
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
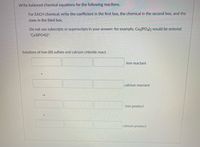
Transcribed Image Text:Write balanced chemical equations for the following reactions.
For EACH chemical, write the coefficient in the first box, the chemical in the second box, and the
state in the third box.
Do not use subscripts or superscripts in your answer: for example, Ca3(POa2 would be entered
"Ca3(PO4)2".
Solutions of iron (III) sulfate and calcium chloride react.
iron reactant
calcium reactant
iron product
calcium product
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In an experiment, a student combines 75.0 mL of a 0.200 M iron (III) chloride solution with 125.0 mL of a 0.250 M sodium carbonate solution. Write a balanced equation for the reaction. What is the limiting reactant? What is the theoretical yield of sodium chloride (in grams)? How many grams of sodium chloride need to be produced in the experiment in order to achieve a yield of 93.75%?arrow_forwardPredict the reactants of this chemical reaction. That is, fill in the left side of the chemical equation. Be sure the equation you submit is balanced. (You can edit both sides of the equation to balance it, if you need to.) Note: you are writing the molecular, and not the net ionic equation. [] → ɖ(C103) (aq) + H₂O(1) 0-0 Śarrow_forwardThe balanced equation below shows a simple way of manufacturing hydrogen gas in lab (you've done thisl). For your convenience, the molar mass of each substance is shown below their formulas (in purple). Use this information to make the requested calculation: 2 Al(s) + 6 HCI(aq) -> 2 AICI3(aq) + 3 H2(g) 26.982 36.461 133.341 2.016 What volume of hydrogen gas, in mL, would be produced by the reaction of 922 mg of hydrochloric acid with excess aluminum metal?arrow_forward
- Solid copper can be produced by passing gaseous ammonia over solid copper (II) oxide at high temperatures, according to the following reaction. NH3 (g) + CuO (s) → N2 (g) + Cu (s) + H2O (g) Balance the reaction.arrow_forwardSelect all of the ions that are spectator ions in the below chemical reaction. Incorrect selections will deduct credit. 3 MgBr2 (aq) + 2 NazPO4 (aq) → Mg3(PO4)2 (s) + 6 NaBr (aq) Na+ PO,3- Br Mg2+ O There are no spectator ions.arrow_forward10. The equations below represent precipitation reactions. Rewrite these as complete ionic and net ionic equations. Molecular Equation Complete Ionic Equation Net Ionic Equation Molecular Equation Complete lonic Equation Net Ionic Equation AgNO, (aq) + KCI (og) → KNO, (aq) + AgCl (s) Molecular Equation Complete Ionic Equation Net Ionic Equation Ba(ClO4)2 (aq) + K₂SO4 (ng) BaSO (s) + 2 KCIO₂(g) 11. The equation below represents a neutralization reaction. Rewrite this as complete ionic equations and net ionic equations. 2 HCl(aq) + Ba(OH)2 (aq) → 2 H₂O )+ BaCl₂ (aq) Include phase symbols.arrow_forward
- Write the balanced precipitation reactionsarrow_forward6. Sodium sulfide reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce hydrogen sulfide and sodium chloride. How many grams of sodium sulfide are required for complete reaction with 15.0 mL of 0.250 M hydrochloric acid? The molar mass of sodium sulfide is 78.046 g/mol. (Hint: start by writing the balanced equation for the reaction.)arrow_forward1. Label each of the following reactions as combination (synthesis), decomposition, single replacement, or double replacement. Then complete and balance the following reactions. Reaction Type of reaction? Redox or nonredox? H2(g) + 02 (g) → K (s) + N2 (g) → C (s) + 02 (g) → H2CO3 (aq) → electrical current H₂O (1) 300°C Au2O3 (s) 300°C Ag2O (s) → NH3 (g) → Pb (s) + Cu(NO3)2 (aq) → Na (s) + HOH (1) -> BaBr2 (aq) + Na3PO4 (aq) → H2SO4 (aq) + NH4OH(aq) → Cl2 (g) + NaI (aq) → Na2S (s) + HCl(aq) → Fe (s) + 02 (g) →arrow_forward
- Balance the following reaction in basic solution then enter the coefficients of the balanced reaction into the blank spaces. Remember to include "understood" coefficients of 1! 9. Type your answer here Ag20(s) + Type your answer here Al(s) + Type your answer here OH (aq) + H20(1) → Type your answer here Type your answer here Ag(s) + Type your answer here H2A!O3 (aq)arrow_forwardCobalt(II) chloride solution reacts with sodium hydroxide solution. Identity the spectator ion(s). Note: you may choose more than one answer. O Co2+ Na OHarrow_forwardHere is some information to help. In this experiment, magnesium metal is heated until it reacts with oxygen in the air according to the following balanced equation: 2Mg(s)+ O2(g) → 2MgO(s) (silver metal) (white-gray ash) As the magnesium burns in air, it may also combine with nitrogen in air. To remove any nitride product, water is added, and the product is reheated. Any nitride product is converted to magnesium oxide and ammonia. 3Mg(s)+ N2(g) → Mg3N2(s) Mg3N2(s)+3H2O(l)→3MgO(s)+2NH3(aq) A weighed amount of the magnesium metal is used, and the mass of the oxide product formed is determined at the end of the experiment. The mass of oxygen that combines with the magnesium is obtained from the difference between the mass of the oxide product and the original mass of magnesium. mass of oxide product-mass of magnesium=mass of oxygen in oxide product The empirical formula of the oxide…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY