
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
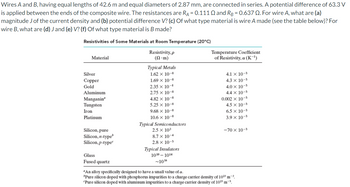
Transcribed Image Text:Wires A and B, having equal lengths of 42.6 m and equal diameters of 2.87 mm, are connected in series. A potential difference of 63.3 V
is applied between the ends of the composite wire. The resistances are RA = 0.111 Q and Rg = 0.637 Q. For wire A, what are (a)
magnitude J of the current density and (b) potential difference V? (c) Of what type material is wire A made (see the table below)? For
wire B, what are (d) J and (e) V? (f) Of what type material is B made?
Resistivities of Some Materials at Room Temperature (20°C)
Resistivity, p
(N-m)
Material
Silver
Copper
Gold
Aluminum
Manganin
Tungsten
Iron
Platinum
Silicon, pure
Silicon, n-type
Silicon,p-type
Glass
Fused quartz
Typical Metals
1.62 x 10-8
1.69 x 10-8
2.35 x 10-8
2.75 X 10-8
4.82 x 10-8
5.25 x 10-8
9.68 x 10-8
10.6 × 10-8
Typical Semiconductors
2.5 × 10³
8.7 x 10-4
2.8 x 10-3
Typical Insulators
10101014
-1016
Temperature Coefficient
of Resistivity, a (K-¹)
4.1 x 10-3
4.3 × 10-3
4.0 × 10-3
4.4 x 10-3
0.002 × 10-3
4.5 x 10-3
6.5 x 10-3
3.9 x 10-3
-70 × 10-³
"An alloy specifically designed to have a small value of a.
*Pure silicon doped with phosphorus impurities to a charge carrier density of 10²3 m³.
"Pure silicon doped with aluminum impurities to a charge carrier density of 102³ m-³.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A rear window defroster consists of a long, flat wire bonded to the inside surface of the window. When current passes through the wire, it heats up and melts ice and snow on the window. For one window the wire has a total length d = 11.6 m , a width a = 1.8 mm, and a thickness w = 0.11 mm. The resistivity of the metal is ρ = 2.6 × 10^−8Ωm. The wire is connected to the car’s 12.0 V battery. (a) What is the current flowing through the wire? (b) What is the power of the window defroster?arrow_forwardKiting during a storm. The legend that Benjamin Franklin flew a kite as a storm approached is only a legend — he was neither stupid nor suicidal. Suppose a kite string of radius 2.10 mm extends directly upward by 0.802 km and is coated with a 0.520 mm layer of water having resistivity 155 Ω·m. If the potential difference between the two ends of the string is 176 MV, what is the current through the water layer? The danger is not this current but the chance that the string draws a lightning strike, which can have a current as large as 500 000 A (way beyond just being lethal).arrow_forwardNerve impulses are carried along axons, the elongated fibers that transmit neural signals. We can model an axon as a tube with an inner diameter of 10 μm. The tube wall is insulated, but the fluid inside it has a resistivity of 0.50 Ω⋅m. What is the resistance of a 5.0-mm-long axon?arrow_forward
- A copper wire of radius a = 0.240 mm has an aluminum jacket of outer radius b = 0.329 mm. There is a current i = 1.57 A in the composite wire. Take the resistivity for copper and aluminum to be 1.69 × 10-8Ω·m and 2.75 × 10-8Ω·m. Calculate the current in (a) the copper and (b) the aluminum. (c) If a potential difference V = 13.1 V between the ends maintains the current, what is the length in meters of the composite wire?arrow_forwardA lightning rod on top of a building consists of an iron spike 1.5 m long with a circular crosssection of diameter 1.5 cm. During a lightning strike, the rod carries a current of 1000 A. What is the potential difference across the rod when this current flows? The resistivity of iron is 1.0 x 10-7 Ωm.arrow_forwardAn aluminum wire having a cross-sectional area equal to 3.10 x 10-6 m² carries a current of 6.00 A. The density of aluminum is 2.70 g/cm³. Assume each aluminum atom supplies one conduction electron per atom. Find the drift speed of the electrons in the wire. The equation for the drift velocity includes the number of charge carriers per volume, which in this case is equal to the number of atoms per volume. How do you calculate that if you know the density and the atomic weight of aluminum? mm/sarrow_forward
- A wire 3.43 m long and 6.38 mm in diameter has a resistance of 11.6 mQ. A potential difference of 17.7 V is applied between the ends. (a) What is the current in amperes in the wire? (b) What is the magnitude of the current density? (c) Calculate the resistivity of the material of which the wire is made. (a) Number Units (b) Number i Units (c) Number i Units >arrow_forwardAs part of a class project you are given 0.900 g of copper and asked to fabricate a wire with uniform cross-section. You use up 95% of the copper and make a wire with a resistance of 0.723 Ω. The resistivity of copper is 1.72 10-8 Ω · m and its density is 8.92 103 kg/m3. (a) What length of wire do you end up with? (m)(b) What is the diameter of the wire? (mm)arrow_forwardElectric current passing through a human body can be dangerous, even fatal, depending on the amount of current, the duration of the current, and the region of the body through which the current passes. However, currents less than about 0.5 mA are typically imperceptible. A current caused by a low potential difference typically travels through the outer layer of the skin. The resistance of the skin therefore determines how much current flows for a given potential difference. The resistance can be influenced by a number of factors, including whether the skin is wet or dry . For example, suppose an electric current of 89.0 µA follows a path through the thumb and index finger. When the skin is dry, the resistance along this path is 4.40 ✕ 105 Ω. What voltage (in V) is required for this current, in the case of dry skin? V When the skin is wet, the resistance is lowered to 1,950 Ω. What voltage (in V) is required for the same current, in the case of wet skin? Varrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON