
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
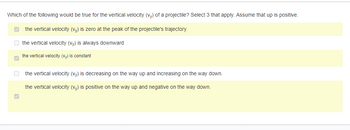
Transcribed Image Text:Which of the following would be true for the vertical velocity (vy) of a projectile? Select 3 that apply. Assume that up is positive.
the vertical velocity (vy) is zero at the peak of the projectile's trajectory.
the vertical velocity (vy) is always downward
the vertical velocity (vy) is constant
the vertical velocity (vy) is decreasing on the way up and increasing on the way down.
the vertical velocity (vy) is positive on the way up and negative on the way down.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A projectile is launched at ground level with an intial vertical velocity of 25.0m/s and a horizontal velocity of 43.3m/s. It strikes a target above the ground 3.00 seconds later. a) How high is the target above the gound? b) How far did the projectile travel before hitting the target? c) What is the horizontal component of the velocity of the projectile right as it hits the target? d) What is the vertical component of the velocity of the projectile right as it hits the target?arrow_forwardAn arrow has an initial velocity of 32 m/s, 30° to the horizontal. a) Find the time it takes for the arrow to reach the ground if it is shot from an original height of 22 m. (G.R.A.S.S.) b) What is the horizontal displacement of the arrow in this amount of time? (G.R.A.S.S)arrow_forward24. A shell is fired with a horizontal velocity in the positive x direction at a speed of 330 m/s from the top of an 80- m high cliff. The shell strikes the ground 1330 m from the base of the cliff. What is the magnitude of the velocity of the shell as it hits the ground? Hint: you need to determine horizontal and vertical components of the final velocity first, from the kinematic equations, then calculate magnitude of the velocity. While the horizontal velocity remains constant, the vertical velocity does not. You will need time of flight to determine the latter. 80 m 1330 m A) 4.0 m/s B) 9.8 m/s B) 9.8 m/s C) 82 m/s D) 170 m/s (E) 332 m/sarrow_forward
- When there is no air resistance what best describes the vectors of a projectile in motion O The acceleration vector and velocity vector are both constant magnitude. The acceleration vector is constant and points straight down. The velocity vector is perpendicular to the trajectory O The acceleration vector is constant magnitude and perpendicular to the trajectory. The velocity vector is at a tangent to the trajectory O The acceleration vector is constant and points straight down. The velocity vector is at a tangent to the trajectoryarrow_forwardA cannonball is launched from ground level. The launch angle is 60°, with an initial speed of vi = 120 m/s. How far away does the cannonball land? Express your answer with the appropriate units. HA ? Value Units d = Submit Request Answerarrow_forwardTwo velocity vectors are defined as follows: ₁ = 40.0 m/s, 50.0° cw from the +x axis v₂ = 30.0 m/s, 75.0° cw from the -y axis a) b) Sketch the vector ₁ on an x-y grid. Label any relevant angle. Calculate the x- and y-components of ₁. Write the vector in terms of its components using unit vector notation. c) d) e) v₂ – v- Calculate the x- and y-components of the change in velocity defined as A = Write the vector Av in terms of its components using unit vector notation. Sketch the vector A on an x-y grid. Define a relevant angle symbolically whose numerical value you will calculate in the next part. f) g) Calculate the magnitude and direction of the vector Av. h) Finally, write the vector Av in terms of its magnitude and direction. Sketch the vector v₂ on an x-y grid. Label any relevant angle. Calculate the x- and y-components of 7₂. Write the vector ₂ in terms of its components using unit vector notation.arrow_forward
- A plane releases a package from an altitude of 300 meters. At the time of release, both the plane and package are moving at 100 meters per second, directed at an angle of 20 degrees below the horizontal. How long is the package in the air? Find the magnitude and direction of the velocity of the package just before impact? Draw a sketch or diagram of the problem. Thank you for your help.arrow_forwardThe x-component of a velocity vector that has an angle of 35 ∘ to the +x axis has a magnitude of 4.9 m/s. What is the magnitude of the velocity? Express your answer using two significant figures. What is the magnitude of the yy-component of the velocity? Express your answer using two significant figures.arrow_forwardTable 1. Shot velocity (V) of the projectile at an angle of 30. Two shots were made for each distance. Column 1 and 2 correspond to the throw from 1 meter away. To determine the velocity of fire of the projectile on the x-axis, use the equation: Vxo = Vo * cos 30°.arrow_forward
- If a boat points its prow directly across a river, and its engine has one speed of 8.22 m/s. What is its speed, relative to the river bank, if the river has a velocity of 3.28 m/s? Number Units If the river is 63.4 m wide, how far down stream does it land when it reaches the opposite shore? Number Unitsarrow_forwardA projectile is launched from ground level at a velocity of 28 m/s and an initial angle of 37 degrees. What is the projectile's velocity the instant before it hits the ground? Include a drawing and all steps. Use the projectile motion equations.arrow_forwardOn level ground a shell is fired with an initial velocity of 39.0 m/s at 62.0° above the horizontal and feels no appreciable air resistance. ▼ Submit Request Answer Part D How far from its firing point does the shell land? Express your answer using three significant figures. 1 = Submit Part E Value ah, av = μA Submit Part F Request Answer At its highest point, find the horizontal and vertical components of its acceleration. Enter your answers numerically separated by a comma. 15. ΑΣΦ Units Request Answer ? Pearson ? m/s²arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON