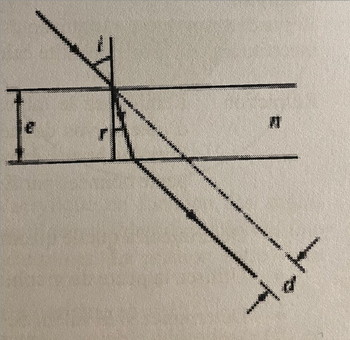
Write a first general equation giving the angle of refraction (r) as a function of the angle of incidence (i) on a rectangular piece of acrylic and the refractive index (n) of the acrylic.
Then write a second general equation giving the lateral deviation (d) of an incident beam as a function of the angle of incidence (i), the angle of refraction (r) and the thickness (e) of the rectangular piece of acrylic. Note that there are 2 ways to calculate (d), which result in 2 mathematically equivalent equations.
Finally, combine the two equations to obtain the physical model of the experiment, an equation that allows you to calculate the dependent variable (d) based on the independent variable (i), as well as the parameters of the experiment (e). and N). The variable (r) is an intermediate variable that should not be in the final equation.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

- A light ray travelling in medium a is refracted into medium b. The angle of incidence is 50.5° and the angle or refraction is 60.8°. Both angles are measured from the normal to the interface. What is the ratio of the index of refraction of medium a to that of medium b?arrow_forwardA light beam reflects off two parallel reflecting surfaces that are = 202 cm long and separated by a distance of s = 65.0 cm. If the beam of light enters this region as shown, with the angle 0 = 25.1°, determine the following. Ꮎ (a) the number of times the light beam reflects off the left surface Have you redrawn the figure with all angles and distances labeled? How is the entrance angle related to the angle of Incidence and the angle of reflection for the mirrors? times (b) the number of times the light beam reflects off the right surface timesarrow_forwardA beaker with a mirrored bottom is filled with a liquid whose index of refraction is nliq = 2.37. A light ray from air strikes the top surface of the liquid at an incident angle θin = 72.9° from the normal line to the liquid surface, as shown in the figure. What is the refraction angleθ1 of the light ray as it enters the liquid (in degrees; remember to use the scientific notation of numbers)?arrow_forward
- The index of refraction for red light in water is 1.331 and that for blue light is 1.340. If a ray of white light enters the water at an angle of incidence of 50.15°, what are the underwater angles of refraction for the blue and red components of the light? (Enter your answers to at least two decimal places.) (a) blue component (b) red componentarrow_forwardA ray of light crosses the boundary between some substance with n = 1.54 and air, going from the substance into air. If the angle of incidence is 29◦ what is the angle of refraction? Calculate to 1decimal.arrow_forwardThe refractive index of a transparent material can be determined by measuring the critical angle when the solid is in air. If 0c = 20° what is the index of refraction of the material? с Units no units required The index of refraction, n = What will be the critical angle when the same material is immersed in a medium with the index of refraction 1.17? The critical angle, 0c = Units degarrow_forward
- A ray of light strikes a flat block of glass at an incidence angle of ?1 = 38.6°. The glass is 2.00 cm thick and has an index of refraction that equals ng = 1.52. (a) What is the angle of refraction, ?2,that describes the light ray after it enters the glass from above? (Enter your answer in degrees to at least 2 decimal places.) b.)With what angle of incidence, ?3,does the ray approach the interface at the bottom of the glass? (Enter your answer in degrees to at least 2 decimal places.)arrow_forwardConsider a layer of Oil, Glass, and Air where the oil/glass boundary is parallel to the glass/air boundary. Let the index of refraction for the glass be 1.48 and the index of refraction for the oil to be 1.25. At what angle relative to the normal should a ray of light be directed upon the oil/glass interface such that it strikes the glass/air interface at the critical angle?arrow_forwardThree sheets of plastic have unknown indices of refraction.Sheet 1 is placed on top of sheet 2, and a laser beam is directed unto the sheets from above so that it strikes the interface at an angle of 26.5 degrees with the normal. The refracted beam in sheet 2 makes an angle of 31.7 degrees with the normal. The experiment is repeated with sheet 3 on top of sheet 2, and with the same angle of incidence, the refracted beam makes an angle of 36.7 degrees with the normal. If the experiment is repeated again with sheet 1 on top of sheet 3, determine the expected angle of refraction in sheet 3?. Assume the same angle of incidence.arrow_forward