
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edition)
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780133594140
Author: James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
i |JI|) e lul o LA um;m LIk M( e function and queue is used
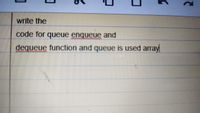
Transcribed Image Text:write the
code for queue enqueue and
dequeue function and queue is used array
2.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- [] [] partite_sets In the cell below, you are to write a function "partite_sets (graph)" that takes in a BIPARTITE graph as its input, and then returns a single list whose two entries are the partite sets of the graph as lists (the order of the sets outputed does not matter). After compiling the above cell, you should be able to compile the following cell and obtain the desired outputs. print (partite_sets({"A" : ["B", "C"], "B" : partite_sets({"A" : ["B", "C"], "B" : ["A"], "C" : ["A"]}), ["A", "D"], "C" : ["A", "D"], "D" : ["B", "C"]})) This should return [["B","C"], ["A"]] [["A","D"], ["B","C"]] (the order in which the entries appear does not matter) Python Pythonarrow_forward4) Recursive Analysis Homework • Unanswered The following algorithm takes an unsorted list of positive integers, along with two integers a and y. It returns the largest number, z, in the list such that either 2* = y or z9 = x is true. It returns 0 if no such z exists. The algorithm assumes that the list size, n, is a power of 2 with n > 1. 1 : integer xyMax(x, y, {a0,a1, ..., an-1}) 2 : if n == 1 3 : if (að у) or (až x) 4 return ao 5 : else 6 : return 0 7 : 8 : # process the left half 9 : 10 : m1 = xyMax(x,y,{a0,..., a4 J-1}) 11 : 12 : # process the right half 13 : m2 = xyMax(x,y,{a ;,.., an-1}) 14 : 15 : 16 : # find the largest 17 : 18 : max %3D тi 19 : if (m2 > max) 20 : 21 : 22 : max %3D тg return max 23 : end xyMax What is the recurrence relation that counts the number of comparisons for this algorithm? (The critical steps are at lines 2, 3, and 19.) What is a good big-O reference function for algorithm xyMax? (Hint: Which Master Theorem applies here?)arrow_forwardstruct insert_at_back_of_sll { // Function takes a constant Book as a parameter, inserts that book at the // back of a singly linked list, and returns nothing. void operator()(const Book& book) { /// TO-DO (3) /// // Write the lines of code to insert "book" at the back of "my_sll". Since // the SLL has no size() function and no tail pointer, you must walk the // list looking for the last node. // // HINT: Do not attempt to insert after "my_sll.end()". // ///// END-T0-DO (3) ||||// } std::forward_list& my_sll; };arrow_forward
- C++ Consider the following function as a property of a LinkedBag that contains a Doubly Linked List. Assume a Node has pointers prev and next, which can be read and changed with the standard get and set methods. Assume that the doubly linked list is: 1 <--> 2 <--> 3 <--> 4 <--> 5 <-->6 If you are uncertain what the above diagram depicts, it is a doubly linked list such that: The head of this doubly linked list is the node that contains the value 1. The tail of this doubly linked list is the node that contains the value 6. The 3rd node in this list contains the value 3. The contents of this list are the values 1 through 6 in sequential order. The following questions are regarding the linked list after after the test_function is run. A. The head of the list after the test_function is run contains the value: B. The tail of the list after the test_function is run contains the value: C. The 3rd node in the list after the test_function is run…arrow_forwardWrite a user defined function named as “length_list” function that finds the length of a list of list_node_t nodes. This code should fit with the following code.Partial Code: #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> /* gives access to malloc */ #define SENT -1 typedef struct list_node_s { int digit; struct list_node_s *restp; } list_node_t; list_node_t *get_list(void); int main(void) { list_node_t *x;int y; x=get_list(); printf("%d\n",x->digit); printf("%d\n",x->restp->digit); printf("%d\n",x->restp->restp->digit); // your length_list function should be called from here printf("Length is: %d",y); } /* * Forms a linked list of an input list of integers * terminated by SENT */ list_node_t * get_list(void) { int data; list_node_t *ansp; [20]scanf("%d", &data); if (data == SENT) { ansp = NULL; } else { ansp = (list_node_t *)malloc(sizeof (list_node_t)); ansp->digit = data; ansp->restp = get_list(); } return (ansp);arrow_forwardc++arrow_forward
- Suppose a node of a doubly linked list is defined as follows: struct Node{ int data; struct Node* next; struct Node* prev; }; Write the function definition of the function deleteElement as presented below. This function deletes a node at position n from a doubly linked list. struct Node* deleteElement(struct Node* head, int n){ //write the function definition }arrow_forward#include <iostream> using namespace std; #define SIZE 5 //creating the queue using array int A[SIZE]; int front = -1; int rear = -1; //function to check if the queue is empty bool isempty() { if(front == -1 && rear == -1) return true; else return false; } //function to enter elements in queue void enqueue ( int value ) { //if queue is full if ((rear + 1)%SIZE == front) cout<<"Queue is full \n"; else { //now the first element is inserted if( front == -1) front = 0; //inserting element at rear end rear = (rear+1)%SIZE; A[rear] = value; } } //function to remove elements from queue void dequeue ( ) { if( isempty() ) cout<<"Queue is empty\n"; else //only one element if( front == rear ) front = rear = -1; else front = ( front + 1)%SIZE; } //function to show the element at front void showfront() { if( isempty()) cout<<"Queue is empty\n"; else cout<<"element at front is:"<<A[front]; } //function to display the queue void…arrow_forward20 T OR F An application programmer can prevent accessing an empty queue by using the isEmpty method in an if-statement to prevent such access.arrow_forward
- Exercise 3 Write a function called middle that takes a list and returns a new list that contains all but the first and last elements. For example: >>> t = [1, 2, 3, 4] >>> middle(t) [2, 3]arrow_forwardEXERCISE 1 Consider a function doubles :: Cint]Eint] that doubles every item in list doubles [3, 4,1,2] [6,8, 2,4] a) write a version doubles Rec using recursion for the aboe functionarrow_forwardstruct node{int num;node *next, *before;};start 18 27 36 45 54 63 The above-linked list is made of nodes of the type struct ex. Your task is now to Write a complete function code to a. Find the sum of all the values of the node in the linked list. b. Print the values in the linked list in reverse order. Use a temporary pointer temp for a and b. i dont need a full code just the list partarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780133594140Author:James Kurose, Keith RossPublisher:PEARSON
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780133594140Author:James Kurose, Keith RossPublisher:PEARSON Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780124077263Author:David A. Patterson, John L. HennessyPublisher:Elsevier Science
Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780124077263Author:David A. Patterson, John L. HennessyPublisher:Elsevier Science Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)Computer EngineeringISBN:9781337569330Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean AndrewsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)Computer EngineeringISBN:9781337569330Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean AndrewsPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of Database ManagementComputer EngineeringISBN:9781337093422Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. LastPublisher:Cengage Learning
Concepts of Database ManagementComputer EngineeringISBN:9781337093422Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. LastPublisher:Cengage Learning Prelude to ProgrammingComputer EngineeringISBN:9780133750423Author:VENIT, StewartPublisher:Pearson Education
Prelude to ProgrammingComputer EngineeringISBN:9780133750423Author:VENIT, StewartPublisher:Pearson Education Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...Computer EngineeringISBN:9781119368830Author:FITZGERALDPublisher:WILEY
Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...Computer EngineeringISBN:9781119368830Author:FITZGERALDPublisher:WILEY

Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780133594140
Author:James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:PEARSON

Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780124077263
Author:David A. Patterson, John L. Hennessy
Publisher:Elsevier Science

Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781337569330
Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean Andrews
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Concepts of Database Management
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781337093422
Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. Last
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Prelude to Programming
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780133750423
Author:VENIT, Stewart
Publisher:Pearson Education

Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781119368830
Author:FITZGERALD
Publisher:WILEY