an empty flask, and then answer the following questions. O Zero. What is the rate of the reverse reaction before any NH, has been added to the flask? O Greater than zero, but less than the rate of the forward reaction. O Greater than zero, and equal to the rate of the forward reaction. O Greater than zero, and greater than the rabe of the forward reaction. O Zero. What is the rate of the reverse reaction just after the NH, has been added to the flask? O Greater than zero, but less than the rabte of the forward reaction. O Greater than zero, and equal to the rate of the forward reaction. O Greater than zero, and greater than the rate of the forward reaction O Zero. O Greater than zero, but less than the rate of the forward reaction. What is the rate of the reverse reaction at equilibrium? O Greater than zero, and equal to the rate of the forward reaction. O Greater than…arrow_forwardA reaction involves the following elementary steps:H2(g)+O2(g)---->H2O2(g)H2(g)+H2O2(g)----->2H2O(g) What is the net reaction when reactive intermediates are canceled? Please include states of matter.arrow_forwardA proposed mechanism for a reaction is: NO + NO -> N2O2 N2O2 + O2 -> 2NO2 a) What is the overall balanced chemical equation for the reaction? b) WHat are the intermediates in the proposed reaction mechanism? c) The rate law equation was determined to be: rate= k[NO(g)]. Is this mechanism plausible? Explain why or why not. If this mechanism is correct, which is the rate-determining step?arrow_forward
- At 40°C, H₂O₂ (aq) will decompose according to the following reaction: 2H₂O₂ (aq) → 2H₂O(l) + O₂(g) The following data were collected for the concentration of H₂O2 at various times. Time (s) [H₂O₂] (mol/L) 0 2.45 x 10¹ 4.90 x 10¹ 1.000 0.456 0.208 a. Calculate the average rate of decomposition of H₂O₂ between 0 and 2.45 x 10¹ s. Average rate= mol/L s Use this rate to calculate the average rate of production of O2 (g) over the same time period. Average rate= mol/L s b. What are these rates for the time period 2.45 x 10¹ s to 4.90 × 10¹ s? Rate of H₂O₂ decomposition= Rate of O₂ production a mol/L s mol/L sarrow_forwardConsider the Following unbalanced Reaction: H2S + 02 - SO2 + H20 If sulfur dioxide is being formed at a rate of 1.2 mol L s', what are the rates of disappearance of oxygen? O 0.45 mol L-1s1 O 0.3 mol L1s-1 O 1.8 mol L-1s1 O 0.6 mol L-1 s-1 O 0.9 mol L-1s-1arrow_forwardPlease answer in tipping format with explanationarrow_forward
- The oxidation of ammonia produces nitrogen and water via the following reaction: 4NH3(g) + 302(g) → 2N2(g) + 6H2O() Suppose the rate of formation of H,0() is 3.0 mol/(L • s). Which of the following statements is true? The rate of consumption of NH3 is 2.0 mol/(L • s). O The rate of consumption of O2 is 2.0 mol/(L• s). The rate of formation of N2 is 1.3 mol/(L s). The rate of formation of N, is 2.0 mol/(L• s). The rate of consumption of NH3 is 0.50 mol/(L • ).arrow_forward11. The elementary steps for the catalyzed decomposition of dinitrogen monoxide are shown below. Step 1: N20(g) + NO(g) → N2(g) + NO2(g) (slow) Step 2: NO2(g) → NO(g) + 1/2 O2(g) (fast) Which of the following statements is/are CORRECT? The overall balanced reaction is N20(g) → N2(g) + 1/2 O2(g). 2. NO2(g) is a catalyst for the reaction. 3. NO(g) is a reaction intermediate. 1. a) 1 only c) 3 only d) 1 and 3 e) 1, 2, and 3 f) none of the above b) 2 onlyarrow_forwardSulfuric acid is an important industrial acid used in making chemicals, refining ores, and processing wastewater. The final step in the production of sulfuric acid involves the following reaction: H2S,07(aq) + H2O() → 2H,SO,(aq) Using your knowledge collision theory and the factors that affect the rate of a reaction, describe 3 ways that the rate of this reaction can be increased to produce more sulfuric acid. Include specific reasons why it would increase. (A:3)arrow_forward
- 13.53arrow_forwardThe decomposition of N₂O, can be described by the equation 2N₂O5(soln) -> - →→→ 4NO₂ (soln) + O₂(g) Consider the data in the table for the reaction at 45 °C in carbon tetrachloride solution. t (s) 0 225 556 755 average rate of reaction: PRE average rate of reaction: [N₂O,] (M) Given the data, calculate the average rate of reaction for each successive time interval. What is the average rate of reaction for the time interval from 0 s to 225 s? average rate of reaction: 2.381 2.067 What is the average rate of reaction for the time interval from 225 s to 556 s? TOOLS 1.678 1.481 What is the average rate of reaction for the time interval from 556 s to 755 s? a M/s M/S M/s Rese Question Sou 994arrow_forwardFor the reaction: 4NH3 (g) + 7O2 (g) → 4NO2 (g) + 6H2 (g), if H2 is produced at a rate of 3.5 x 10-3 M/s, O2 is consumed at a rate of... A. -2.5 x 10-2 M/s B. -4.1 x 10-3 M/s C. -2.1 x 10-2 M/s D. -3.0 x 10-3 M/s E. -5.8 x 10-4 M/sarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY