
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Wire C and wire D are made from different materials and have length LC = LD = 3.6 m. The resistivity and diameter of wire C are 4.8 × 10-6 Ω·m and 1.06 mm, and those of wire D are 4.0 × 10-6 Ω·m and 0.73 mm. The wires are joined as shown in the figure and a current of 4.3 A is set up in them. What is the electric potential difference between (a) points 1 and 2 and (b) points 2 and 3? What is the rate at which energy is dissipated between (c) points 1 and 2 and (d) points 2 and 3?
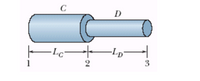
Transcribed Image Text:**Diagram Explanation:**
The image is a diagram showing a two-part cylindrical object with labeled sections. Here's the detailed explanation:
- The larger cylinder on the left is labeled as section \( C \).
- The smaller cylinder to the right is labeled as section \( D \).
- The length of section \( C \) is denoted by \( L_C \).
- The length of section \( D \) is denoted by \( L_D \).
- The connection points are marked and numbered:
- Point 1 marks the start of section \( C \).
- Point 2 marks the transition from section \( C \) to section \( D \).
- Point 3 marks the end of section \( D \).
This diagram might represent a mechanical component with varying diameters, often used in engineering to demonstrate concepts such as torsion, stress, or fluid flow through differing cross-sections.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The drawing shows three different resistors in two different circuits. The battery has voltage of V = 26V, and the resistors have resistances of R one = 50.0, 2 = 25.0 and 3 = 10.0 determine the current through the voltage across each resistor. For circuit you’ll have six parts to the answer: l1,l2,l3, V1, V2, V3. For circut B you will have 6 parts to the answer: l1, l2, l3, V1, V2, V3. arrow_forward3.0 A of electric current pass through a 4.0 Ω resistor. How many electrons pass through the resistor in 5 minutes?arrow_forwardThree resistors of 12 , 12 0, and 6.0 Q are connected in parallel. A 12-V battery is connected to the combination. What is the current through the 6.0 N resistor? O 0.4 A O 2 A O 0.5 A 4 Aarrow_forward
- Resistors R1 = 3.0 Q and R2 = 5.0 Q are connected to a battery as shown. The current through resistor R2 is 2.0 A. V a) What is the current through resistor R1? b) What is the voltage across the battery? R1 R2 c) What is the voltage across resistor R2?arrow_forwardTwo cylindrical resistors are made from the same material and are equal in diameter. The first resistor has length L, and the second resistor has length 2L. If the same current flows through both, compare the voltage across the two resistors: V1 > V2 V1 = V2 V1 < V2 none of the abovearrow_forwardThe circuit shown in the diagram contains a battery and two wires made of the same material, but with different diameters. Each wire is 10 cm long, has 7 x 1027 mobile electrons per cubic meter, and an electron mobility of 5 x 10-5 (m/s)/(V/m). The diameter of wire 1 is 3 mm, and the diameter of wire 2 is 0.8 mm. Location A is inside wire 1, and location B is inside wire 2. A steady state current flows through the circuit. Show Transcribed Text B wire 1 wire 2 What is average drift speed of electrons at location B, inside wire 2? VB = m/sarrow_forward
- Hi everyone, hope you all are doing well. I need help in Physics, please. Regardsarrow_forwardYour car battery is dead, and your friends are helping you start your car with cheap jumper cables. One cable carries current from their car to your car, and a second cable returns that current to their car. As you try to start your car, a current of 80.0 A flows through the cables to your car and back, and a voltage drop of 6.00 V appears across each cable. If you replace the cheap cables with cables having half their electric resistance, what voltage drop will appear across each new cable if the current doesn't change? AV= iarrow_forwardWhat is the time constant for charging this capacitor? Incorrect 4Sarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON