
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
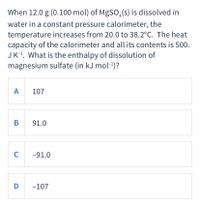
Transcribed Image Text:When 12.0 g (0.100 mol) of MgSO,(s) is dissolved in
water in a constant pressure calorimeter, the
temperature increases from 20.0 to 38.2°C. The heat
capacity of the calorimeter and all its contents is 500.
JK-!. What is the enthalpy of dissolution of
magnesium sulfate (in kJ mol-1)?
A
107
В
91.0
C
-91.0
D
-107
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Mg(s) + 1/2 O2(g) -> MgO(s). Determind the value of the standard enthalphy change for the reaction. Mg(s) + 2 HCI(aq) -> MgCl2(aq) + H2(g). ∆Hrxn = -316 kJ mol-1 MgO(s) + 2 HCI(aq) -> MgCl2(aq) + H2O. ∆Hrxn = -45.7 kJ mol-1 H2(g) + 1/2 O2(g) -> H2O. ∆Hrxn = -286 kJ mol-1arrow_forwardhen the oxide of generic metal MM is heated at 25.0 ∘C25.0 ∘C, a negligible amount of MM is produced. MO2(s)↽−−⇀M(s)+O2(g)Δ?∘=290.6kJmolMO2(s)↽−−⇀M(s)+O2(g)ΔG∘=290.6kJmol When this reaction is coupled to the conversion of graphite to carbon dioxide, it becomes spontaneous. What is the chemical equation of this coupled process? Show that the reaction is in equilibrium. Include physical states and represent graphite as C(s). chemical equation: MO2(s)+C(s)↽−−⇀M(s)+CO2(g) What is the thermodynamic equilbrium constant for the coupled reaction?arrow_forwardWhen ammonium chloride (NH_(4)Cl) is added to water, it breaks into positive and negative ions and decreases the temperature of the medium. Which statement is TRUE about this reaction?arrow_forward
- For the reaction below, ΔrH° = −3307.9 kJ mol−1. What is the standard enthalpy of formation of FeS2(s)? 4 FeS2(s) + 11 O2(g) ⟶ 2 Fe2O3(s) + 8 SO2(g) Give your answer in kilojoules per mole (kJ mol−1). Data: Substance Standard enthalpyof formation (in kJ mol−1) Fe2O3(s) −833.1 SO2(g) −297.0 Please double check your answer.arrow_forwardFor each reaction equation, calculate the internal energy change, ΔE, of the reaction at 25 ∘C 2H2(g)+O2(g)⟶2H2O(l)Δ?=−571.6 kJ Δ?= kJ H2(g)+Cl2(g)⟶2HCl(g)Δ?=−184.6 kJ/mol Δ?= kJarrow_forwardCalculate the standard enthalpy change for the reaction at 25 °C. Standard enthalpy of formation values can be found in this list of thermodynamic properties. Mg(OH), (s) + 2 HCI(g) → MgCl, (s) + 2 H,O(g) AHixn kJarrow_forward
- Calculate the standard enthalpy change for the reaction at 25 °C. Standard enthalpy of formation values can be found in this list of thermodynamic properties. C₂H₂ (g) + 50₂ (g) - AHixn = 3 CO₂(g) + 4 H₂O(g) kJarrow_forwardIn the following experiment, solid CaCl2 (M = 110.98 g/mol) is dissolved in water:CaCl2(s) → Ca2+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) ΔsolnH = ? kJ mol−1A 4.00 g sample of CaCl2 is added to a coffee-cup calorimeter containing 125 g of H2O. The initial temperature of water in the calorimeter is 22.0°C and the final temperature is 27.5°C. What is the enthalpy change for the dissolution reaction (ΔsolnH) in kJ per mole of CaCl2? Assume the specific heat capacity of the solution is the same as water (Cs=4.18 J g-1 °C-1) and that no heat is lost to the calorimeter.arrow_forwardWhat is ΔHrxn if mixing 50.0 mL of 0.500 M HCl (aq) with 50.0 mL of 0.500 M NaOH (aq), both initially at 24.0 °C results in a Tmix of 27.3 °C? Assume that the reaction goes 100% HCl (aq) + NaOH (aq) → H2O (l) + NaCl(aq) **answer in kJ/mol of H2O producedarrow_forward
- Calculate the standard enthalpy change for the reaction at 25 °C. Standard enthalpy of formation values can be found in this list of thermodynamic properties. MgCl₂ (s) + H₂O(1) AH;xn= V → B MgO(s) + 2 HCl(g) MacBook Air H N M 1 9 DD $10 P m kJarrow_forwardCalcium ΔHof (kJ/mol) ΔGof (kJ/mol) So (J/mol K) Ca (s) 0 0 41.4 Ca (g) 178.2 144.3 158.9 Ca2+ (g) 1925.9 CaC2 (s) -59.8 -64.9 70.0 CaCO3 (s, calcite) -1206.9 -1128.8 92.9 CaCl2 (s) -795.8 -748.1 104.6 CaF2 (s) -1219.6 -1167.3 68.9 CaH2 (s) -186.2 -147.2 42.0 CaO (s) -635.1 -604.0 39.8 CaS (s) -482.4 -477.4 56.5 Ca(OH)2 (s) -986.1 -898.5 83.4 Ca(OH)2 (aq) -1002.8 -868.1 -74.5 Ca3(PO4)2 (s) -4126.0 -3890.0 241.0 CaSO4 (s) -1434.1 -1321.8 106.7 CaSiO3 (s) -1630.0 -1550.0 84.0 Carbon ΔHof (kJ/mol) ΔGof (kJ/mol) So (J/mol K) C (s, graphite) 0 0 5.7 C (s, diamond) 1.9 2.9 2.4 C (g) 716.7 671.3 158.1 CCl4 (l) -135.4 -65.2 216.4 CCl4 (g) -102.9 -60.6 309.9 CHCl3 (l) -134.5 -73.7 201.7 CHCl3 (g) -103.1 -70.3 295.7 CH4 (g) -74.8 -50.7 186.3 CH3OH (g)…arrow_forward11. What is the ΔHº-value for the dissolution of NaOH (s) to yield 1.00... m NaOH (aq), given: Na (s) + 1/2 O2 (g) + 1/2 H2 (g) → NaOH (s) ΔHfº = -425.9 kJ/mol Na (s) + 1/2 O2 (g) + 1/2 H2 (g) → NaOH (aq, 1 m) ΔHfº = -469.2 kJ/mol Multiple Choice -895.1 kJ/mol -43.3 kJ/mol +1.102 kJ/mol +43.3 kJ/mol +895.1 kJ/molarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY