
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Leigh is doing a knee extension exercise using a 100 N weight strapped to her ankle 40 cm from her knee joint. She holds her leg so that the horizontal distance from her knee joint to the weight is 30 cm.
a. For this position, what torque is created by the dumbbell about her knee joint axis?
b. If the moment arm of the knee extensor muscles is 4 cm about the knee joint axis, what amount of force must these muscles produce to hold the leg in the position described? Ignore the weight of the leg.
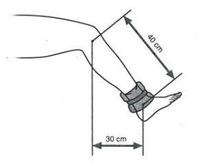
Transcribed Image Text:The image depicts a leg bent at the knee with a weight attached to the ankle. The upper leg is positioned horizontally, while the lower leg is angled downward. Two distance measurements are indicated with arrows and labels:
1. The horizontal distance from the knee to the ankle is labeled as "30 cm."
2. The vertical distance from the knee to the foot is labeled as "40 cm."
This diagram is likely used in an educational context to illustrate principles of biomechanics or physics, such as torque or lever systems, by demonstrating the impact of weights and positioning on joint movement.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
Why must the torque due to the weight be equal in magnitude?
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
Why must the torque due to the weight be equal in magnitude?
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A meter stick has a pivot placed ate 30 cm. The following masses are placed at the following locations. The meter stick is basically an inertial balance and thus doesn’t rotate. Sum the torques in order to determine the mass of the meter stick. 500 g placed at 10 cm, 200 g placed at 40 cm and 150 g placed at 75 cm .arrow_forwardA disc with a radius of 0.53 m is fixed to rotate about its center. Three forces act on the object as noted below. What magnitude net torque acts on the object? F1 = 14.7 N tangentially applied to the outer edge. F2 = 11.1 N tangentially applied to the outer edge. F3 = 11.5 N tangentially applied at a distance 0 m above the axis of rotation at an angle theta = 34.3 degrees with respect to the vertical. The location of F3 is at the center of the circle (a distance of 0 from the axis)arrow_forwardA worker opens a 1.50 m wide door by pushing on it with a force of 39.5 N directed perpendicular to its surface. ENT (a) What magnitude torque (in N. m) does she apply about an axis through the hinges if the force is applied at the center of the door? N.m (b) What magnitude torque (in N. m) does she apply at the edge farthest from the hinges? N. marrow_forward
- Figure 4.0 cm 30 N 20 N < 1 of 1 In (Figure 1), what is the net torque about the axle? Express your answer in newton-meters to two significant figures. T = Π ΑΣΦ Check your signs. No credit lost. Try again. Submit Provide Feedback Previous Answers Request Answer ? N.marrow_forwardQuestion is attachedarrow_forwardLook at the picturearrow_forward
- What is the torque by the trash can about the center of the seesaw, in N-m? Use g = 10 m/s². Your answer needs to have 3 significant figures, including the negative sign in your answer if needed. Do not include the positive sign if the answer is positive. No unit is needed in your answer, it is already given in the question statement. 8 17 6 5 4 3 2 2 3 10 kg 4 5 6 7 8arrow_forward20kg mass is at the 1.25 meter mark. Package G is at 1 meter mark. What must the mass of object G be? Calculate the torque that each object creates. The 20 kg mass on the left creates a positive torque. If the system is in equilibrium, the magnitude of the torque on the right must equal the magnitude of the torque on the left.arrow_forwardI need help with this physics torque questionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON