
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
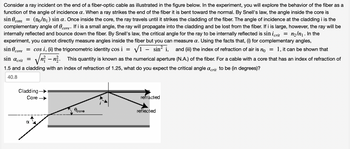
Transcribed Image Text:Consider a ray incident on the end of a fiber-optic cable as illustrated in the figure below. In the experiment, you will explore the behavior of the fiber as a function of the angle of incidence α. When a ray strikes the end of the fiber it is bent toward the normal. By Snell's law, the angle inside the core is
sin θ_core = (n₀/n₁) sin α.
Once inside the core, the ray travels until it strikes the cladding of the fiber. The angle of incidence at the cladding i is the complementary angle of θ_core. If i is a small angle, the ray will propagate into the cladding and be lost from the fiber. If i is large, however, the ray will be internally reflected and bounce down the fiber. By Snell's law, the critical angle for the ray to be internally reflected is
sin i_crit = n₂/n₁.
In the experiment, you cannot directly measure angles inside the fiber but you can measure α. Using the facts that, (i) for complementary angles,
sin θ_core = cos i,
(ii) the trigonometric identity
cos i = √(1 - sin² i),
and (iii) the index of refraction of air is n₀ = 1, it can be shown that
sin α_crit = √(n₁² - n₂²).
This quantity is known as the numerical aperture (N.A.) of the fiber. For a cable with a core that has an index of refraction of 1.5 and a cladding with an index of refraction of 1.25, what do you expect the critical angle α_crit to be (in degrees)?
40.8
**Diagram Explanation:**
The diagram shows the structure of a fiber-optic cable with two main parts: the core and the cladding. A light ray enters the core at an angle α. As it enters, it refracts and bends towards the normal, traveling through the core with an angle θ_core. The ray then reaches the boundary between the core and cladding, where it encounters the critical angle i. If this angle is greater than i_crit, the ray reflects internally and continues to bounce down the fiber. Otherwise, it refracts out into the cladding and is lost.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A ray of light crosses the boundary between some substance with n=1.58 and air, going from the substance into air. If the angle of incidence is 17° What is the angle of refraction?arrow_forwardA ray of light enters a narrow prism along the normal as shown. Calculate the angle (degrees) at which the ray exits the prism, relative to North (i.e. up the page, not the normal to the glass). The index of refraction of the prism is n = 1.54. The angle of the prism is theta = 19.42 deg.arrow_forwardA ray of light travels from air into another medium, making an angle of ?1 = 45.0° with the normal as in the figure attached. A light ray in air is moving down and to the right and is incident on a second medium. It makes an angle ?1 with the vertical. Inside the vertical, it continues to move down and to the right but at a steeper slope than the incident ray. It makes an angle ?2 with the vertical. (a). Find the angle of refraction ?2 if the second medium is diamond. (b). Find the angle of refraction ?2 if the second medium is polystyrene. (c). Find the angle of refraction ?2 if the second medium is carbon tetrachloride.arrow_forward
- A ray of monochromatic light is incident on the face of a prism in the shape of an equilateral triangle (that is, the apex angle of the prism is 60.0°). The incidence angle of the light ray is 75.9°. The prism is made of a transparent material with an index of refraction of 1.460 (at the light ray's wavelength). (a) Calculate the angle of refraction at the first surface (in degrees). (Round your answer to at least one decimal place.) (b) Calculate the angle of incidence at the second surface (in degrees). (Round your answer to at least one decimal place.) (c) Calculate the angle of refraction at the second surface (in degrees). (Round your answer to at least one decimal place.) (d) Calculate the angle between the incident and emerging rays (in degrees). (Round your answer to at least one decimal place.)arrow_forwardA light ray traveling in air strikes the surface of a slab of glass at an angle of incidence of 50 degrees. Part of the light is rejected and part is refracted. Find the angle the refracted ray makes with respect to the normal to the air/glass interface.arrow_forwardA light ray travelling in medium a is refracted into medium b. The angle of incidence is 50.5° and the angle or refraction is 60.8°. Both angles are measured from the normal to the interface. What is the ratio of the index of refraction of medium a to that of medium b?arrow_forward
- A light beam traveling in the air makes an angle θi with respect to an air-plastic interface. After it enters a rectangular block of plastic, it travels at an angle of θr with respect to the normal. Write an equation for the index of refraction of the plastic in terms of the given variables. Assume that the index of refraction for air is 1.001.00, and apply this value to your equation.arrow_forwardA ray of light crosses the boundary between some substance with n = 1.54 and air, going from the substance into air. If the angle of incidence is 29◦ what is the angle of refraction? Calculate to 1decimal.arrow_forwardThree sheets of plastic have unknown indices of refraction.Sheet 1 is placed on top of sheet 2, and a laser beam is directed unto the sheets from above so that it strikes the interface at an angle of 26.5 degrees with the normal. The refracted beam in sheet 2 makes an angle of 31.7 degrees with the normal. The experiment is repeated with sheet 3 on top of sheet 2, and with the same angle of incidence, the refracted beam makes an angle of 36.7 degrees with the normal. If the experiment is repeated again with sheet 1 on top of sheet 3, determine the expected angle of refraction in sheet 3?. Assume the same angle of incidence.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON