
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Please, I do not understand this question. An explanation leading to the CORRECT answer would be helpful!
Question: White matter in your spinal cord typically are neurons involved in transferring signals very rapidly throughout the central nervous system. The white color of white matter is the result of myelin sheaths around axons
Which of the following is the most important major difference between signals moving through white matter vs gray matter?
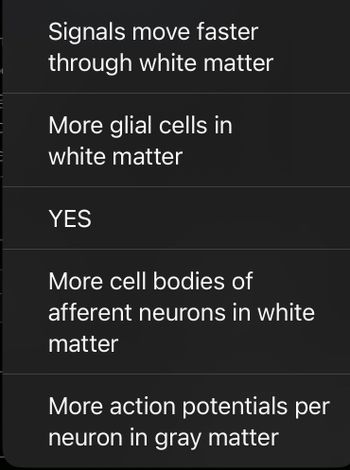
Transcribed Image Text:Signals move faster
through white matter
More glial cells in
white matter
YES
More cell bodies of
afferent neurons in white
matter
More action potentials per
neuron in gray matter
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1: Understanding White Matter
White matter is a critical component of the central nervous system (CNS) and plays a vital role in transmitting information between different regions of the brain and spinal cord. It derives its name from its pale, white appearance, which is attributed to the abundance of myelinated nerve fibers within it.
Key characteristics of white matter include:
1. Myelinated Axons: White matter primarily consists of myelinated axons, which are long, thread-like extensions of neurons. Myelin, a fatty substance, forms an insulating sheath around these axons. This insulation enhances the speed and efficiency of nerve signal transmission.
2. Connective Function: White matter acts as a network of highways or communication cables within the CNS. It facilitates the transmission of information between different regions of the brain, allowing for the coordination of various cognitive and motor functions.
3. Role in Brain Connectivity: White matter pathways, often referred to as tracts or fiber bundles, connect different brain regions. These pathways enable the exchange of sensory, motor, and cognitive information, ensuring seamless communication and integration of functions.
4. Located Beneath Gray Matter: White matter is typically found beneath the gray matter in the brain. Gray matter contains neuronal cell bodies, while white matter contains axons. This arrangement allows for the processing and integration of information in gray matter and its rapid transmission through white matter.
5. Vulnerability to Disease: White matter can be affected by various neurological disorders and diseases, including multiple sclerosis, which leads to the degradation of myelin, and white matter hyperintensities seen in some neurological conditions, such as aging-related changes and certain forms of dementia.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Please help me, idk if my answer is correct and I am trying to use this to study!!arrow_forwardWhat is one way that a chemical can alter normal functioning at the synapse? Give me the specifics of what the chemical interacts with in the synapse and what that does.arrow_forward# 3 0000O LS À Moving to another question will save this response. Question 5 These neurons belongs to the CNS: (More than one possible choice) A neuron in the brain UA neuron carrying a signal into a skeletal muscle A neuron carrying a signal into cardiac muscle A neuron carrying signals form receptors in the skin A neuron carrying signals from the stomach a neuron in the spinal cord grey matter A Moving to another question will save this response. APR étv 9. 1. 08 F2 F4 F5 93 %24 %arrow_forward
- How do selective-serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIS) increase serotonin in the synapse? O They cause excessive 5-HT release from the pre-synaptic neuron O SRIS prevent the inactivation of 5-HT in the synapse O SRIS block the reuptake of 5-HT into the pre-synaptic neuron O They actually don't increase 5-HT! D Question 10 Stimulants such as cocaine increase the neurotransmitter in the synapse O acetylcholine O serotonin O none of these O dopamine D Question 11 What brain area that is a target of the mesolimbic dopamine pathway is important for the rewarding effects of drugs? O nucleus accumbens O No answer text provided. O hippocampus O prefrontal cortexarrow_forwardi need the answer quicklyarrow_forwardWhich one of the following statements is FALSE? Question 36 options: Cranial nerves IV, VII, X and XII all have parasympathetic functions The cornea is the first structure to focus incoming light Cone cells are found primarily within the fovea The auricle helps focus sound waves into the external acoustic meatus The ANS is a motor system onlyarrow_forward
- QUESTION 9 Identify the indicated functional classification of neuron in the image. Sensory receptor -Effector organ effector sensory neuron motor neuron O interneuronarrow_forwardPlease fill out 3,4,5 and 6 if possible. #1 is mechanoreceptor #2 is dorsal root gangliaarrow_forwardQuestion: Suggest two reasons why people had the drug injected into the cerebrospinal fluid (lines 12–13) rather than taking a pill containing the drug.arrow_forward
- Please read questions carefully, they are purposefully written to be trick question 39. Which of the following statements about the reticular formation is false? a. it arises from the brain stem and has wide-ranging axonal connections b. it is responsible for arousal to keep the cortex conscious and alert via RAS c. it filters 99% of all stimuli via ascending reticular formation d. it regulates visceral motor functions via descending reticular formation e. none of the abovearrow_forwardStructure A is alan A. Structure B is a/an Structure C is a/an The small dark staining dots surrounding the neuron in this image are Barrow_forwardThe peripheral nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord. Question 11 options: True Falsearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)Anatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)Anatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Anatomy & PhysiologyAnatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyAnatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Human AnatomyAnatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9780135168059Author:Marieb, Elaine Nicpon, Brady, Patricia, Mallatt, JonPublisher:Pearson Education, Inc.,
Human AnatomyAnatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9780135168059Author:Marieb, Elaine Nicpon, Brady, Patricia, Mallatt, JonPublisher:Pearson Education, Inc., Anatomy & Physiology: An Integrative ApproachAnatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9780078024283Author:Michael McKinley Dr., Valerie O'Loughlin, Theresa BidlePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Anatomy & Physiology: An Integrative ApproachAnatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9780078024283Author:Michael McKinley Dr., Valerie O'Loughlin, Theresa BidlePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Human Anatomy & Physiology (Marieb, Human Anatomy...Anatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9780321927040Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (Marieb, Human Anatomy...Anatomy and PhysiologyISBN:9780321927040Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja HoehnPublisher:PEARSON

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Anatomy and Physiology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Anatomy & Physiology
Anatomy and Physiology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Human Anatomy
Anatomy and Physiology
ISBN:9780135168059
Author:Marieb, Elaine Nicpon, Brady, Patricia, Mallatt, Jon
Publisher:Pearson Education, Inc.,

Anatomy & Physiology: An Integrative Approach
Anatomy and Physiology
ISBN:9780078024283
Author:Michael McKinley Dr., Valerie O'Loughlin, Theresa Bidle
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (Marieb, Human Anatomy...
Anatomy and Physiology
ISBN:9780321927040
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON