
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
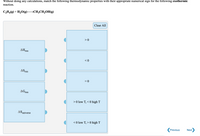
Transcribed Image Text:Without doing any calculations, match the following thermodynamic properties with their appropriate numerical sign for the following exothermic
reaction.
C,H4(g) + H20(g)
→CH3CH,OH(g)
Clear All
> 0
AHrxn
< 0
ASrxn
= 0
AGrxn
> 0 low T, < 0 high T
ASuniverse
< 0 low T, > 0 high T
Previous
Next
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which of the following statements are true about the exothermic reaction H2(g)+12O2(g)→H2O(l) ? Because the reaction is exothermic, the products are at a higher temperature than the reactants. All reactants and products are in their standard reference state. ΔH∘Rcan only be measured if the reaction is carried out at a constant temperature of 298.15 K. ΔH∘R<0arrow_forwardRead the descriptions of physical or chemical changes in the table below. Then decide whether the change will be spontaneous, if you can. Change A gas expands, absorbing heat from its surroundings. A solid precipitates from a solution, releasing heat as it does so. During an endothermic chemical reaction, four moles of gaseous reactants are turned into two moles of gaseous products. Is this change spontaneous? O Yes. No. O Can't decide with information given. O Yes. O No. O Can't decide with information given. Yes. O No. Can't decide with information given.arrow_forwardCalculate ΔH for the following reaction: CH4 (g) + O2 (g) ⇌ CO2 (g) + H2O (l) Compound ΔH CH4 (g) -74.8 kJ/mol H2O (l) -285.8 kJ/mol CO2 (g) -393.5 kJ/moarrow_forward
- Calculate the standard enthalpy change for the following reaction at 25 °C. MgCl, (s) + H,0(1) → MgO(s) + 2 HC1(g) AH; values can be found in this table of thermodynamic values. kJ/mol rxnarrow_forwardAbove what temperature (in Kelvin) does the following reaction become nonspontaneous? FeO(s) + CO(g) → CO2(g) + Fe(s) ΔH = -11.0 kJ; ΔS = -17.4 J/Karrow_forwardThe reaction of gaseous H2H2 and liquid Br2Br2 to give gaseous HBrHBr has ΔHΔH = -17.4 kcal/molkcal/mol (-72.8 kJ/molkJ/mol) and ΔSΔS = 27.2 (cal/mol⋅K)(cal/mol⋅K) (114 J/(mol⋅K)J/(mol⋅K)). What is the value of ΔGΔG (in kcalkcal and kJkJ) for the reaction at 280 KK ? Enter your answers numerically separated by a comma.arrow_forward
- The following reaction is classified as and CHĄ(g) + 202(g) - > CO2(g) + 2H20(g) exothermic reactionarrow_forwardWhat is the change in internal energy (in kJ/mol) of the given reaction if 2 moles of sulfur dioxide is converted to 2 moles of sulfur trioxide at 32°C? 2502 (g) + + 02 (9) → 2503 (g) AH = –198.2 kJ/mol |arrow_forwardDefine enthalpy, entropy and free energy. Include their chemical symbols in your explanation.arrow_forward
- Consider the following reaction at 25 °C: 3 NiO(s) + 2 NH (g)→3 Ni(s) + N,(g) + 3 H,O(g) | kJ If AG° = -18.1 kJ/mol, determine the value of AG assuming that a mixture contains 57.6 g of NiO, 182.3g of Ni, 0.24 atm of NH, 8.54 atm of N, and 10.07 atm of H,O. %3D 1 3 3 4 6. C 8. 9. +/- 0. x 100 2. 5arrow_forwardCalculate The change in the Gibbs free energy for each set of delta H reaction Delta S reaction and tea assume the reactants and products are in their standard states. DeltaHrxn= +123 kJ, DeltaSrxn= -244 J/K; T=290 Karrow_forwardAccording to Le Chatelier’s Principle, does the following reaction shift towards reactants, towards products, or have no shift when heat is added to the following exothermic reaction? C(s) + CO2(g) ⇆ 2CO(g) + heatarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY