
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Why might it be more advantageous for a taxpayer to demonstrate that they ...
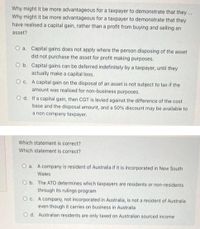
Why might it be more advantageous for a taxpayer to demonstrate that they
have realised a capital gain, rather than a profit from buying and selling an
asset?
O a. Capital gains does not apply where the person disposing of the asset
did not purchase the asset for profit making purposes.
O b. Capital gains can be deferred indefinitely by a taxpayer, until they
actually make a capital loss.
O c. A capital gain on the disposal of an asset is not subject to tax if the
amount was realised for non-business purposes.
O d. If a capital gain, then CGT is levied against the difference of the cost
base and the disposal amount, and a 50% discount may be available to
a non company taxpayer.
Which statement is correct?
Which statement is correct?
O a. A company is resident of Australia if it is incorporated in New South
Wales
O b. The ATO determines which taxpayers are residents or non-residents
through its rulings program
O c. A company, not incorporated in Australia, is not a resident of Australia
even though it carries on business in Australia
O d. Australian residents are only taxed on Australian sourced income
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which of the following statements is false? Group of answer choices A realized gain that is never recognized results in the temporary recovery of more than the taxpayer’s cost or other basis for tax purposes. A realized loss on which recognition is postponed results in the temporary recovery of less than the taxpayer’s cost or other basis for tax purposes A realized loss that is never recognized results in the permanent recovery of less than the taxpayer’s cost or other basis for tax purposes. A realized gain on which recognition is postponed results in the temporary recovery of more than the taxpayer’s cost or other basis for tax purposes.arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements is incorrect? Assume that the rental activity is classified as ‘production-of-income.’ If the taxpayer sells the rental property later at a loss, the loss will be treated as a capital loss (i.e., $3,000/$1,500 deduction limit in the current year). An amount that would have been paid in an arm’s-length transaction is considered a reasonable amount as deduction. Payment (except for medical or educational expense) of another person’s obligation does not result in a tax deduction for the payer. Regarding the start-up costs, if the new business is in the same line of business as the existing one and if the new business is not launched, then none of the start-up costs are deductible. Payments for a speeding ticket are nondeductible. HELParrow_forwardThe deductibility of interest on borrowed money is limited to the extent that it was invested to generate an income that is not tax exempt. Question 10 options: True Falsearrow_forward
- One-half of capital gain is treated as taxable capital gain and one-half of capital loss is deductible as allowable capital loss. Question 11 options: True Falsearrow_forwardAn individual's current year capital loss from investment property not offset against capital gains and ordinary income is carried forward indefinitely. True or falsearrow_forwardExplain when a firm may recognize a deferred tax asset under SFAS No. 109. Howshould deferred tax assets that are not expected to be realized be accounted for?arrow_forward
- THe depreciation recapture provisions are designed to prevent taxpayers from converting capial gains into ordinary income.arrow_forwardSection 1221(a) of the Internal Revenue Code defines what: a. is a capital asset. b. is not a capital asset. c. is a ordinary gain. d. is capital gainarrow_forwardAn allowable capital loss realized in a year can first be deducted in the current year against taxable capital gain. If any amount of the loss is still not deducted what other options does the taxpayer have? Write-off from current year employment income Forget about the remaining loss Carry back or carry forward to taxable capital gains Carry back or carry forward to all sources of incomearrow_forward
- 1. When a business ceases to operate and its inventories are disposed of a gain on the inventories will be treated as a capital gain unless an election is made by the selling taxpayer True or False 2. When a business ceases to operate and its accounts receivable are disposed of with the other business assets any loss on the receivables will be treated as a capital loss unless a joint election is made by the purchaser and seller. True or Falsearrow_forwardThe income tax rates are the same for capital gains and depreciation recapture of an asset that is depreciated. O True O Falsearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education