
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
Write structures for the carbonyl electrophile and enolate nucleophile that react to give the aldol below.
- You do not have to consider stereochemistry.
- Draw the enolate nucleophile in its carbanion form.
- Draw one structure per sketcher. Add additional sketchers using the drop-down menu in the bottom right corner.
- Separate multiple reactants using the + sign from the drop-down menu.
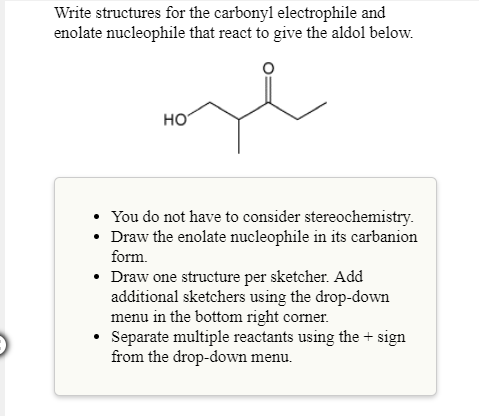
Transcribed Image Text:Write structures for the carbonyl electrophile and
enolate nucleophile that react to give the aldol below.
HO
You do not have to consider stereochemistry.
carbanion
late nucleophile in its
Draw the eno
form.
Draw one structure per sketcher. Add
additional sketchers using the drop-down
menu in the bottom right comer.
°
Separate multiple reactants using the+ sign
from the drop-down menu.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- This reaction is an example of conjugate addition of a nucleophile to an a,ẞ-unsaturated carbonyl. H3C LOCH3 H₂O H3C OCH3 OCH3 Draw the two resonance structures of the enolate anion intermediate for this reaction. • Draw an R1 group in place of CoA. The R group tool is located in the charges and lone pairs drop-down menu. • Draw one structure per sketcher. Add additional sketchers using the drop-down menu in the bottom right corner. Separate resonance structures using the symbol from the drop-down menu. • O H CH3 ? [Farrow_forwardPlease help me with this i am very confused, if I have a current answer it is incorrect and I am just using this to study and I am very confusedarrow_forwardDraw the structure(s) of the major product(s) of the following reaction after workup to neutralize acid. NH₂ excess Br • You do not have to consider stereochemistry. • Draw one structure per sketcher. Add additional sketchers using the drop-down menu in the bottom right corner. • Include the counterion when the product is a quaternary ammonium salt. Draw the counterion in its own sketcher. • Separate multiple products using the + sign from the drop-down menu. • If no reaction occurs, draw all starting materials.arrow_forward
- CH21/23) [Review Topics] [References] Draw structures for the carbonyl electrophile and enolate nucleophile that react to give the aldol or enone below. OH CI You do not have to consider stereochemistry. Draw the enolate ion in its carbanion form. Draw one structure per sketcher. Add additional sketchers using the drop-down menu in the bottom right corner. Separate multiple reactants using the + sign from the drop-down menu. ChemDoodle ? Previous Nexarrow_forward4. Complete the phrases with one or more of the following terms: SNI, SN2, E1, E2. a) The reaction takes place in two or more steps. b) The reaction goes through a carbocation. c) The rate determining step has two reactants. d) The rate is independent of the concentration of nucleophile or base. e) Zaitsev's rule is often applicable to the products..arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts and the alcohol side product. 1. H3O*, heat 2. Neutralizing work-up Type here to searcharrow_forward
- Write structures for the carbonyl electrophile and enolate nucleophile that react to give the aldol below. ОН You do not have to consider stereochemistry. • Draw the enolate nucleophile in its carbanion form. • Draw one structure per sketcher. Add additional sketchers using the drop-down menu in the bottom right corner. • Separate multiple reactants using the + sign from the drop-down menu.arrow_forward3. How does the presence of the tBu group influence the attack of a nucleophile e.g. Br- onto the Br ? Buarrow_forward5. Our base choice determines how much of the original acid is left in solution at equilibrium. This will have significant consequences during our discussion of the Aldol and Claisen reactions. For each of the reactions below determine which is the most acidic proton in the first molecule. Assign a pKa value to at least the most acidic proton. Draw the expected conjugate base and acid. Assign a pKa value to the conjugate acid then determine the approximate position of the equilibrium (towards the starting material, towards the product, or near the middle - for example there would be a significant amount of starting material and product at equilibrium). Then predict the product of the reaction of the conjugate base with the reagent over the next arrow. An example is provided below. Alcohol 16 Lowest pKa =Most acidic Alcohol OH OH 16 OH NaOCH3 Br HO HOCH HO HO HO 16 10 Phenol 38 Amine Albuterol pKa 10 stronger acid pka 16 weaker acid = favored at equilibrium Difference in pKa values = 6…arrow_forward
- In the solvolysis experiment changing the reagent from t-butyl chloride to t-butyl iodide does it affect the rate of reaction? Is the new reaction faster, slower or no change? Please explain?arrow_forward4. The issue with enol/enolate syntheses is that a lot of the starting materials and products have the same functional groups (carbonyls). To determine which enolate reaction is needed, thus, can depend on more than functional group identification: it sometimes depends on identifying how many carbons are between each carbonyl. So we're going to create a new synthetic map for carbon-carbon bond formations with enols and enolates. Fill in the missing starting materials, reagents, or products as needed, and answer the given questions. a. The aldol, Option 1 ai nip b. The aldol, Option 2 R3 R R3 R² What kind of functional group is this product? · R3 c. The Claisen Condensation R3 OH R¹ R2 Circle the correct answer: The alcohol is (alpha/beta) to the carbonyl. base · + R² OR3 R1 R1 and R2 alkyl, aryl, OR R² Fill in the answer: The product is a (1, ) dicarbonylarrow_forwardDraw the organic product(s) of this intramolecular aldol condensation reaction. Consider only the formation of 5- and 6-membered rings.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY