
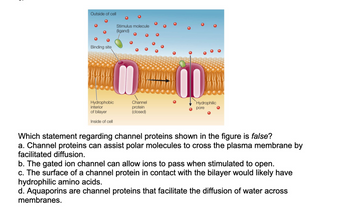
Channel proteins are proteins found in the transmembrane region of the plasma membrane. They help in the movement of molecules down the concentration gradient, that is, from high to low concentration.
They do not require any energy to carry out their function. This is a passive transport and they don't need to bind with these molecules to be moved across either.
Thus, channel proteins carry out facilitated diffusion where polar molecules are moved across the membrane through them.
Each channel protein is made up of specific amino acid sequences that determine which molecules it will transport.
These proteins also have a property of being either gated or non-gated. Non-gated ones always remain open whereas the gated ion channel have a binding site and will allow ions to pass through only when a certain stimuli to open is generated by a ligand upon binding to this site.
Some examples of channel proteins are: the Voltage gated potassium channels, Voltage gated sodium channels, Aquaporins.
Aquaporins are examples of a kind of channel proteins that facilitate transport of water across membranes.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

- If a membrane protein in an intact erythrocyte reacts with a membrane-impermeable reagent, what can you conclude about the protein? A. It is a transmembrane protein. B. It is a peripheral membrane protein. C. At least one domain of the protein is located on the outer face of the membrane. D. It is not a plasma membrane protein.arrow_forwardWhich of the following is incorrect about membrane transport systems? a. Glucose transport in red blood cells is a uniport system b. The Na+/K+ ATPase is an antiport system c. The H+/K+ ATPase is an active transport system d. The chloride-bicarbonate exchanger in erythrocytes is a uniport systemarrow_forwardNa+ moves from high to low concentration, across the plasma membrane, through a protein channel that is permenantly open. Which statement is true about this process? a. It does not require ATP b. It is a form of active transport c. Movement is against the concentration gradient of Na+ d. The channel probably allows many different molecules and ions to crossarrow_forward
- Model 4: Active Transport Area of detail ion binding site ATP binding site ATP ADParrow_forwardWhat is the role of cholesterol in animal cell membranes? A. Blocks the association of the fatty acyl chains of phospholipids at high temperature. B. Is a receptor site for hormones on the surface of membranes. C. Broadens the temperature range of optimum membrane fluidity. D. Aids in the transport of small hydrophobic molecules across the membrane. A fatty acid designated as 20:0 is ________, while one that is designated 20:3 delta ^5,8,11 is ________. A. complex; simple B. unsaturated; saturated C. saturated; unsaturated D. simple; complex E. monounsaturated; polyunsaturatedarrow_forwardYou find a membrane protein that moves molecules across a membrane. What type of transport could that protein be involved in?arrow_forward
- Emodin (a laxative) is used to treat constipation. This drug inhibits Aquaporin 3 located in the cells lining the colon. a. What can you infer regarding the function of Aquaporin 3? b. How will the drug treat constipation? Answer the questions as stated above. Use the information as guidearrow_forwardIn which situation would passive transport not use atransport protein for entry into a cell?a. water flowing into a hypertonic environmentb. glucose being absorbed from the bloodc. an ion flowing into a nerve cell to create anelectrical potentiald. oxygen moving into a cell after oxygen deprivationarrow_forwardWhich of the following statements is not true? A. Lidocaine cannot function as a channel blocker if it is not charged B. TTX cannot function as a channel blocker if it is charged C.Lidocaine must fit inside the channel to work as a blocker D.TTX can access its binding site even if the channel is closedarrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





